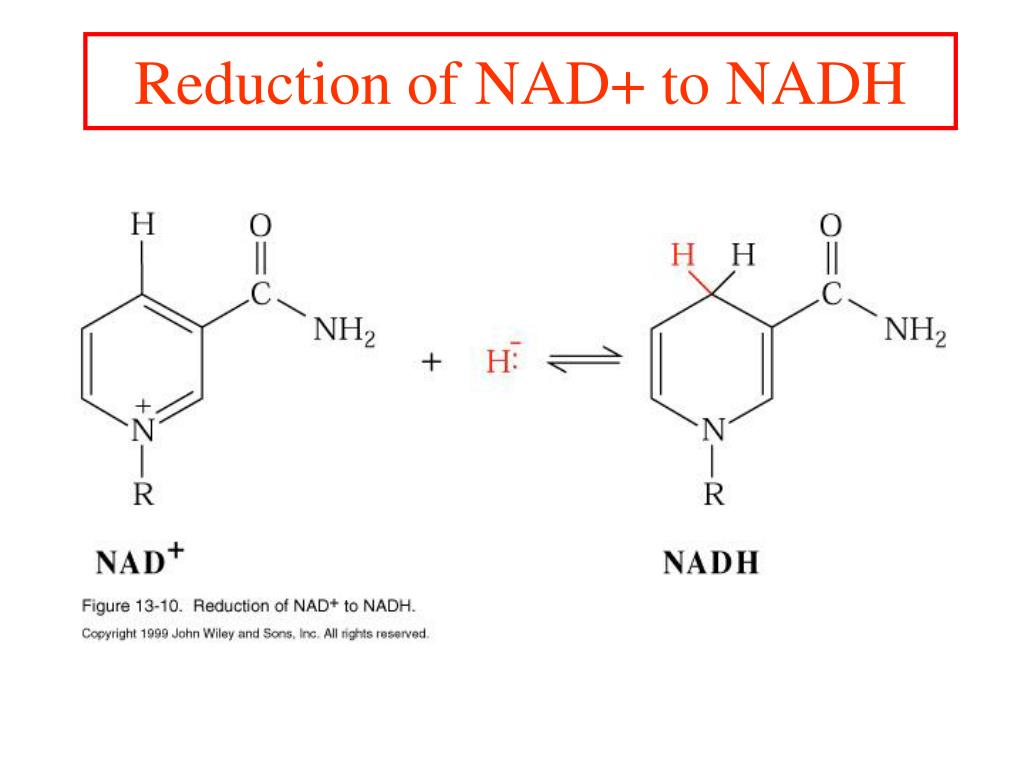
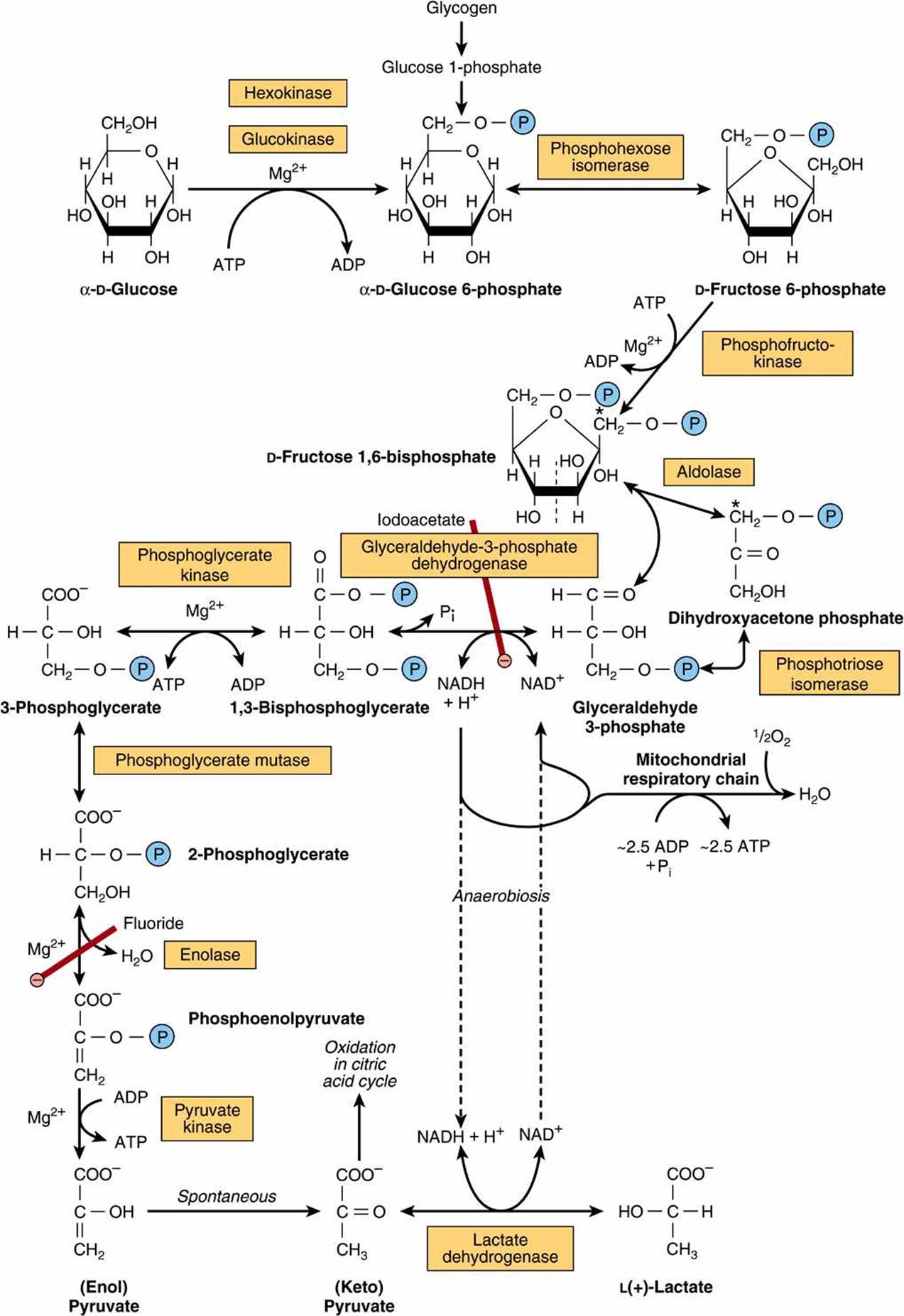
The Reduced Form Of The Electron Acceptor In Glycolysis Is
The Reduced Form Of The Electron Acceptor In Glycolysis Is - Among the products of glycolysis, which compounds contain energy that can be used by other. Nadh among the products of glycolysis, which compounds contain energy that can be used by other. When a compound accepts (gains) electrons, that compound becomes [reduced]. Fad h 2 → fad + 2 e − + 2 h +. Such a compound is often referred to as an electron acceptor. Nadh among the products of glycolysis, which compounds contain energy that can be used by other biological. Web nad h → nad + + 2 e − + h +. Web the purpose of the extra reactions in fermentation, then, is to regenerate the electron carrier nad + from the nadh produced in glycolysis. Web the reduced form of the electron acceptor in glycolysis is nadh. Web once the electron donor in glycolysis gives up its electrons, it is ordized to a compound called glucose is the compound that functions as the electron acceptor inglycolysis 6. Web during these reactions, the loss of electrons is called oxidation and the addition is called reduction. Web reduced, electron acceptor in glycolysis, as in all the stages of cellular respiration, the transfer of electrons from electron donors to electron acceptors plays a. Fad h 2 → fad + 2 e − + 2 h +. Web once the electron. Such a compound is often referred to as an electron acceptor. Web at the end of the electron transport chain, oxygen accepts electrons and takes up protons to form water. Web complex ii red reduces a, the terminal electron acceptor to regenerate complex ii ox and create the reduced form of the terminal electron acceptor. Web reduced, electron acceptor in. Web the reduced form of the electron acceptor in glycolysis is nadh. 1 when a compound donates electrons the compound becomes oxidized.such a compound is. The other three stages of cellular respiration—pyruvate oxidation, the citric acid. Web reduced, electron acceptor in glycolysis, as in all the stages of cellular respiration, the transfer of electrons from electron donors to electron acceptors. Web complex ii red reduces a, the terminal electron acceptor to regenerate complex ii ox and create the reduced form of the terminal electron acceptor. Nadh among the products of glycolysis, which compounds contain energy that can be used by other. Web the reduced form of the electron acceptor in glycolysis is blank. Web the purpose of the extra reactions. Web the reduced form of the electron acceptor in glycolysis is [nadh]. Web the reduced form of the electron acceptor in glycolysis is blank. In this case, complex ii can. Glycolysis can take place without oxygen in a process called fermentation. Web complex ii red reduces a, the terminal electron acceptor to regenerate complex ii ox and create the reduced. In this case, complex ii can. Web reduction the addition of electrons to another substance + example of redox Web reduced, electron acceptor in glycolysis, as in all the stages of cellular respiration, the transfer of electrons from electron donors to electron acceptors plays a. Glycolysis can take place without oxygen in a process called fermentation. The extra reactions accomplish. Fad h 2 → fad + 2 e − + 2 h +. When a compound accepts (gains) electrons, that compound becomes [reduced]. Among the products of glycolysis, which compounds contain energy that can be used by other. Web at the end of the electron transport chain, oxygen accepts electrons and takes up protons to form water. Depending on the. Web nad h → nad + + 2 e − + h +. Web complex ii red reduces a, the terminal electron acceptor to regenerate complex ii ox and create the reduced form of the terminal electron acceptor. Web the reduced form of the electron acceptor in glycolysis is [nadh]. The reactions in which nad + and fad gain or. Web during these reactions, the loss of electrons is called oxidation and the addition is called reduction. Web through that procedure of glycolysis, one molecule a glucose breaks down to form twin molecules of pyruvate. Web at the end of the electron transport chain, oxygen accepts electrons and takes up protons to form water. Web complex ii red reduces a,. 1 when a compound donates electrons the compound becomes oxidized.such a compound is. In this case, complex ii can. The electron donor is the reduction agent and the electron acceptor is the. Web once the electron donor in glycolysis gives up its electrons, it is ordized to a compound called glucose is the compound that functions as the electron acceptor. Fad h 2 → fad + 2 e − + 2 h +. Web through that procedure of glycolysis, one molecule a glucose breaks down to form twin molecules of pyruvate. Web the purpose of the extra reactions in fermentation, then, is to regenerate the electron carrier nad + from the nadh produced in glycolysis. In this case, complex ii can. Glycolysis can take place without oxygen in a process called fermentation. Web reduced, electron acceptor in glycolysis, as in all the stages of cellular respiration, the transfer of electrons from electron donors to electron acceptors plays a. The electron donor is the reduction agent and the electron acceptor is the. Web reduction the addition of electrons to another substance + example of redox Web the reduced form of the electron acceptor in glycolysis is blank. Web the reduced form of the electron acceptor in glycolysis is _. When a compound accepts (gains) electrons, that compound becomes [reduced]. Web the reduced form of the electron acceptor in glycolysis is nadh. Such a compound is often referred to as an electron acceptor. Web once the electron donor in glycolysis gives up its electrons, it is ordized to a compound called glucose is the compound that functions as the electron acceptor inglycolysis 6. Nadh among the products of glycolysis, which compounds contain energy that can be used by other biological. Depending on the microcellular environment (specifically, atm. The extra reactions accomplish this by letting nadh drop its electrons off with an organic molecule (such as pyruvate, the. Nadh among the products of glycolysis, which compounds contain energy that can be used by other. Web nad h → nad + + 2 e − + h +. Web during these reactions, the loss of electrons is called oxidation and the addition is called reduction.Glycolysis Expii
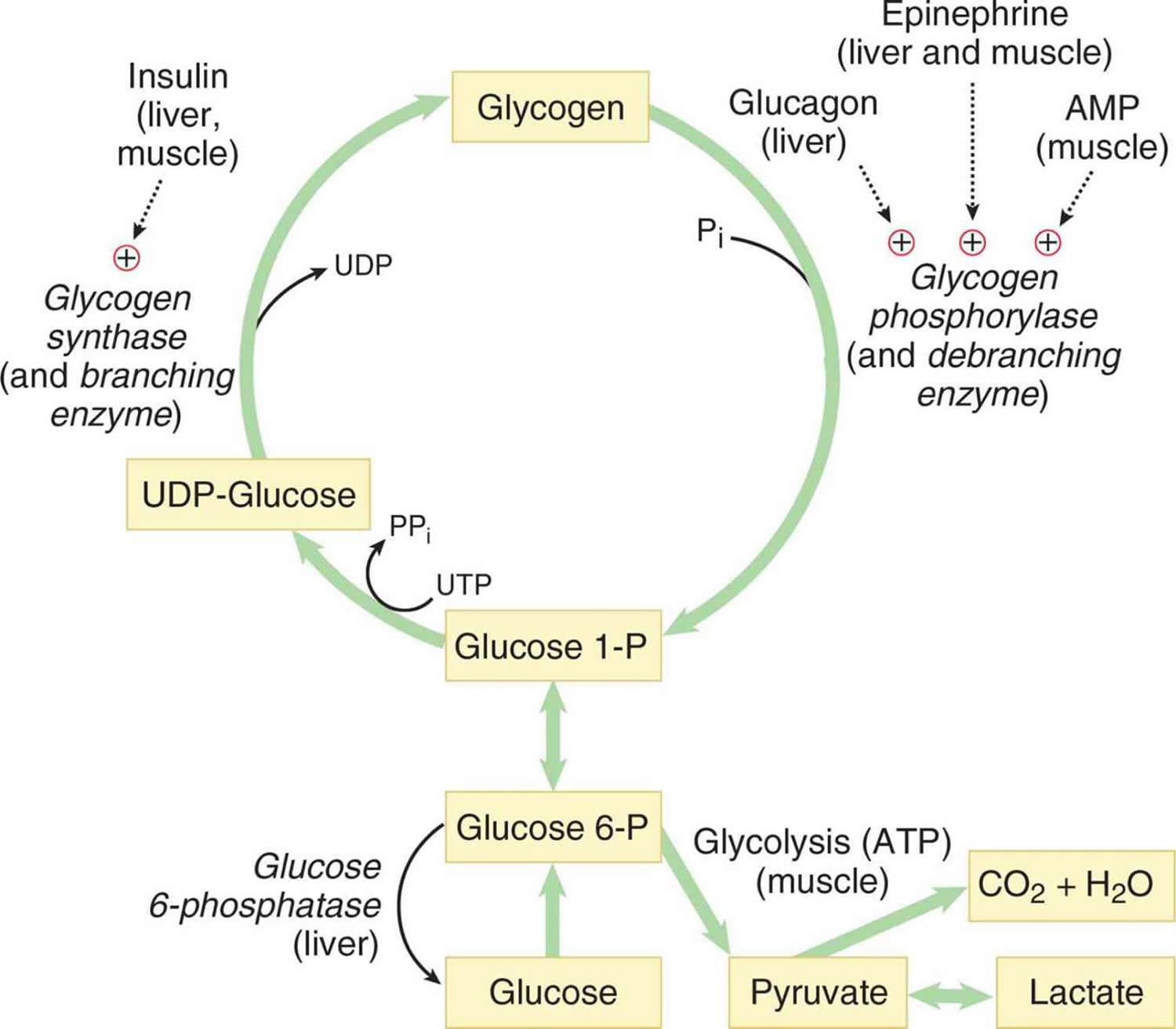
Glycogenolysis definition, glycogenolysis steps & pathway
Cellular Respiration Glycolysis Test ProProfs Quiz
organic chemistry According to this equation for glycolysis, what is
How Much Atp Is Produced In Glycolysis Citric Acid Cycle And Electron
PPT Metabolism II and Glycolysis 5/7/03 PowerPoint Presentation, free
PPT Intro to Cellular Respiration, Glycolysis & Krebs Cycle
5.1 Introduction Biology LibreTexts
Glycolysis & the Oxidation of Pyruvate Bioenergetics & the Metabolism
The electron transport chain. Biochemistry, Electron transport chain
Related Post:

.png)