How Do Disulfide Bonds Form
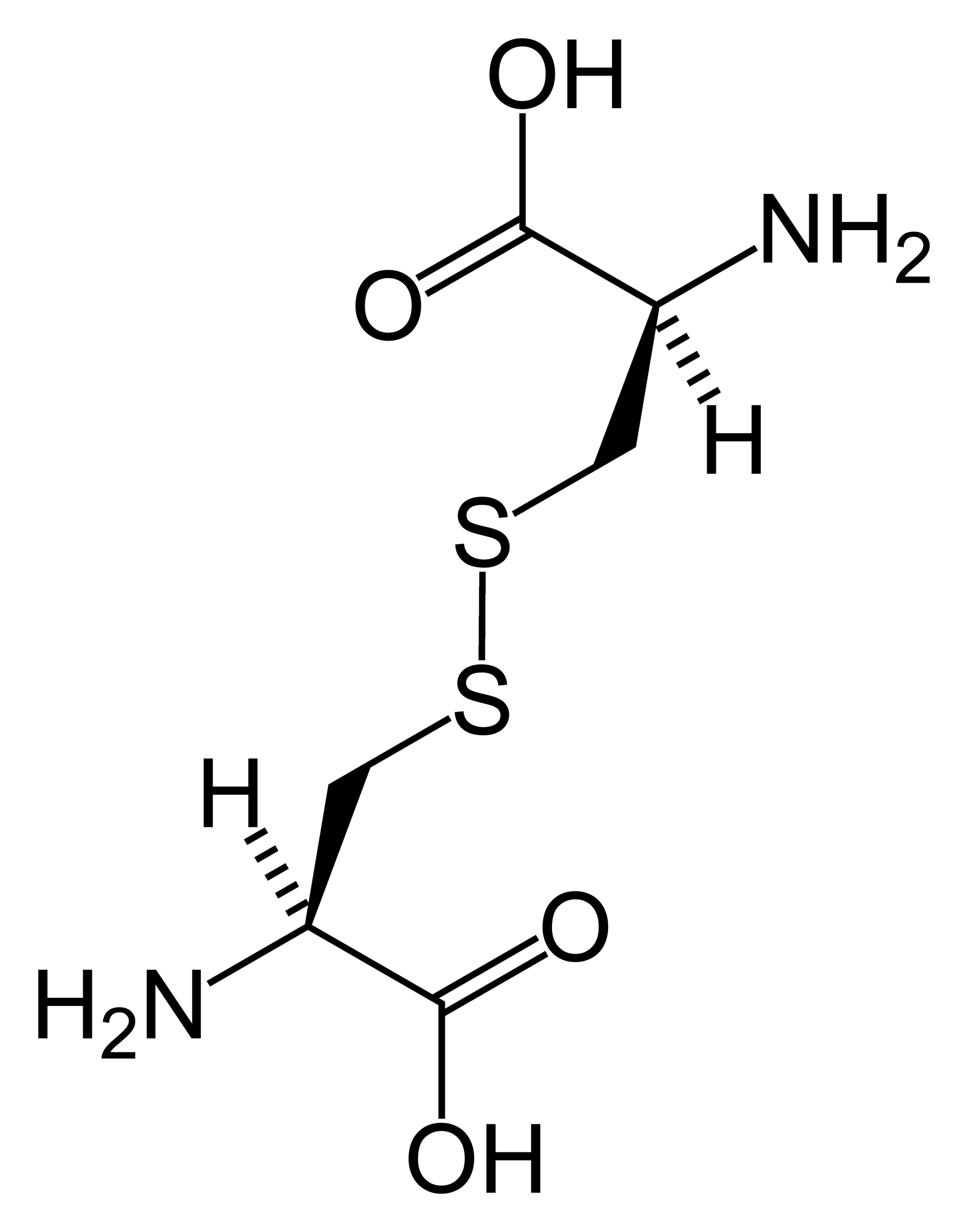
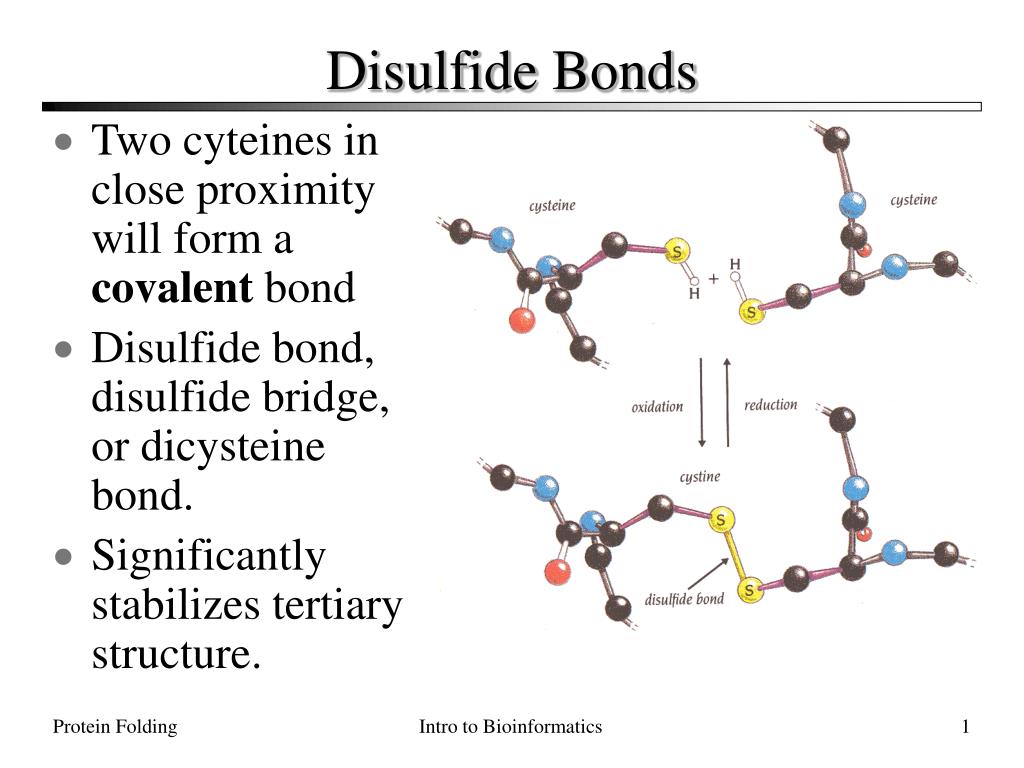
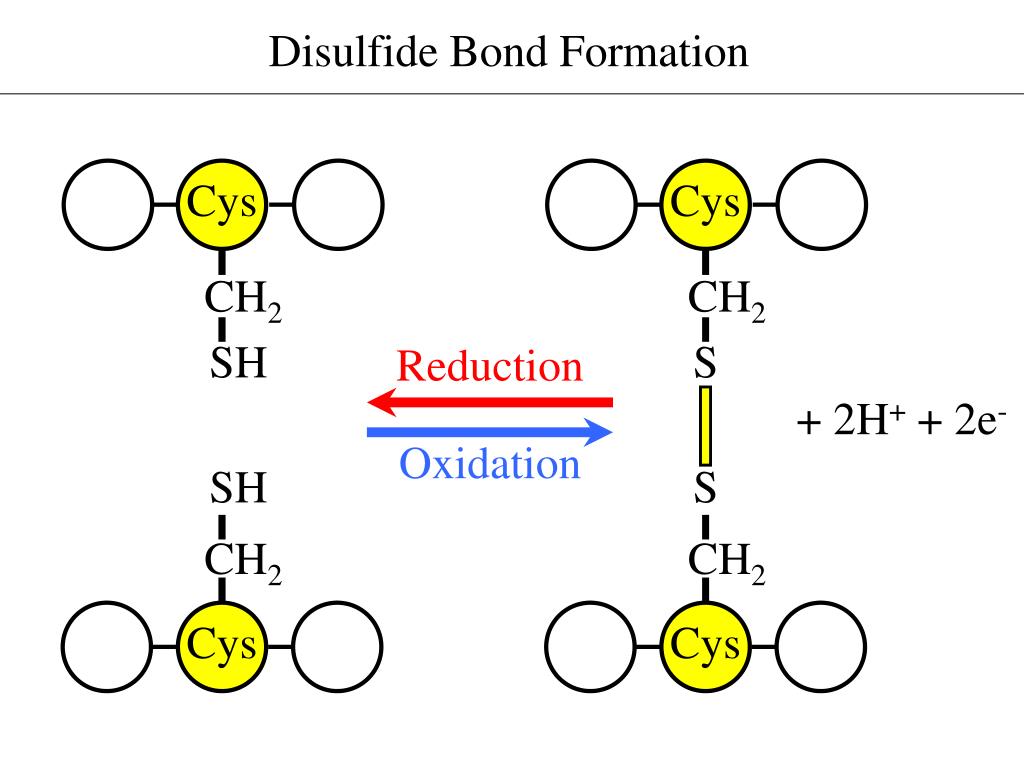
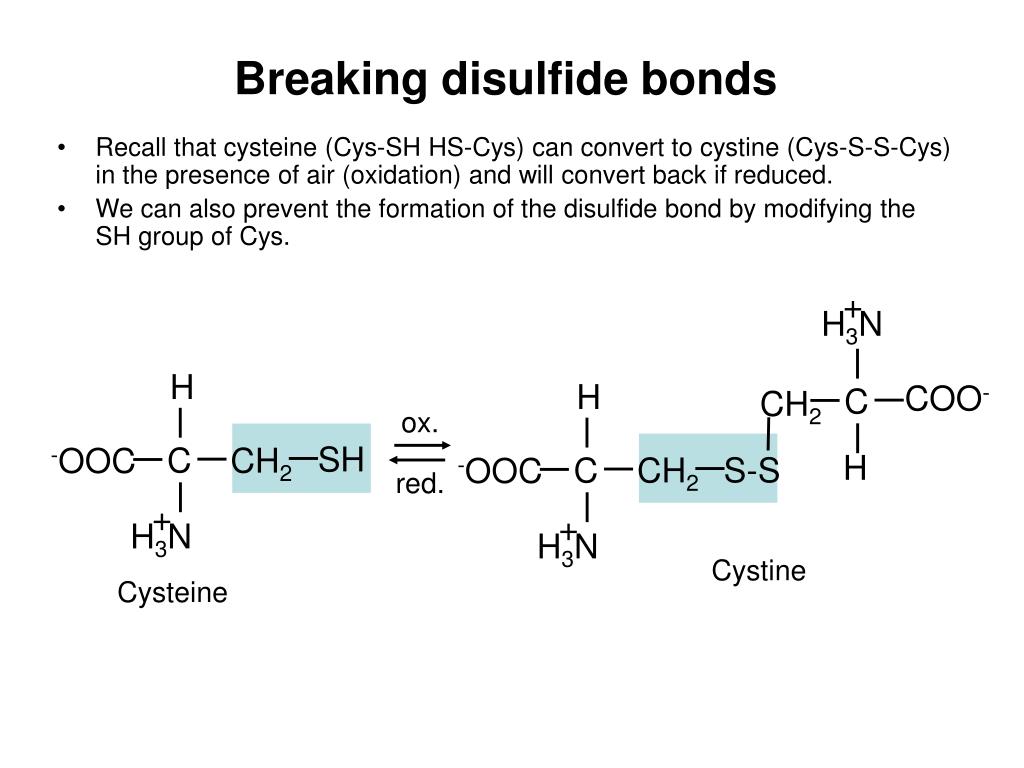
How Do Disulfide Bonds Form - Web recently, kaiser and frand [9]•• delineated how ero1p and pdi accomplish the first step of this process (figure 1). Web key points the formation of structural disulphide bonds in cellular proteins is a catalysed process that involves many proteins and small molecules. The oxidation of cysteine residues occurs through the transfer of electrons. Cysteine is an amino acid that contains a sulfhydryl group, which. Web the formation of a disulfide bridge involves a series of steps: The received wisdom is that disulphides are. Web disulfide bonds are formed by the oxidation of sulfhydryl groups between two cysteine side chains, resulting in a covalent bond, greatly increasing the stability of the protein. Intermolecular disulfide bonds occur between polypeptide chains. Web functions of disulfide bonds. Web disulphide bonds occur in proteins, not amino acids, although they involve a covalent bond between two amino acids (both cysteine). Web the formation of a disulfide bridge involves a series of steps: Web the formation of disulfide bonds (dsbs) in proteins is an oxidative process that generates a covalent bond linking the sulfur atoms of two cysteine residues. Intermolecular disulfide bonds occur between polypeptide chains. It involves a chemical reaction resulting in the formation of disulfide. Ad provides disulfide linkers. It is proposed to consider: Web the formation of a disulfide bridge involves a series of steps: Disulfide bond synonyms, disulfide bond pronunciation, disulfide bond translation, english dictionary definition of disulfide bond. Web key points the formation of structural disulphide bonds in cellular proteins is a catalysed process that involves many proteins and small molecules. Ad provides disulfide linkers to. The form of a bond, namely, the words by which it may be made, and the ceremonies required. Web disulfide bond formation involves a reaction between the sulfhydryl (sh) side chains of two cysteine residues: Web disulfide bond formation involves a reaction between the sulfhydryl (sh) side chains of two cysteine residues: It involves a chemical reaction resulting in the. Web the formation of a disulfide bridge involves a series of steps: Intrachain disulfide bonds are formed during. An s − anion from one sulfhydryl group acts. The oxidation of cysteine residues occurs through the transfer of electrons. Web functions of disulfide bonds. Web recently, kaiser and frand [9]•• delineated how ero1p and pdi accomplish the first step of this process (figure 1). [ bond ] the linkage between atoms or radicals of a chemical compound, or the symbol representing this linkage and indicating the number and attachment of the. Bonds vary widely in maturity, security, and type of issuer, although most are. Web disulphide bonds occur in proteins, not amino acids, although they involve a covalent bond between two amino acids (both cysteine). Intrachain (within a polypeptide chain) and interchain (between separate chains). [ bond ] the linkage between atoms or radicals of a chemical compound, or the symbol representing this linkage and indicating the number and attachment of the. Intermolecular disulfide. It involves a chemical reaction resulting in the formation of disulfide. Web disulfide bonds are formed by the oxidation of sulfhydryl groups between two cysteine side chains, resulting in a covalent bond, greatly increasing the stability of the protein. Web disulfide bonds are of two types: Web disulfide bond formation involves a reaction between the sulfhydryl (sh) side chains of. The form of a bond, namely, the words by which it may be made, and the ceremonies required. Web disulfide bond formation involves a reaction between the sulfhydryl (sh) side chains of two cysteine residues: Web disulfide bond formation involves a reaction between the sulfhydryl (sh) side chains of two cysteine residues: Web disulfide bonds are formed by the oxidation. Cysteine is an amino acid that contains a sulfhydryl group, which. An s − anion from one sulfhydryl group acts. Web functions of disulfide bonds. Web disulfide bonds are formed by the oxidation of sulfhydryl groups between two cysteine side chains, resulting in a covalent bond, greatly increasing the stability of the protein. Web disulfide bond formation involves a reaction. Ad provides disulfide linkers to conjugate various payloads.higher stability.call! Web the formation of a disulfide bridge involves a series of steps: Web disulfide bonds can occur in two ways: [ bond ] the linkage between atoms or radicals of a chemical compound, or the symbol representing this linkage and indicating the number and attachment of the. It is proposed to. Web the formation of disulfide bonds (dsbs) in proteins is an oxidative process that generates a covalent bond linking the sulfur atoms of two cysteine residues. Disulfide bond synonyms, disulfide bond pronunciation, disulfide bond translation, english dictionary definition of disulfide bond. An s − anion from one sulfhydryl group acts. Web disulfide bond formation involves a reaction between the sulfhydryl (sh) side chains of two cysteine residues: It is proposed to consider: The received wisdom is that disulphides are. Bonds vary widely in maturity, security, and type of issuer, although most are sold in $1,000 denominations or, if a municipal bond, $5,000. Intermolecular disulfide bonds occur between polypeptide chains. [ bond ] the linkage between atoms or radicals of a chemical compound, or the symbol representing this linkage and indicating the number and attachment of the. An s − anion from one sulfhydryl group acts as a nucleophile,. The oxidation of cysteine residues occurs through the transfer of electrons. Web how proteins form disulfide bonds the identification of protein disulfide isomerase, almost 50 years ago, opened the way to the study of oxidative protein folding. Web the formation of a disulfide bridge involves a series of steps: Intrachain (within a polypeptide chain) and interchain (between separate chains). Ad provides disulfide linkers to conjugate various payloads.higher stability.call! Web disulphide bonds occur in proteins, not amino acids, although they involve a covalent bond between two amino acids (both cysteine). Web key points the formation of structural disulphide bonds in cellular proteins is a catalysed process that involves many proteins and small molecules. Web disulfide bonds are formed by the oxidation of sulfhydryl groups between two cysteine side chains, resulting in a covalent bond, greatly increasing the stability of the protein. Web functions of disulfide bonds. Web disulfide bond formation involves a reaction between the sulfhydryl (sh) side chains of two cysteine residues:Mechanisms of cleavage of allosteric disulfide bonds. Disulfide bond
Disulfide bond wikidoc
PPT Disulfide Bonds PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID165240
Disulfide bond wikidoc
PPT Making the right connections Disulfide Bond Formation in the
DsbB pathway and screening basis. E. coli disulfide bond formation
Disulfide Bond Formation in the Mammalian Endoplasmic Reticulum
PPT Lecture 4 Amino Acids PowerPoint Presentation ID399998
LabXchange
Disulfide Bond Formation in the Mammalian Endoplasmic Reticulum
Related Post: