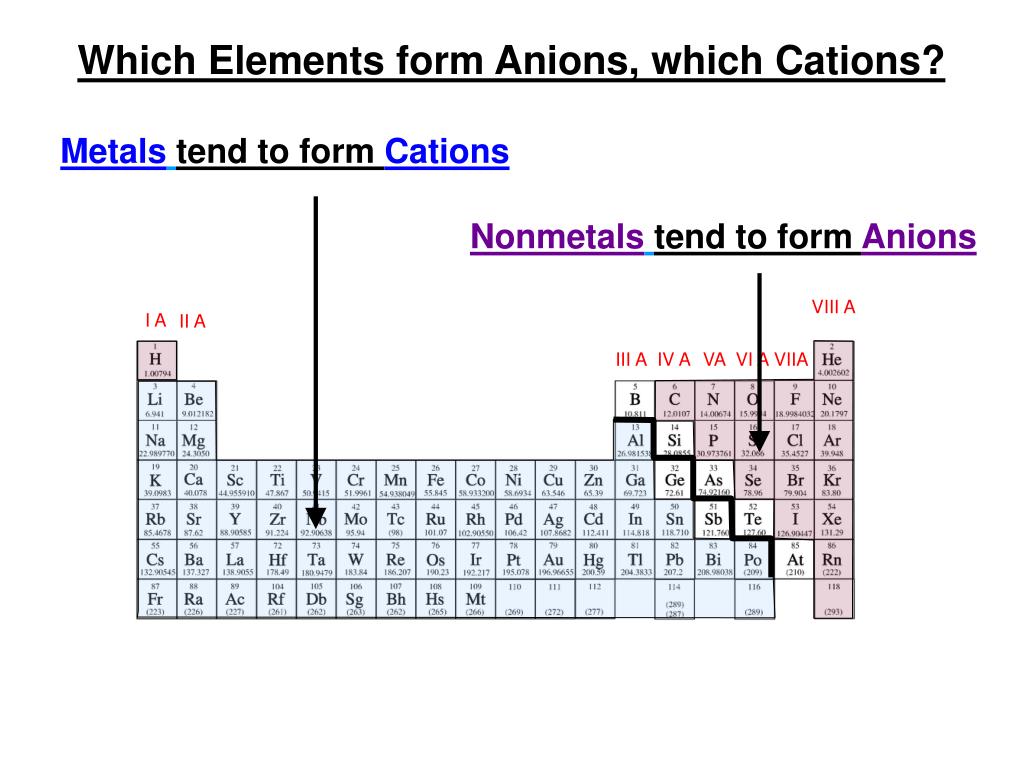
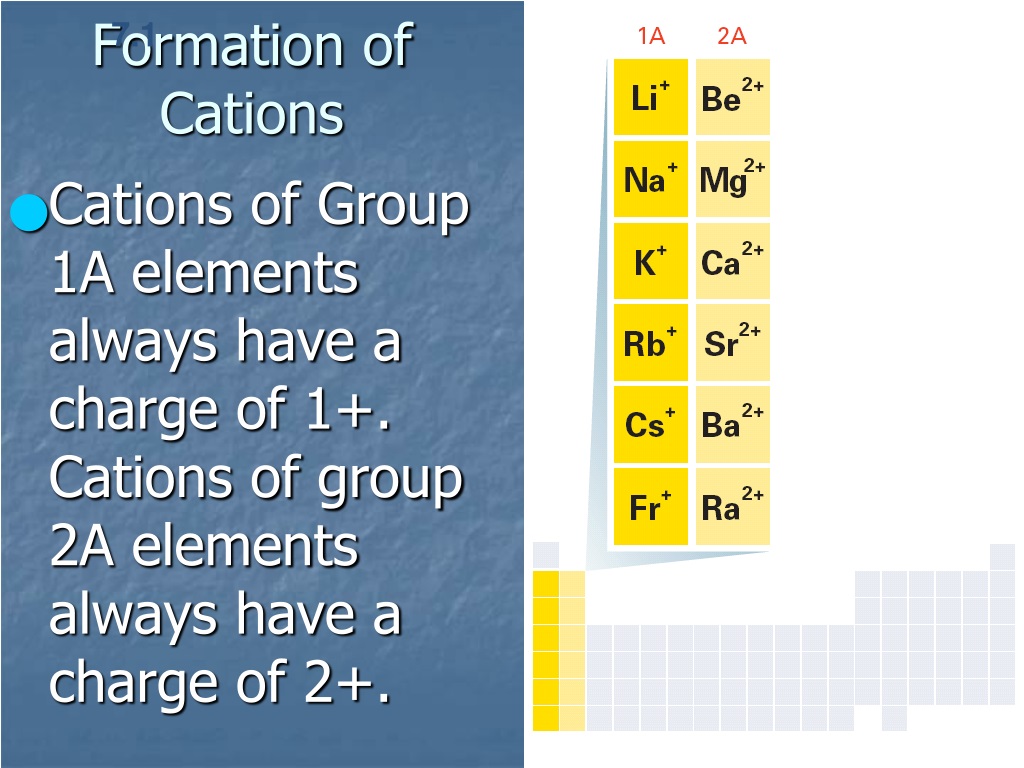
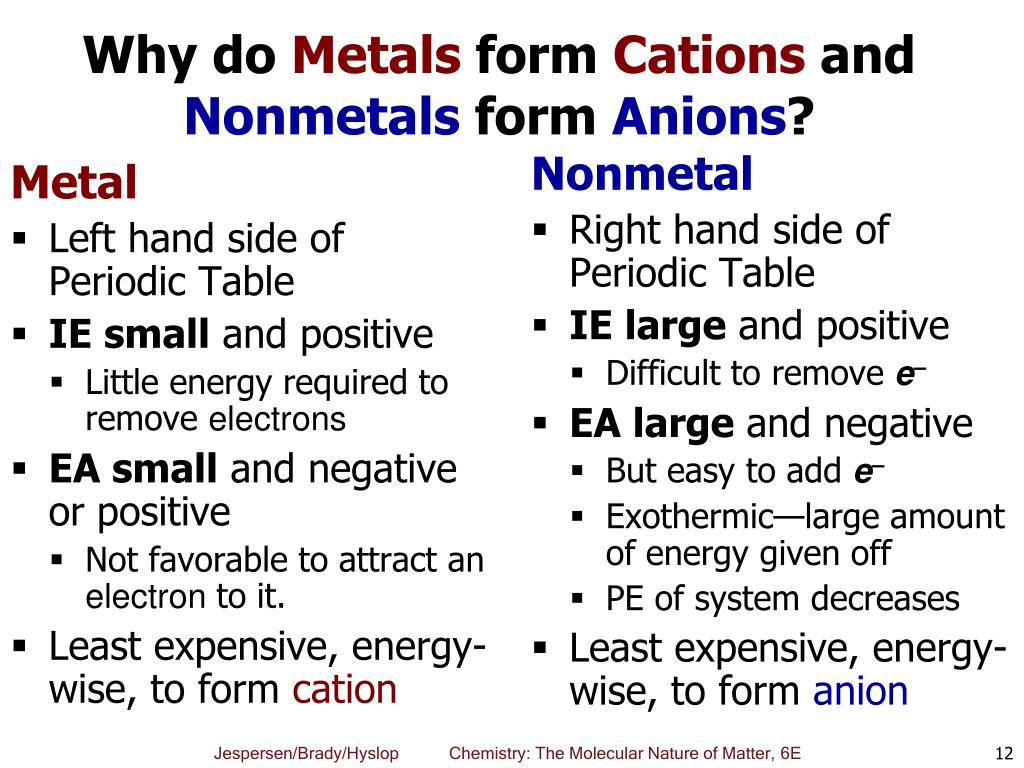
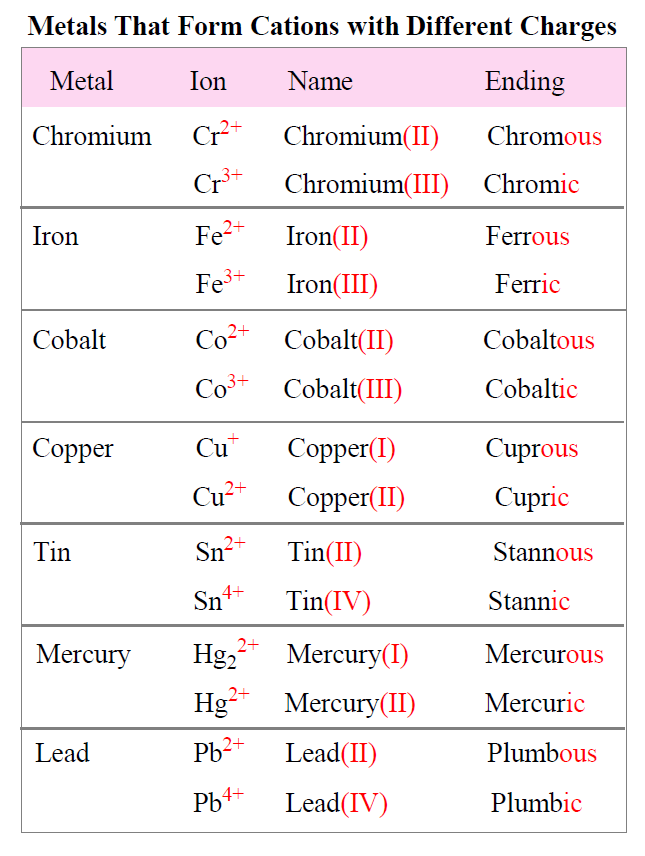
Why Do Metals Form Cations
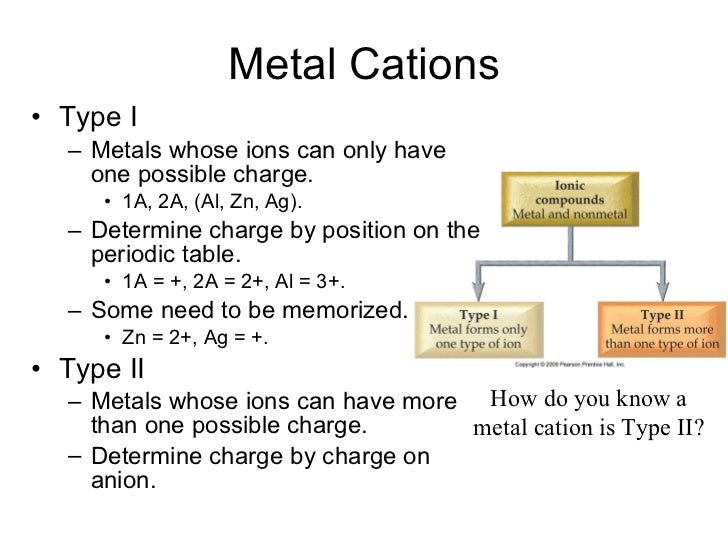
Why Do Metals Form Cations - Alkali and alkaline earth metals tend to form cations because when losing 1 or 2. Web so this question we are talking about why medals like to form cat ions and non models like the form and ions. Perhaps you mean they both have 1 valence electron that must. Because their electrons are mobile, metallic. We will take a closer look at why is that so. Web we would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Cation formation is favored by the relatively low ionization energies of the free metal (which makes it easier to form the. Web transition metals achieve stability by arranging their electrons accordingly and are oxidized, or they lose electrons to other atoms and ions. Metallic solids are composed of metal cations held together by a delocalized sea of valence electrons. So let's first get appear at a table. Metallic solids are composed of metal cations held together by a delocalized sea of valence electrons. Cations have a positive charge. Web metals tend to become cations because they have a tendency to lose electrons and form positively charged ions. Alkali and alkaline earth metals tend to form cations because when losing 1 or 2. Because their electrons are mobile,. Web the strength of the bonds between the metal ion and water molecules in the primary solvation shell increases with the electrical charge, z, on the metal ion and decreases as. At least at first glance, it's not an element that suggests metallic properties. Then, there's hydrogen, a colorless and odorless gas. Web most transition metals differ from the metals. Web so this question we are talking about why medals like to form cat ions and non models like the form and ions. Because their electrons are mobile, metallic. It is easiest to achieve noble gas configurations by removing valence electrons from metals (which. Web metal atoms lose electrons to form positive ions ( cations. So let's first get appear. Web we would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Cations have a positive charge. Then, there's hydrogen, a colorless and odorless gas. Web the answer is usually a metal. Metallic solids are composed of metal cations held together by a delocalized sea of valence electrons. Alkali and alkaline earth metals tend to form cations because when losing 1 or 2. Perhaps you mean they both have 1 valence electron that must. Web the answer is usually a metal. Potassium is in the 4th period and therefore has at least 4 shells occupied with electrons while lithium is in period 2 and thus only has 2. This is due to the arrangement of electrons. It is easiest to achieve noble gas configurations by removing valence electrons from metals (which. Then, there's hydrogen, a colorless and odorless gas. Web so this question we are talking about why medals like to form cat ions and non models like the form and ions. Web cations are atoms that contain. At least at first glance, it's not an element that suggests metallic properties. Web most transition metals differ from the metals of groups 1, 2, and 13 in that they are capable of forming more than one cation with different ionic charges. Web the answer is usually a metal. It is easiest to achieve noble gas configurations by removing valence. Metallic solids are composed of metal cations held together by a delocalized sea of valence electrons. Web the alkali metals tend to form +1 cations. This is due to the arrangement of electrons. Then, there's hydrogen, a colorless and odorless gas. Web most transition metals differ from the metals of groups 1, 2, and 13 in that they are capable. Web it is generally known that metals tend to form cations. Web transition metals achieve stability by arranging their electrons accordingly and are oxidized, or they lose electrons to other atoms and ions. So let's first get appear at a table. Web the alkali metals tend to form +1 cations. Cation formation is favored by the relatively low ionization energies. Web the answer is usually a metal. Web it is generally known that metals tend to form cations. Cation formation is favored by the relatively low ionization energies of the free metal (which makes it easier to form the. Perhaps you mean they both have 1 valence electron that must. It is easiest to achieve noble gas configurations by removing. Web cations are atoms that contain a positive charge, and they are formed when the atoms lose electrons which are negatively charged. Web so this question we are talking about why medals like to form cat ions and non models like the form and ions. We will take a closer look at why is that so. Web the strength of the bonds between the metal ion and water molecules in the primary solvation shell increases with the electrical charge, z, on the metal ion and decreases as. At least at first glance, it's not an element that suggests metallic properties. Perhaps you mean they both have 1 valence electron that must. Web metal atoms lose electrons to form positive ions ( cations. Web it is generally known that metals tend to form cations. Metallic solids are composed of metal cations held together by a delocalized sea of valence electrons. Web metals tend to become cations because they have a tendency to lose electrons and form positively charged ions. Web the answer is usually a metal. Cations have a positive charge. Energy is released when electrons are removed from metal ions. Cation formation is favored by the relatively low ionization energies of the free metal (which makes it easier to form the. Web we would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. So let's first get appear at a table. Potassium is in the 4th period and therefore has at least 4 shells occupied with electrons while lithium is in period 2 and thus only has 2 shells occupied with electrons. Web most transition metals differ from the metals of groups 1, 2, and 13 in that they are capable of forming more than one cation with different ionic charges. Then, there's hydrogen, a colorless and odorless gas. It is easiest to achieve noble gas configurations by removing valence electrons from metals (which.PPT Ionic Bonding PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5679234
Chem matters ch6_ionic_bond
PPT Lecture 4. Chapter 2. Structure of the Atom (Contd.) PowerPoint
Cations and Anions Definitions, Examples, and Differences
PPT Chapter 7 Ionic and Metallic Bonding PowerPoint Presentation
PPT Chapter 9 The Basics of Chemical Bonding PowerPoint Presentation
[Solved] Why do metals form cations? 9to5Science
Writing Chemical Formulas For Ionic Compounds Chemistry Steps
Chapter 5 compounds
Chem matters ch6_ionic_bond
Related Post: