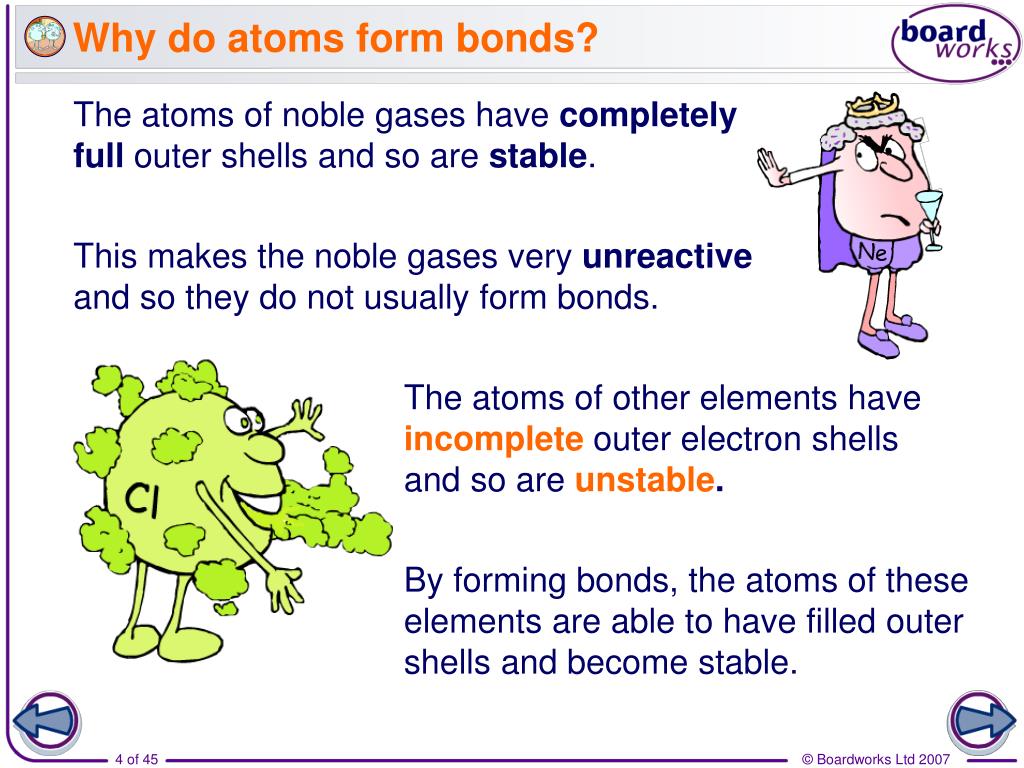
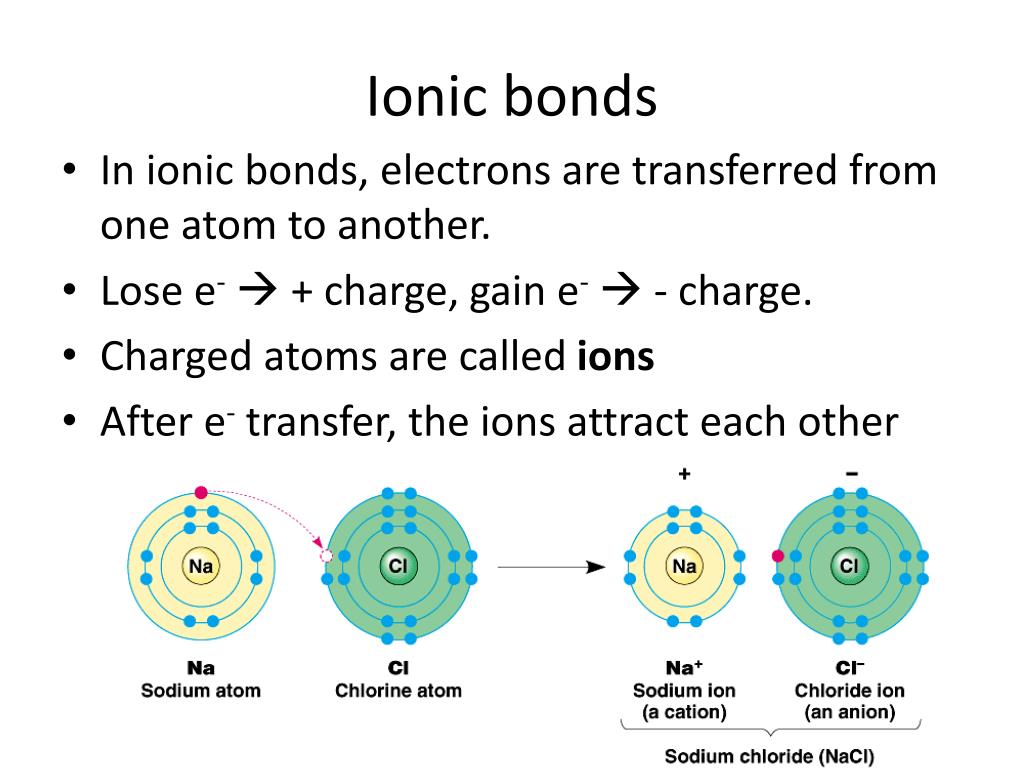
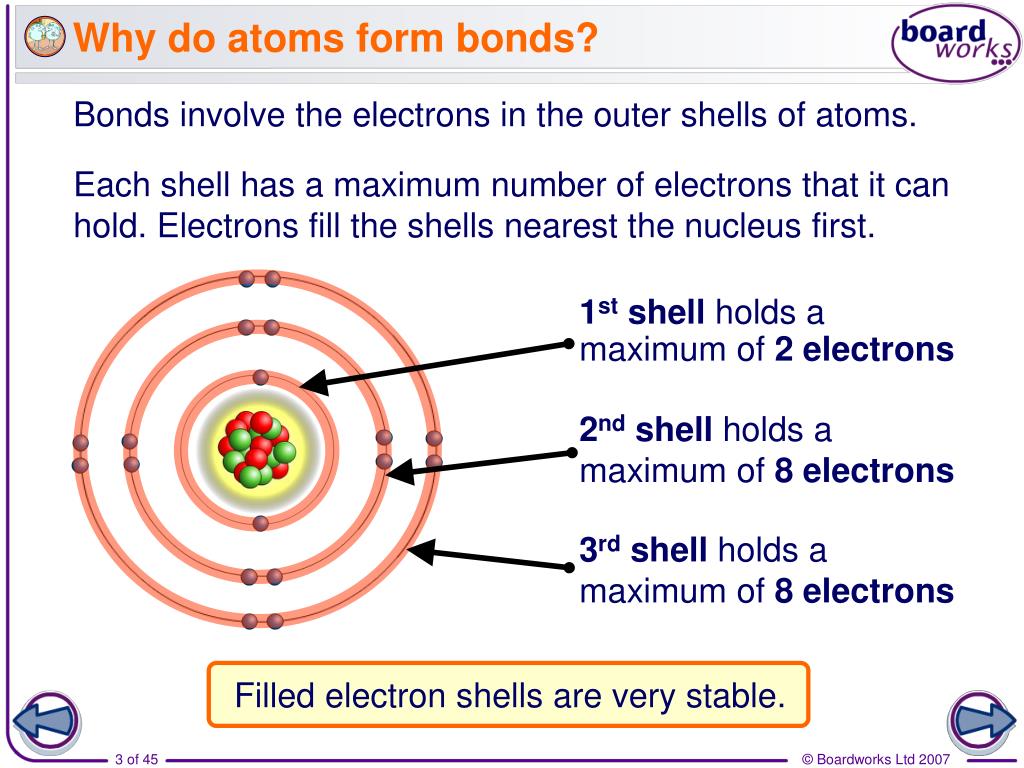
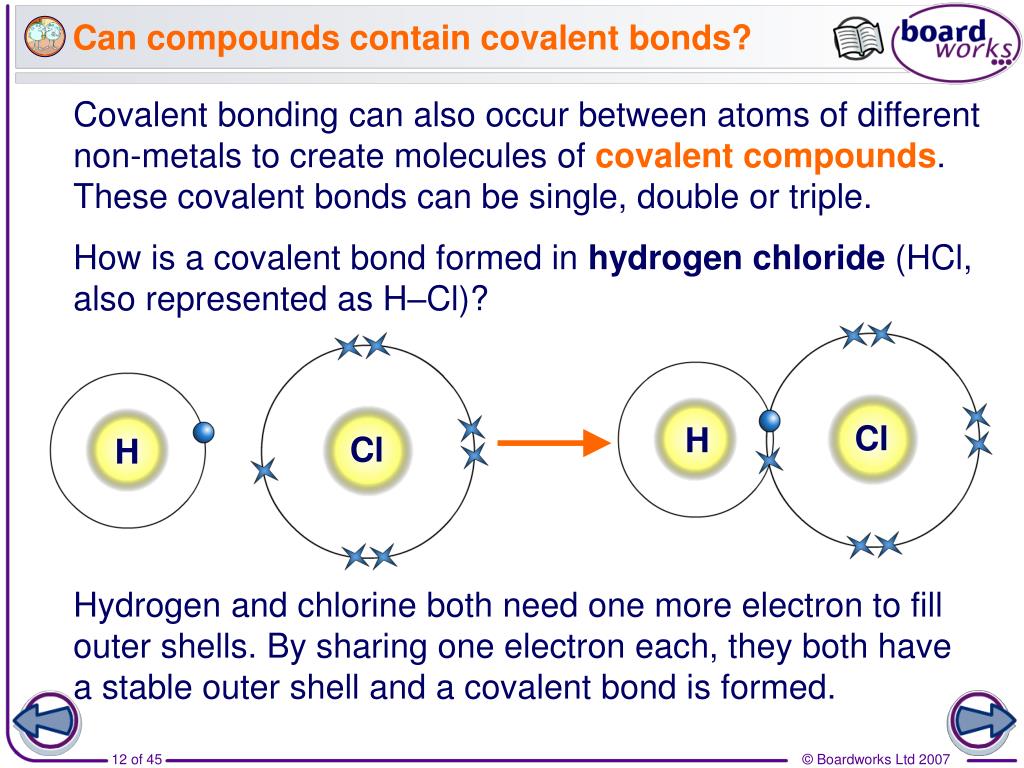
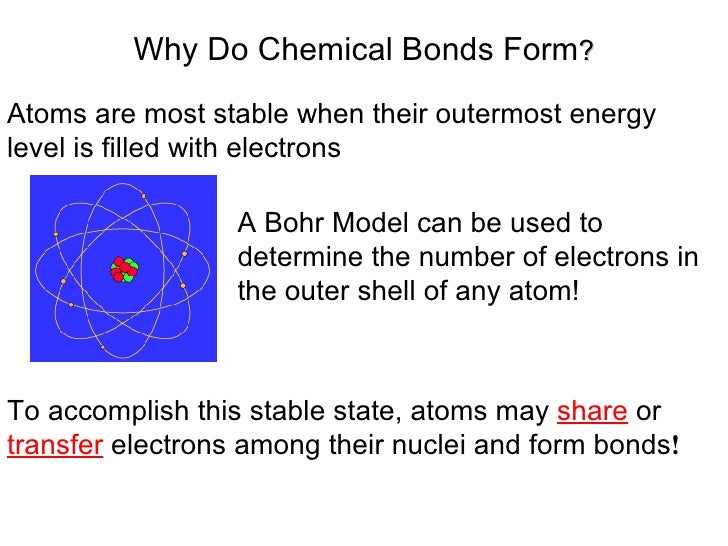
Why Do Atoms Form Chemical Bonds With Other Atoms
Why Do Atoms Form Chemical Bonds With Other Atoms - Web why do atoms form bonds with each other? Web a chemical bond is a force of attraction between atoms or ions. Atoms form bonds because the products are more stable than the isolated atoms; Valence electrons are the electrons in the outer energy level of an atom that may be involved in chemical interactions. So those electrons belong to both of those atoms. Bonding interactions are characterized by a particular energy (the bond energy or lattice energy), which is the amount of energy required to dissociate the substance into its components; The kl bond in ki the nb bond in h,nbci, d. It becomes a positive hydrogen ion (h+). Classify the following bonds as ionic, polar covalent, or nonpolar covalent: A hydrogen atom (atomic number 1) has one proton and a lone electron, so it can readily share its electron with the outer shell of another atom. Bonds form when atoms share or transfer valence electrons. Web why do atoms form bonds with each other? Web just as the structure of the atom is held together by the electrostatic attraction between the positively charged nucleus and the negatively charged electrons surrounding it, the stability within chemical bonds is also due to electrostatic attractions. The cc bond in. The cf bond in cf, (chang, 11 edition, 9.39) 3. The two electrons complete its outer. Valence electrons are the basis of all chemical bonds. Web a chemical bond is a force of attraction between atoms or ions. Is determined by the distance at which the lowest potential energy is achieved. In covalent bonding electrons are shared between two atoms. Web main types of chemical bonds. A hydrogen atom (atomic number 1) has one proton and a lone electron, so it can readily share its electron with the outer shell of another atom. Chemical bonds are formed when electrons in different atoms interact with each other to make an arrangement that. A hydrogen atom (atomic number 1) has one proton and a lone electron, so it can readily share its electron with the outer shell of another atom. Valence electrons are the electrons in the outer energy level of an atom that may be involved in chemical interactions. A covalent bond is formed when atoms share valence electrons. Understand why and. The two electrons complete its outer. Interpret the properties of elements that are important for life from the periodic table. When a hydrogen atom loses its single electron. Understand why and how atoms form bonds. Web main types of chemical bonds. Web to achieve a full valence electrons shell. Bonds form when atoms share or transfer valence electrons. Bonding interactions are characterized by a particular energy (the bond energy or lattice energy), which is the amount of energy required to dissociate the substance into its components; The kl bond in ki the nb bond in h,nbci, d. Web the atoms of. Valence electrons are the basis of all chemical bonds. Web we would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Interpret the properties of elements that are important for life from the periodic table. Ad generationgenius.com has been visited by 100k+ users in the past month The cf bond in cf, (chang, 11 edition, 9.39). Because of its position midway in the second horizontal row of the periodic table, carbon is neither an electropositive. The bond length is the internuclear distance at which the lowest. Web why do atoms form bonds with each other? The kl bond in ki the nb bond in h,nbci, d. In covalent bonding electrons are shared between two atoms. The cf bond in cf, (chang, 11 edition, 9.39) 3. Chemical bonds are formed when electrons in different atoms interact with each other to make an arrangement that is more stable than when the atoms are apart. Valence electrons are the basis of all chemical bonds. Classify the following bonds as ionic, polar covalent, or nonpolar covalent: Interpret the properties. Web we would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Web main types of chemical bonds. Web to achieve a full valence electrons shell. The cc bond in h,cch, b. Web atoms can join together by forming a chemical bond, which is a very strong attraction between two atoms. Classify the following bonds as ionic, polar covalent, or nonpolar covalent: There are three different types of. Ad generationgenius.com has been visited by 100k+ users in the past month The cf bond in cf, (chang, 11 edition, 9.39) 3. The potential energy of two separate hydrogen atoms (right) decreases as they approach each other, and the single electrons on each atom are shared to form a covalent bond. Web atoms can join together by forming a chemical bond, which is a very strong attraction between two atoms. An ionic bond is formed when one atom accepts or donates one or more of its valence electrons to another atom. Web we would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Why do some elements exist as molecules in nature instead of as free atoms? Valence electrons are the electrons in the outer energy level of an atom that may be involved in chemical interactions. Web main types of chemical bonds. Is determined by the distance at which the lowest potential energy is achieved. It becomes a positive hydrogen ion (h+). Web a chemical bond is a force of attraction between atoms or ions. Covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves sharing of electron pairs between atoms. Chemical bonds are formed when electrons in different atoms interact with each other to make an arrangement that is more stable than when the atoms are apart. Bonding interactions are characterized by a particular energy (the bond energy or lattice energy), which is the amount of energy required to dissociate the substance into its components; Web all models of chemical bonding have three common features: Just as atoms can form molecular bonds with other atoms (especially in molecules), some molecules can form bonds with other molecules, as with (oh) radicals and hydrated molecules. Web the atoms of molecules are linked together through a reaction known as chemical bonding.PPT Why do atoms form bonds? PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Ppt Atomic Structure And Chemical Bonding Powerpoint Presentation 7F5
What Happens When Atoms Bond infographic diagram showing how electrons
Covalent bond Definition, Properties, Examples, & Facts Britannica
PPT Types of Bonds PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1996079
PPT Chapter 7 Atoms & Bonding PowerPoint Presentation, free download
PPT Why do atoms form bonds? PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Chemical Bonds · Anatomy and Physiology
PPT Why do atoms form bonds? PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Biochemistry Honors
Related Post: