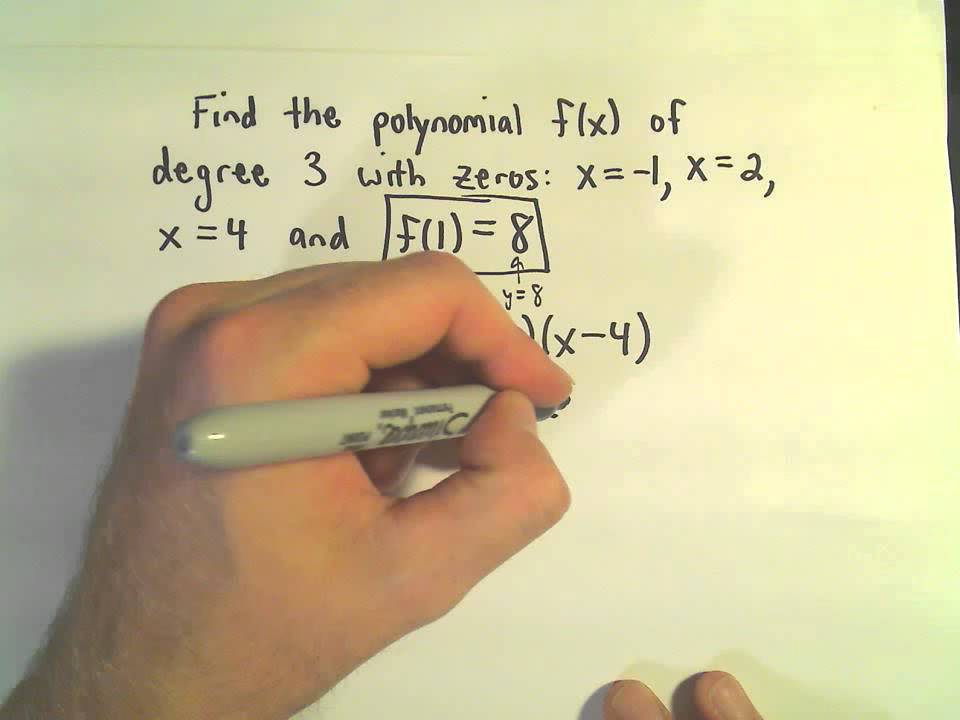How To Form A Polynomial With Given Zeros And Degree
How To Form A Polynomial With Given Zeros And Degree - 6 , multiplicity 1;3, multiplicity 2 ; You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. Degree 3 type a polynomial with integer. Web learn for free about math, art, computer programming, economics, physics, chemistry, biology, medicine, finance, history, and more. Form the quadratic polynomial whose zeros are 4 and 6. Web make polynomial from zeros. Web form a polynomial whose zeros and degree are given. For example, in the polynomial f ( x) = ( x − 1) ( x − 4) 2 , the number 4 is a zero of multiplicity 2. Recall that by roots of a polynomial we are. Use synthetic division to divide the. Web this problem has been solved! Web using the factor theorem to solve a polynomial equation. Web form a polynomial whose zeros and degree are given. Finding a polynomial of given degree with given zeros. Given a polynomial function [latex]f[/latex], evaluate [latex]f\left(x\right)[/latex] at [latex]x=k[/latex] using the remainder theorem. Web we would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. When it's given in expanded form, we can factor it, and then find the zeros! Web up to 6% cash back explanation: Degree 3 type a polynomial with integer. Use the linear factorization theorem to find a polynomial with given zeros. Web to solve a polynomial equation write it in standard form (variables and canstants on one side and zero on the other side of the equation). Form a polynomial whose zeros and degree are given. Ad find polynomial problems in nonfiction books on amazon. Web up to 6% cash back explanation: Degree 3 type a polynomial with integer. A) identify zeros b) write a formula for a possible polynomial function that the graph represents using c as the constant factor. Use synthetic division to divide the. Web form a polynomial whose zeros and degree are given. Starting with the factored form: Web steps on how to find a polynomial of a given degree with given complex zeros. Web when a polynomial is given in factored form, we can quickly find its zeros. 6 , multiplicity 1;3, multiplicity 2 ; Starting with the factored form: For each zero (real or complex), a, of your polynomial, include the factor x − a in your. Recall that by roots of a polynomial we are. When a linear factor occurs multiple times in the factorization of a polynomial, that gives the related zero multiplicity. Create the term of the simplest polynomial from the given zeros. Finding a polynomial of given degree with given zeros. Web when a polynomial is given in factored form, we can quickly find its zeros. Khan academy is a nonprofit with. Ad find polynomial problems in nonfiction books on amazon. Web steps on how to find a polynomial of a given degree with given complex zeros. Khan academy is a nonprofit with the. Web form a polynomial whose zeros and degree are given previous question form a polynomial whose zeros and degree are given zeros: For each zero (real or complex),. Web using the factor theorem to solve a polynomial equation. Polyno whose zeros and degree are given. You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. Finding a polynomial of given degree with given zeros. By the fundamental theorem of algebra, since the degree of the polynomial is 4 the polynomial has 4. The factor theorem is another theorem that helps us analyze polynomial equations. Given a polynomial function [latex]f[/latex], evaluate [latex]f\left(x\right)[/latex] at [latex]x=k[/latex] using the remainder theorem. Factor it and set each factor to zero. When it's given in expanded form, we can factor it, and then find the zeros! Ad find polynomial problems in nonfiction books on amazon. Given graph of the 4th degree function. Web to solve a polynomial equation write it in standard form (variables and canstants on one side and zero on the other side of the equation). Web we would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that. Web form a polynomial whose zeros and degree are given. Here is an example of a 3rd. By the fundamental theorem of algebra, since the degree of the polynomial is 4 the polynomial has 4 zeros if you count multiplicity. For example, in the polynomial f ( x) = ( x − 1) ( x − 4) 2 , the number 4 is a zero of multiplicity 2. Web to solve a polynomial equation write it in standard form (variables and canstants on one side and zero on the other side of the equation). 6 , multiplicity 1;3, multiplicity 2 ; Question content area bottom part 1. Web form a polynomial whose zeros and degree are given. = type a polynomial with integer coefficients and a leading coefficient of 1 in the box below. Starting with the factored form: Given a polynomial function [latex]f[/latex], evaluate [latex]f\left(x\right)[/latex] at [latex]x=k[/latex] using the remainder theorem. Web we would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Web when a polynomial is given in factored form, we can quickly find its zeros. The factor theorem is another theorem that helps us analyze polynomial equations. When a linear factor occurs multiple times in the factorization of a polynomial, that gives the related zero multiplicity. Given graph of the 4th degree function. Form the quadratic polynomial whose zeros are 4 and 6. Degree 3 type a polynomial with integer. Web how do you form a polynomial function whose zeros, multiplicities and degrees are given: Create the term of the simplest polynomial from the given zeros.Ex 1 Find a Degree 3 Polynomial Function Given Integer Zeros YouTube
How To Form A Polynomial With Given Zeros And Degree Calculator
Factoring a Polynomial Function given a zero YouTube
Example Finding a Polynomial with Given Zeros (1) YouTube
How To Find The Real Zeros Of A Polynomial
Finding a polynomial function given the zeros, Pt 1 YouTube
Finding Polynomial Given Zeros YouTube
[Solved] Form a polynomial whose real zeros and degree are given. Zeros
Finding the Formula for a Polynomial Given Zeros/Roots, Degree, and
Form a Polynomial with real Coefficients Given Degree And Zeros. 32i
Related Post: