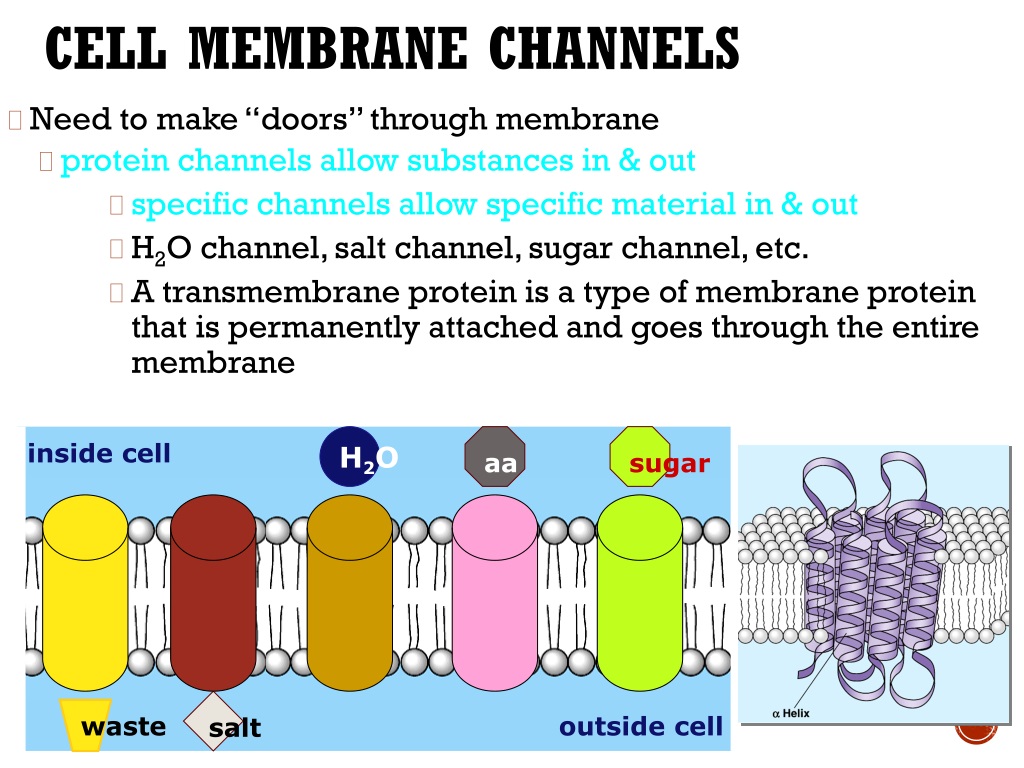
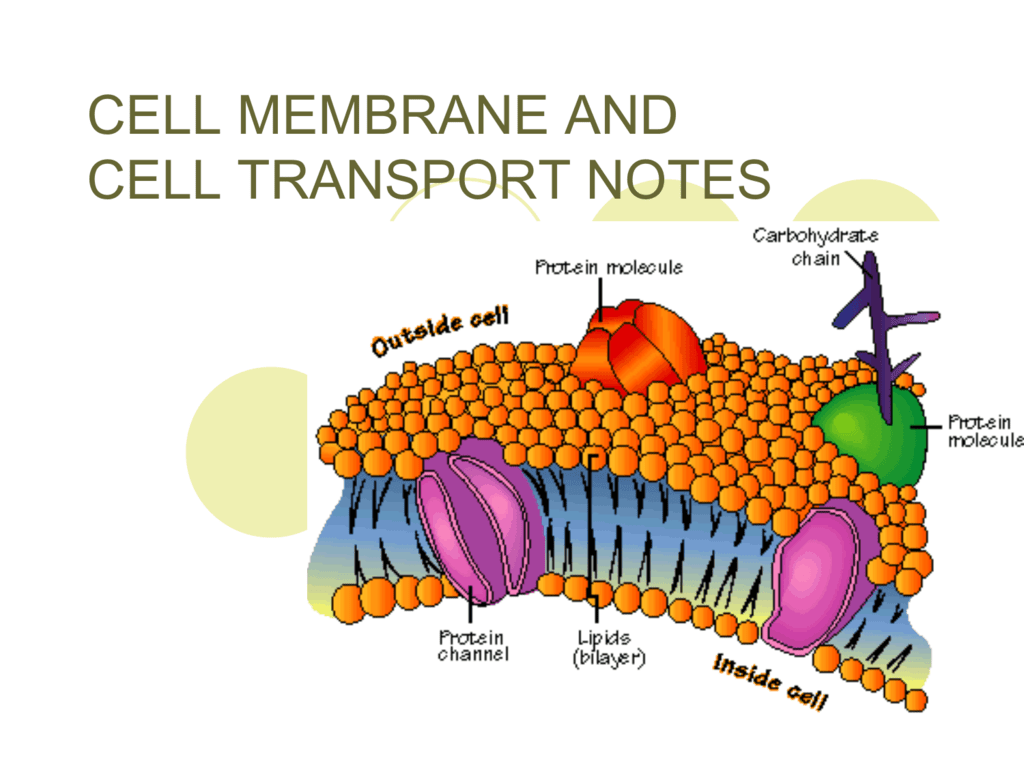
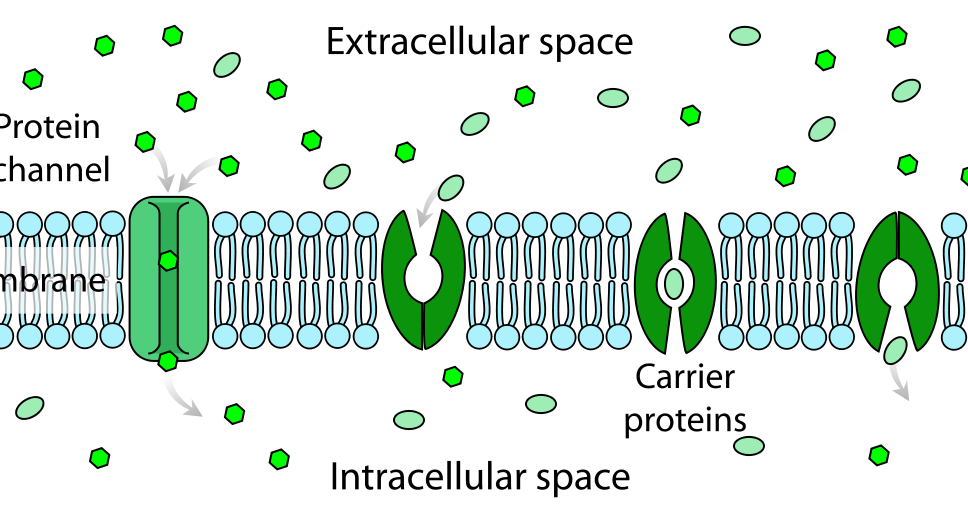
Small Channels That Form Across The Plasma Membrane
Small Channels That Form Across The Plasma Membrane - Small channels that form across the plasma membranes of adjacent cells; Membrane proteins that create a watertight seal between cells; Aid in coordination of activities between cells. Web small channels that form across the plasma membranes of adjacent animal cells; Membrane proteins that create a watertight seal between cells. The structure of a cell membrane allows only small uncharged molecules to diffuse through. Larger and more polar, hydrophilic, molecules, such as amino acids, must instead cross the membrane by way of protein channels, a process that is often regulated by the cell. Biophysicists measuring the electric current passing through cell membranes have found that, in general, cell membranes have a vastly greater electrical conductance than does a membrane bilayer composed only of phospholipids and sterols. Membrane protein complexes that strengthen the adhesion between adjacent cells, like rivets, to protect against pulling forces. Especially important in intercellular communication. Once again, the process requires transmembrane proteins. Web we would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Small channels that form across plasma membranes of adjacent cells, important in intercellular communication; Barrier that prevents fluids from moving between cells. Especially important in intercellular communication. Small channels that form across plasma membranes of adjacent cells, important in intercellular communication; Help coordinate activities of adjacent cells Membrane proteins that create a watertight seal between cells; Help coordinate activities of adjacent cells tight junctions membrane proteins that create a watertight seal between animal cells to connect them and to keep fluid from crossing barriers However, nature has. Web we would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Help coordinate activities of adjacent cells Membrane proteins that create a watertight seal between cells; Small channels that form across the plasma membranes of adjacent cells; Web small channels that form across the plasma membranes of adjacent animal cells, especially important in intercellular communication,. Membrane proteins that create a watertight seal between cells. Web some small, nonpolar molecules, such as oxygen, can pass directly through the phospholipid portion of the membrane. Larger and more polar, hydrophilic, molecules, such as amino acids, must instead cross the membrane by way of protein channels, a process that is often regulated by the cell. Web these channels are. Web the simplest forms of transport across a membrane are passive. The resting potential is determined by concentration gradients of ions across the membrane and by membrane permeability to each type of ion. Some integral membrane proteins form a channel that allows ions or other small molecules to pass, as shown below. Especially important in intercellular communication; Especially important in. An ion channel), and so they are tightly linked to certain physiologic functions. Web the plasma membrane of a cell is a network of lipids and proteins that forms the boundary between a cell’s contents and the outside of the cell. Especially important in intercellular communication; This permeability results from the porins, which form open aqueous channels through the. It. Passive transport does not require the cell to expend any energy and involves a substance diffusing down its concentration gradient across a membrane. Web this review examines how varying types of molecules—namely, small molecules, peptides, and proteins—are thought to cross the mammalian plasma membrane, how such permeation events are measured experimentally, and what kinds of technologies are being developed to. Web these channels are glycoproteins (proteins with carbohydrates attached) that allow molecules to pass through the membrane. The main function of the plasma membrane is to protect the cell from its surrounding environment. Especially important in intercellular communication; Small channels that form across the plasma membranes of adjacent cells; Membrane protein complexes that strengthen the adhesion between adjacent cells, like. Membrane proteins that create a watertight seal between cells; Membrane protein complexes that strengthen the adhesion between adjacent cells, like rivets, to protect against pulling forces. Passive transport does not require the cell to expend any energy and involves a substance diffusing down its concentration gradient across a membrane. Especially important in intercellular communication. Once open, channel proteins form small. The structure of a cell membrane allows only small uncharged molecules to diffuse through. Once open, channel proteins form small pores through which ions of the appropriate size and charge. Web these channels are glycoproteins (proteins with carbohydrates attached) that allow molecules to pass through the membrane. Small channels that form across the plasma membranes of adjacent cells; Web small. However, nature has equipped cell membranes with several ways to control the movement of larger or charged molecules into or out of a cell. Coli, with molecular weights up to 600). Biophysicists measuring the electric current passing through cell membranes have found that, in general, cell membranes have a vastly greater electrical conductance than does a membrane bilayer composed only of phospholipids and sterols. Web these channels are glycoproteins (proteins with carbohydrates attached) that allow molecules to pass through the membrane. Help coordinate activities of adjacent cells Web we would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Web some small, nonpolar molecules, such as oxygen, can pass directly through the phospholipid portion of the membrane. Some integral membrane proteins form a channel that allows ions or other small molecules to pass, as shown below. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like desmosomes, gap junctions, tight junctions and more. Especially important in intercellular communication. The resting potential is determined by concentration gradients of ions across the membrane and by membrane permeability to each type of ion. Web small channels that form across the plasma membranes of adjacent animal cells; Web small channels that form across the plasma membranes of adjacent animal cells, especially important in intercellular communication, help coordinate activities of adjacent cells; Membrane proteins that create a watertight seal between cells; It is also simply called the cell membrane. Web carrier proteins and channel proteins are the two major classes of membrane transport proteins. Membrane protein complexes that strengthen the adhesion between adjacent cells, like rivets, to protect against pulling forces. Small channels that form across plasma membranes of adjacent cells, important in intercellular communication; Web some small, hydrophilic organic molecules, like sugars, can pass through cell membranes by facilitated diffusion. Larger and more polar, hydrophilic, molecules, such as amino acids, must instead cross the membrane by way of protein channels, a process that is often regulated by the cell.TRANSPORT ACROSS Plasma MEMBRANES ! Biological Sciencess
Diffusion across the Plasma Membrane Plasma membrane, Human anatomy
PPT Cell Transport Cell Membranes & Movement Across Them PowerPoint
Transport across the Plasma Membrane
Crossing Membranes A Level Notes
TRANSPORT ACROSS Plasma MEMBRANES ! Biological Sciencess
TJ. Schematic diagram of typical membrane proteins in a biological
Plasma Membrane Plasma membrane, Teaching biology, Membrane
3.1 The Cell Membrane Douglas College Human Anatomy and Physiology I
Cell Membrane Introduction, Structure & Function
Related Post: