Why Do Carbon Form Covalent Bond
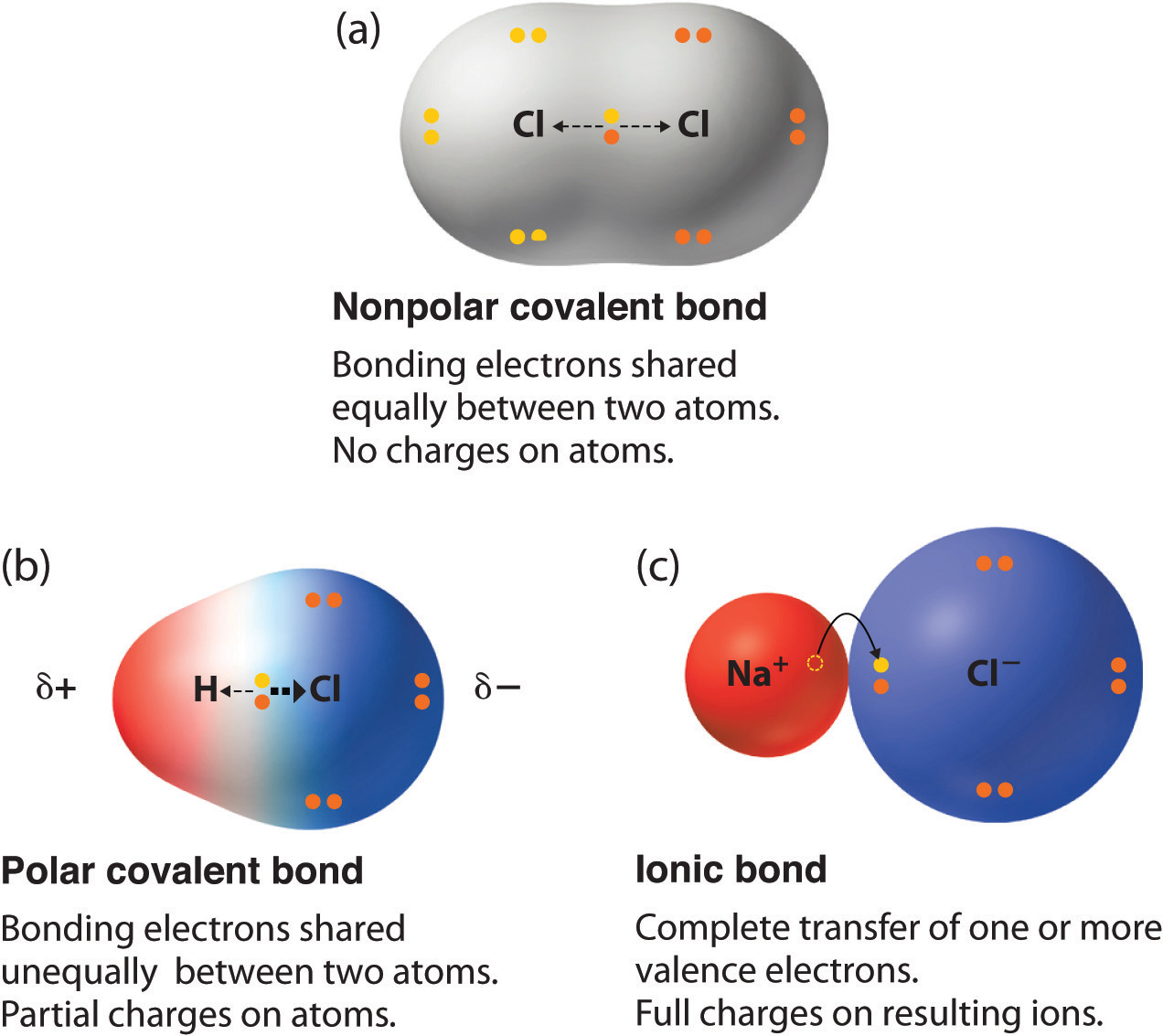
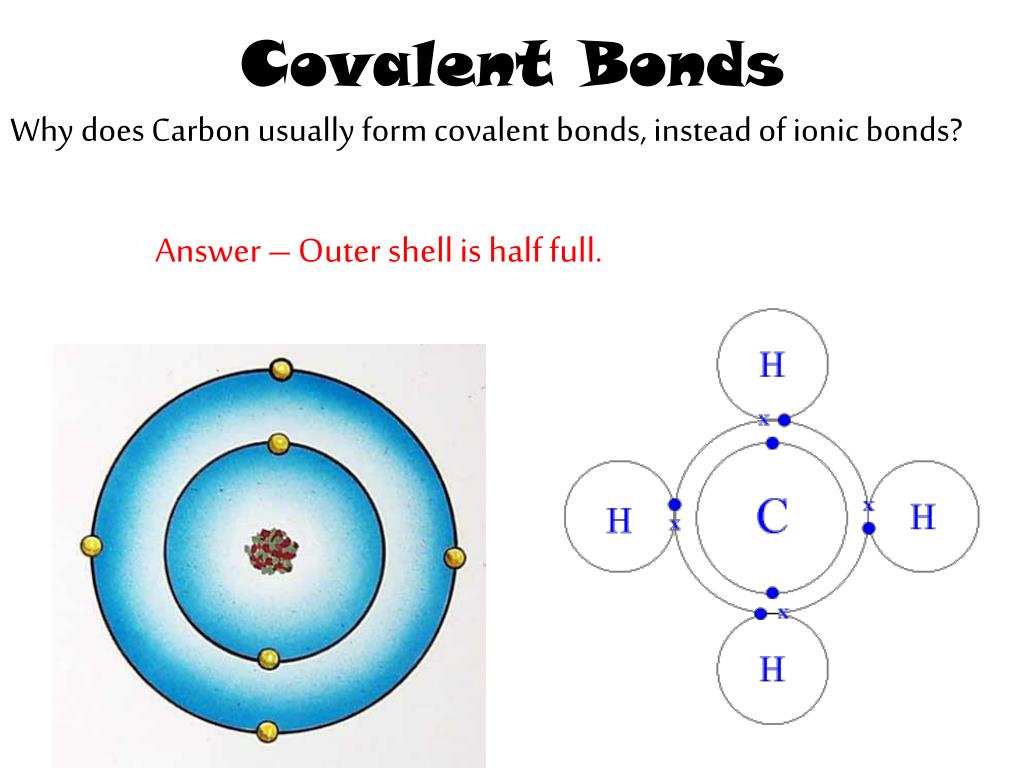
Why Do Carbon Form Covalent Bond - The electrons involved are in the outer shells of the atoms. Web why does carbon form covalent bonds? The most common type of bond formed by carbon is a covalent bond. Web there is only a small energy gap between the 2s and 2p orbitals, and so it pays the carbon to provide a small amount of energy to promote an electron from the 2s to the empty 2p to give 4 unpaired electrons. Well, carbon can form up to four covalent bonds. A covalent bond is formed between two atoms by sharing electrons. Carbon has 4 electrons in its outermost shell, and needs to gain or loss 4 electrons to attain nobel gas configuration. A carbon atom has no tendency to lose its valence electrons or gain 4 electrons from other atoms. The simplest carbon molecule is methane (ch 4 ), depicted here. For example, in methane (ch 4 ), carbon forms covalent bonds with four hydrogen atoms. Well, carbon can form up to four covalent bonds. It cannot lose 4 electrons as it involves. Web there is only a small energy gap between the 2s and 2p orbitals, and so it pays the carbon to provide a small amount of energy to promote an electron from the 2s to the empty 2p to give 4 unpaired electrons.. Web four covalent bonds can be formed by carbon. So, the carbon atom completes. Carbon has 4 electrons in its valence shell. Well, carbon can form up to four covalent bonds. This is because carbon has 4 valence. Is determined by the distance at which the lowest potential energy is achieved. The number of bonds an element forms in a covalent compound is. So, the carbon atom completes. The simplest carbon molecule is methane (ch 4 ), depicted here. Web there is only a small energy gap between the 2s and 2p orbitals, and so it pays the. Web we would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. So, the carbon atom completes. Web carbon atoms may thus form bonds to as many as four other atoms. Is determined by the distance at which the lowest potential energy is achieved. A carbon atom has no tendency to lose its valence electrons or. Web carbon can form four covalent bonds to create an organic molecule. The simplest carbon molecule is methane (ch 4 ), depicted here. Covalent bond helps in the formation of compounds with the help of carbon. The extra energy released when the bonds. Carbon has 4 electrons in its valence shell. Carbon has 4 electrons in its valence shell. Web carbon can form four covalent bonds to create an organic molecule. With hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, and other heteroatoms. Chemical bonds between nonmetals are known as covalent bonds. Carbon does not form ionic bonds because it has 4 valence electrons, half of an octet. Carbon has 4 electrons in its outermost shell, and needs to gain or loss 4 electrons to attain nobel gas configuration. In most cases, carbon shares electrons with other atoms. Web carbon atoms may thus form bonds to as many as four other atoms. Covalent bond helps in the formation of compounds with the help of carbon. The electrons involved. A carbon atom has no tendency to lose its valence electrons or gain 4 electrons from other atoms. They are important in the production of many man. Each bond corresponds to a pair of shared electrons (one from carbon and one from hydrogen), giving carbon. A covalent bond is formed between two atoms by sharing electrons. Is determined by the. For example, in methane (ch 4 ), carbon forms covalent bonds with four hydrogen atoms. This is because carbon has 4 valence. Web why does carbon form covalent bonds? Carbon does not form ionic bonds because it has 4 valence electrons, half of an octet. To attain stability, it should either gain 4 electrons or lose 4 electrons. Carbon has 4 electrons in its valence shell. This is because carbon has 4 valence. Each bond corresponds to a pair of shared electrons (one from carbon and one from hydrogen), giving carbon. The electrons involved are in the outer shells of the atoms. Web why does carbon form covalent bonds? Carbon has 4 electrons in its valence shell. A covalent bond is formed between two atoms by sharing electrons. Two atoms share a pair of electrons in a. To attain stability, it should either gain 4 electrons or lose 4 electrons. The potential energy of two separate hydrogen atoms (right) decreases as. Chemical bonds between nonmetals are known as covalent bonds. Web one carbon atom forms four covalent bonds with four hydrogen atoms by sharing a pair of electrons between itself and each hydrogen (h) atom. This is because carbon has 4 valence. The most common type of bond formed by carbon is a covalent bond. Is determined by the distance at which the lowest potential energy is achieved. Each bond corresponds to a pair of shared electrons (one from carbon and one from hydrogen), giving carbon. With hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, and other heteroatoms. Web there is only a small energy gap between the 2s and 2p orbitals, and so it pays the carbon to provide a small amount of energy to promote an electron from the 2s to the empty 2p to give 4 unpaired electrons. For example, in methane (ch 4 ), carbon forms covalent bonds with four hydrogen atoms. In most cases, carbon shares electrons with other atoms. Web carbon can form four covalent bonds to create an organic molecule. To form ionic bonds, carbon molecules must either gain or. It is because carbon has an electronic configuration and it can neither accept nor donate. The electrons involved are in the outer shells of the atoms. Carbon has 4 electrons in its outermost shell, and needs to gain or loss 4 electrons to attain nobel gas configuration.Chapter 5.6 Properties of Polar Covalent Bonds Chemistry LibreTexts
BONDING IN CARBON THE COVALENT BOND YouTube
Science class 10 Why carbon form covalent bonds YouTube
PPT Unit 1 Biochemistry The Chemistry of Life PowerPoint
PPT 2.1 Nature of Matter PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
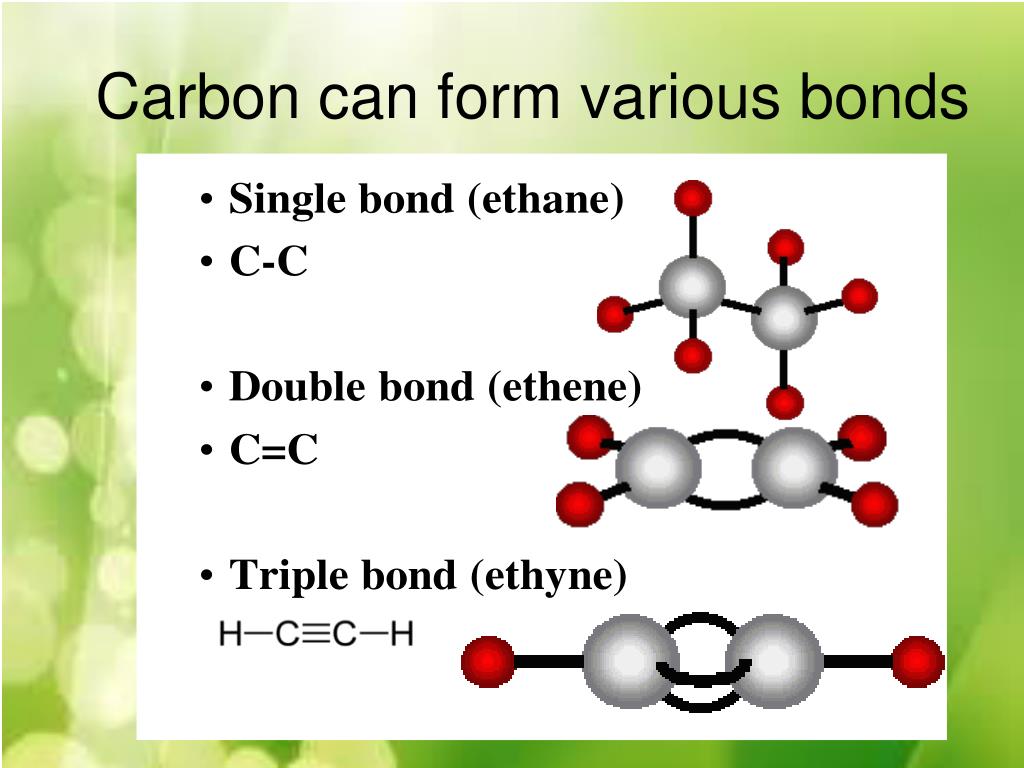
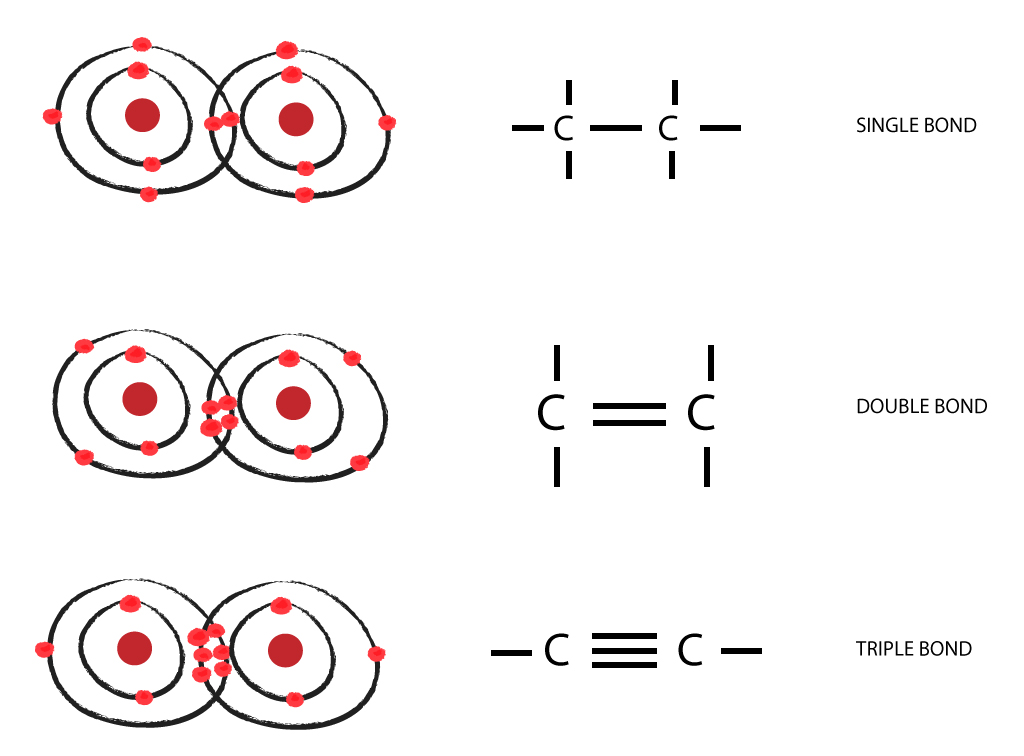
Carbon to Carbon Single, Double & Triple Bonds Surfguppy
Chapter 8 Covalent Bonding Covalent bonding Usually forms
Covalent bond Definition, Properties, Examples, & Facts Britannica
PPT Why do atoms form bonds? PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Four covalent bonds. Carbon has four valence electrons and here a
Related Post: