How Many Nucleotides Are Needed To Form A Codon
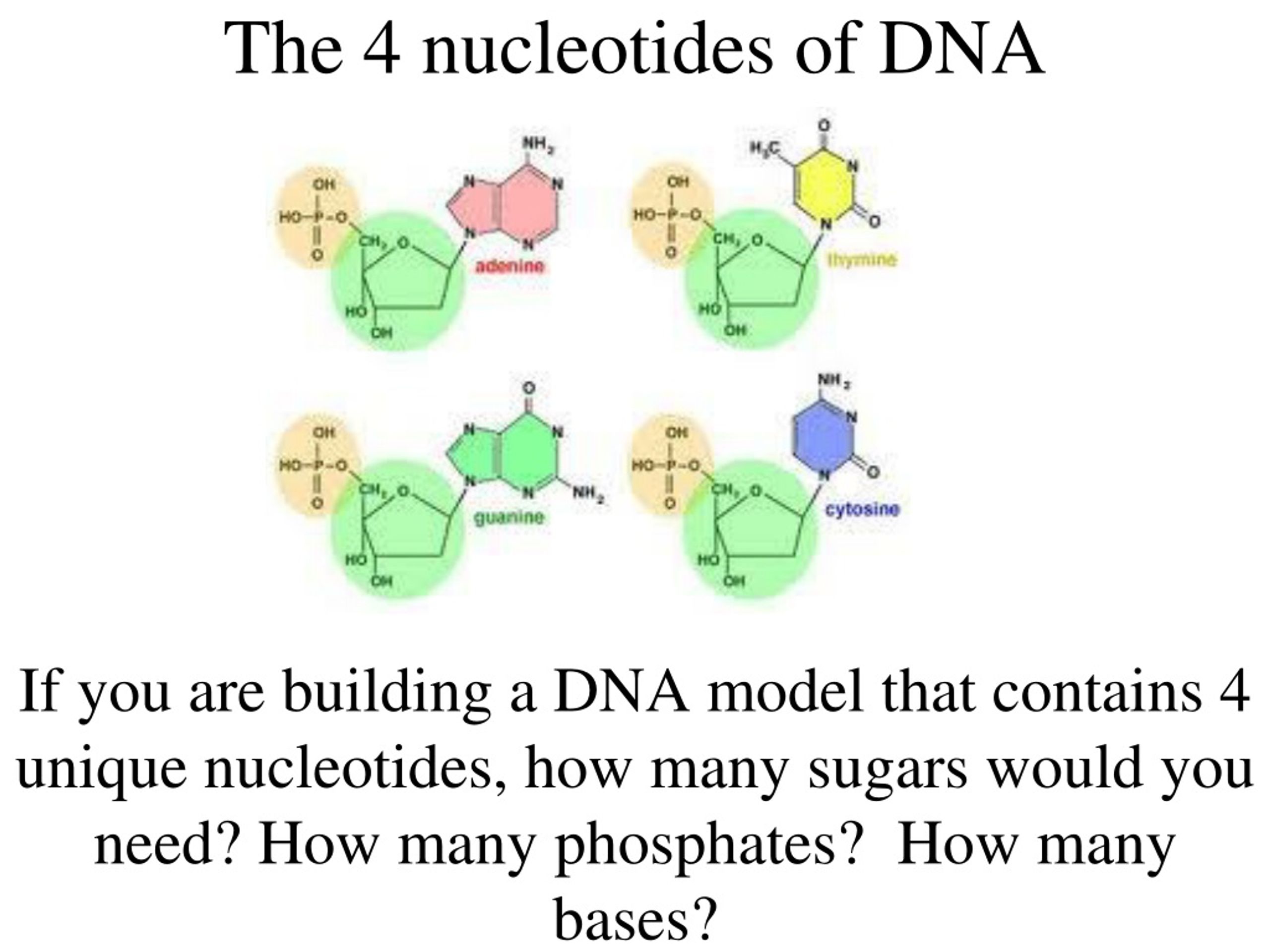
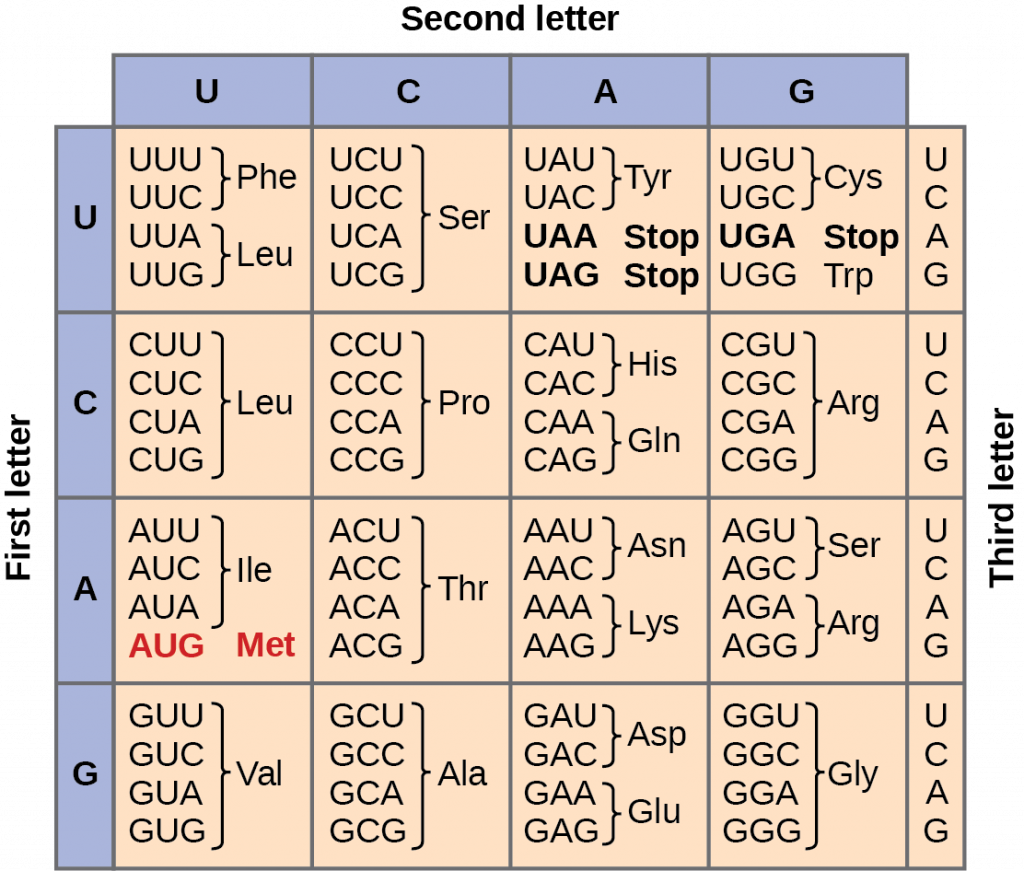
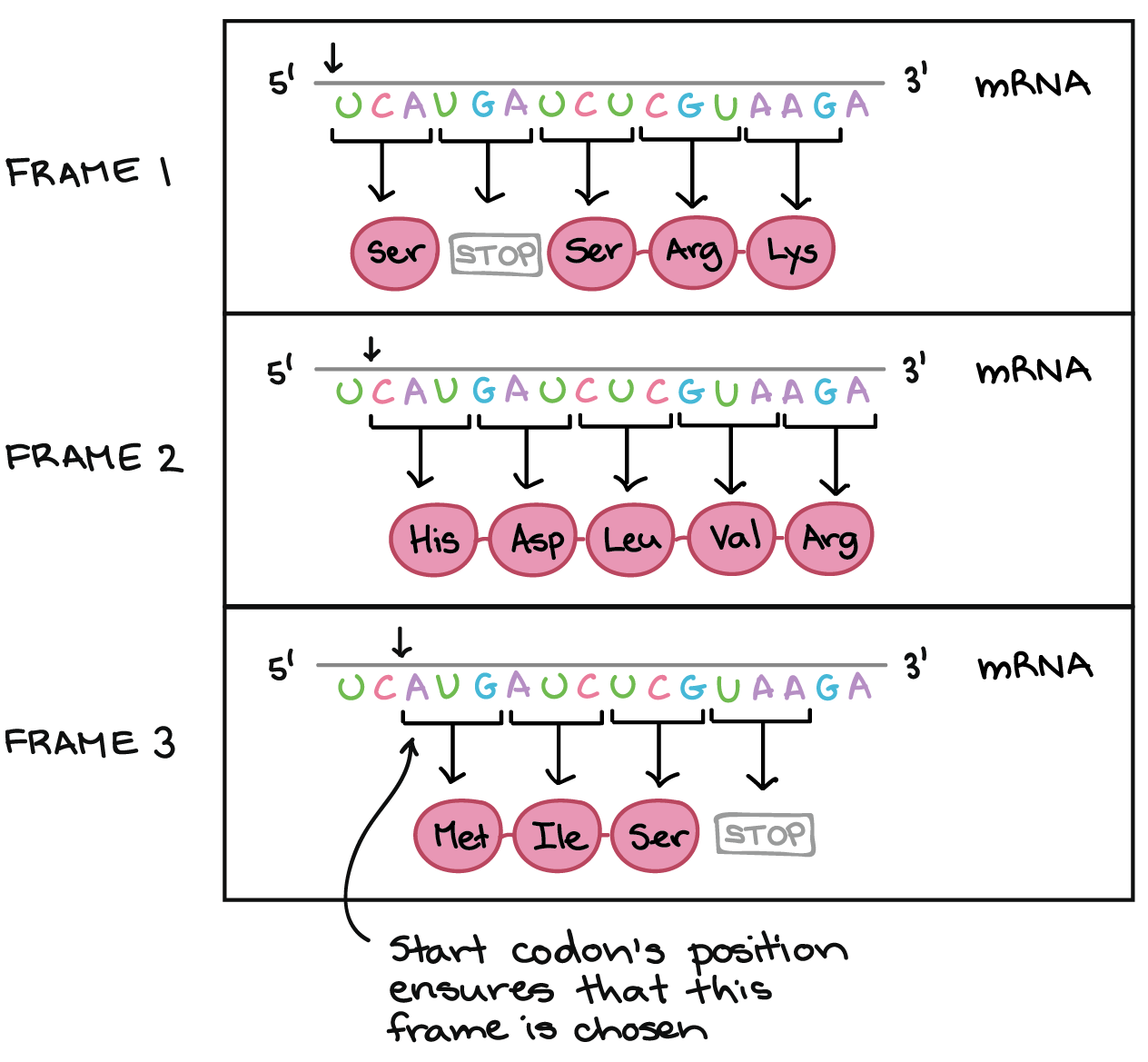
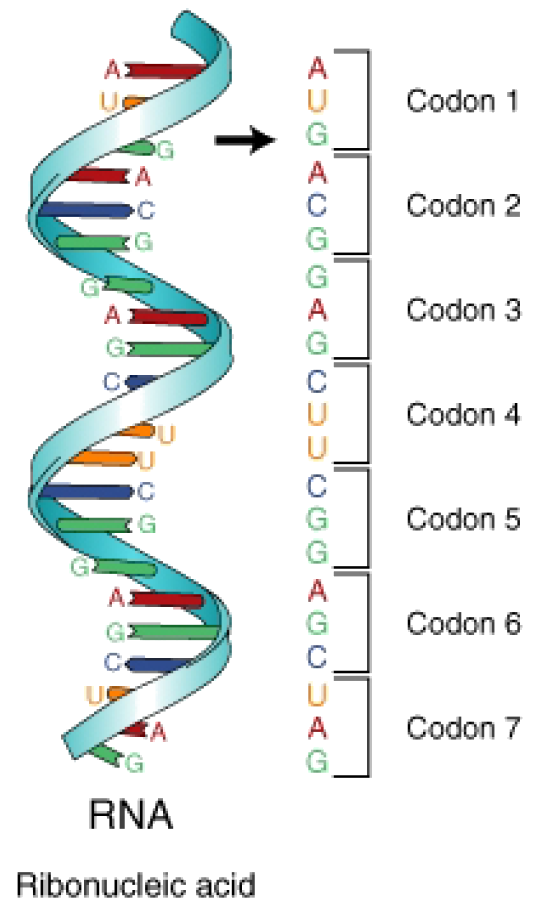
How Many Nucleotides Are Needed To Form A Codon - How many codons are now available? Web cells decode mrnas by reading their nucleotides in groups of three, called codons. This means an amino acid can be encoded by. Web how many codons are possible if the codon consists of only two nucleotides? Web consider a codon of the form nnk (where n = a denine, c ytosine, g uanine or u racil & k = u racil or g uanine). Web how many nucleotides are needed to form a codon? There are differences in sugars, bases, and the number of strands. Web nucleotide is a holonym of codon. Three is the minimum number of nucleotides per codon needed to encode 20 amino acids. 20 amino acids are encoded by combinations of 4 nucleotides. Web how many nucleotides are needed to form a codon? Web 27 nucleotides (3 nucleotides/codon) 1a: Web how many codons are possible if the codon consists of only two nucleotides? Three adjacent nucleotides constitute a unit known as the codon,. This means an amino acid can be encoded by. Three is the minimum number of nucleotides per codon needed to encode 20 amino acids. The difference between dna and rna is that. Web rna is composed of four nucleotides: Web a codon is a sequence of three nucleotides on a strand of dna or rna. Web a codon table can be used to translate a genetic code into a. 20 amino acids are encoded by combinations of 4 nucleotides. Each codon specifies a particular amino acid, or, in some cases, provides a stop signal that. Three is the minimum number of nucleotides per codon needed to encode 20 amino acids. There are differences in sugars, bases, and the number of strands. Adenine (a), uracil (u), guanine (g), and cytosine. Web it was also known that there are only four nucleotides in mrna: Thus, 20 amino acids are coded by only four unique. Web a codon table can be used to translate a genetic code into a sequence of amino acids. There are differences in sugars, bases, and the number of strands. This means an amino acid can be encoded. Web a codon is a sequence of three nucleotides on a strand of dna or rna. Each codon specifies a particular amino acid, or, in some cases, provides a stop signal that. 20 amino acids are encoded by combinations of 4 nucleotides. The standard genetic code is traditionally represented as an rna codon table, because. Three adjacent nucleotides constitute a. The difference between dna and rna is that. Three adjacent nucleotides constitute a unit known as the codon,. Web all 64 codons have been assigned meaning, with 61 of them coding for amino acids and the remaining 3 serving as the termination signals, also called nonsense codons (table. Nucleotide is a meronym of codon. Web in theory can a codon. Three is the minimum number of nucleotides per codon needed to encode 20 amino acids. Adenine (a), uracil (u), guanine (g), and cytosine (c). The difference between dna and rna is that. Web it was also known that there are only four nucleotides in mrna: Web a codon is a sequence of three nucleotides on a strand of dna or. Adenine (a), uracil (u), guanine (g), and cytosine (c). This means an amino acid can be encoded by. Web a codon is a sequence of three nucleotides on a strand of dna or rna. Web a codon table can be used to translate a genetic code into a sequence of amino acids. Since there's 3 nucleotides representing an amino acid,. Web a codon table can be used to translate a genetic code into a sequence of amino acids. 20 amino acids are encoded by combinations of 4 nucleotides. Thus, 20 amino acids are coded by only four unique. When coding for a protein, a sequence of 3 nucleotides is used to code for each amino acid. In biochemistry terms the. Three is the minimum number of nucleotides per codon needed to encode 20 amino acids. Web nucleotide is a holonym of codon. Web consider a codon of the form nnk (where n = a denine, c ytosine, g uanine or u racil & k = u racil or g uanine). Three adjacent nucleotides constitute a unit known as the codon,.. When coding for a protein, a sequence of 3 nucleotides is used to code for each amino acid. Web how many nucleotides are needed to form a codon? How many codons are now available? Three is the minimum number of nucleotides per codon needed to encode 20 amino acids. Web consider a codon of the form nnk (where n = a denine, c ytosine, g uanine or u racil & k = u racil or g uanine). The standard genetic code is traditionally represented as an rna codon table, because. In biochemistry terms the difference between codon and nucleotide is that codon is a sequence of three. Web rna is composed of four nucleotides: Web all 64 codons have been assigned meaning, with 61 of them coding for amino acids and the remaining 3 serving as the termination signals, also called nonsense codons (table. 20 amino acids are encoded by combinations of 4 nucleotides. Web a codon is a sequence of three nucleotides on a strand of dna or rna. There are differences in sugars, bases, and the number of strands. This means an amino acid can be encoded by. Three adjacent nucleotides constitute a unit known as the codon,. Web a codon table can be used to translate a genetic code into a sequence of amino acids. Thus, 20 amino acids are coded by only four unique. Web nucleotide is a holonym of codon. Since there's 3 nucleotides representing an amino acid, then there are 64 possibilities. Why are codons 3 nucleotides in. Web it was also known that there are only four nucleotides in mrna:How Many Nucleotide Bases Make Up A Codon The Code Consists Of 64
How Many Nucleotides Are in 12 Mrna Codons
A Codon Consists of a Sequence of How Many Nucleotides
Codons, Anticodons & Amino Acids Maxwell's Principles of Biology
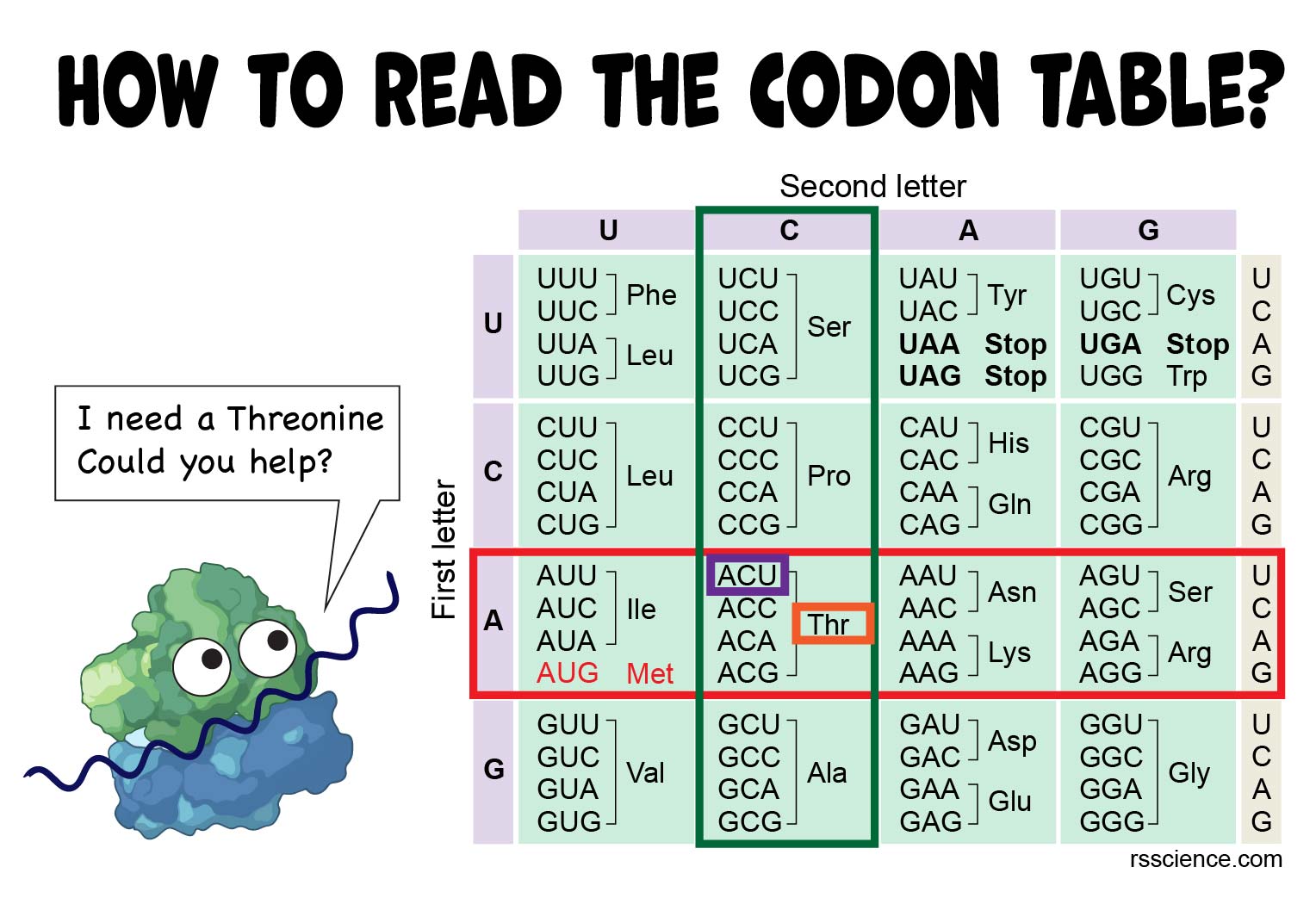
How to Read the Amino Acids Codon Chart? Code and mRNA
Learn how the code is used to translate mRNA into proteins and
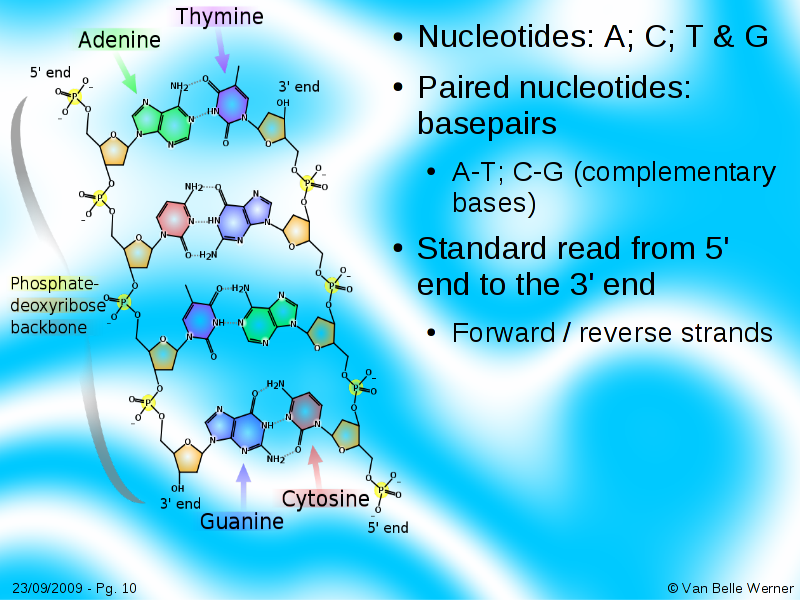
Nucleotides and Bases Generation
Nucleotides to Amino Acids
Codons, nucleotides and amino acids explained YouTube
Stop Codon The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary
Related Post: