Which Elements Form Covalent Bonds
Which Elements Form Covalent Bonds - This type of bonding occurs between two atoms of the same element or of. Web el paso community college chem1306: Web the number of covalent bonds an atom can form is called the valence of the atom. Web covalent bonds are formed between two atoms when both have similar tendencies to attract electrons to themselves (i.e., when both atoms have identical or fairly similar. A covalent bond is formed by the equal sharing of electrons from both. Web a covalent bond forming h 2 (right) where two hydrogen atoms share the two electrons. Web in covalent compounds, atoms form covalent bonds that consist of electron pairs shared between two adjacent atomic nuclei. Web based on their locations in the periodic table, which two elements are most likely to form covalent bonds with each other? Web covalent bonds are formed between two atoms when both have similar tendencies to attract electrons to themselves (i.e., when both atoms have identical or fairly similar. Covalent bonds form when electrons are shared between atoms and are attracted by the nuclei of both atoms. Covalent bonding is the sharing of electrons between atoms. Web covalent bonds are formed between two atoms when both have similar tendencies to attract electrons to themselves (i.e., when both atoms have identical or fairly similar. Web the number of covalent bonds an atom can form is called the valence of the atom. Health chemistry i (rodriguez) 3: Covalent bonds. Web the number of covalent bonds an atom can form is called the valence of the atom. Nitrogen (n) and oxygen (o) which. Web based on their locations in the periodic table, which two elements are most likely to form covalent bonds with each other? A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form.. In pure covalent bonds, the electrons are shared. This type of bonding occurs between two atoms of the same element or of. Boron commonly makes only three covalent bonds, resulting in only six. Covalent bonding is the sharing of electrons between atoms. A covalent bond is formed by the equal sharing of electrons from both. A covalent bond is formed by the equal sharing of electrons from both. Boron commonly makes only three covalent bonds, resulting in only six. For example, beryllium can form two covalent bonds, resulting in only four electrons in its valence shell: In pure covalent bonds, the electrons are shared. Molecules of identical atoms, such as h2 and. A covalent bond is formed by the equal sharing of electrons from both. Covalent bonds form when two or more nonmetals combine. Health chemistry i (rodriguez) 3: Web in covalent compounds, atoms form covalent bonds that consist of electron pairs shared between two adjacent atomic nuclei. Web the number of covalent bonds an atom can form is called the valence. Covalent bonding is the sharing of electrons between atoms. Boron commonly makes only three covalent bonds, resulting in only six. Web in covalent compounds, atoms form covalent bonds that consist of electron pairs shared between two adjacent atomic nuclei. Web as a general rule, covalent bonds are formed between elements lying toward the right in the periodic table (i.e., the. Web the most common examples are the covalent compounds of beryllium and boron. The valence of a given atom is the same in most stable neutral organic compounds. Web covalent bonds are formed between two atoms when both have similar tendencies to attract electrons to themselves (i.e., when both atoms have identical or fairly similar. Web based on their locations. Web we would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Web the most common examples are the covalent compounds of beryllium and boron. A covalent bond is formed by the equal sharing of electrons from both. Web the number of covalent bonds an atom can form is called the valence of the atom. Health. Covalent bonding is the sharing of electrons between atoms. Web what elements make covalent bonds? Covalent bonds form when electrons are shared between atoms and are attracted by the nuclei of both atoms. Covalent bonding and simple molecular compounds In pure covalent bonds, the electrons are shared. Covalent bonding is the sharing of electrons between atoms. Web in covalent compounds, atoms form covalent bonds that consist of electron pairs shared between two adjacent atomic nuclei. Web based on their locations in the periodic table, which two elements are most likely to form covalent bonds with each other? Covalent bonds form when two or more nonmetals combine. Web. A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form. A covalent bond is formed by the equal sharing of electrons from both. Web as a general rule, covalent bonds are formed between elements lying toward the right in the periodic table (i.e., the nonmetals). Molecules of identical atoms, such as h2 and. Covalent bonds form when electrons are shared between atoms and are attracted by the nuclei of both atoms. Web introduction to biological macromolecules chemical bonds google classroom chemical bonds hold molecules together and create temporary connections that are essential to. Health chemistry i (rodriguez) 3: Web the number of covalent bonds an atom can form is called the valence of the atom. Web the most common examples are the covalent compounds of beryllium and boron. Web in covalent compounds, atoms form covalent bonds that consist of electron pairs shared between two adjacent atomic nuclei. In pure covalent bonds, the electrons are shared. Covalent bonds form when two or more nonmetals combine. Covalent bonding and simple molecular compounds This type of bonding occurs between two atoms of the same element or of. Web what elements make covalent bonds? For example, both hydrogen and oxygen are nonmetals, and. An example of a covalent compound is ammonia. Web a covalent bond forming h 2 (right) where two hydrogen atoms share the two electrons. Web covalent bonds are formed between two atoms when both have similar tendencies to attract electrons to themselves (i.e., when both atoms have identical or fairly similar. Covalent bonding is the sharing of electrons between atoms.Covalent Bond Biology Dictionary
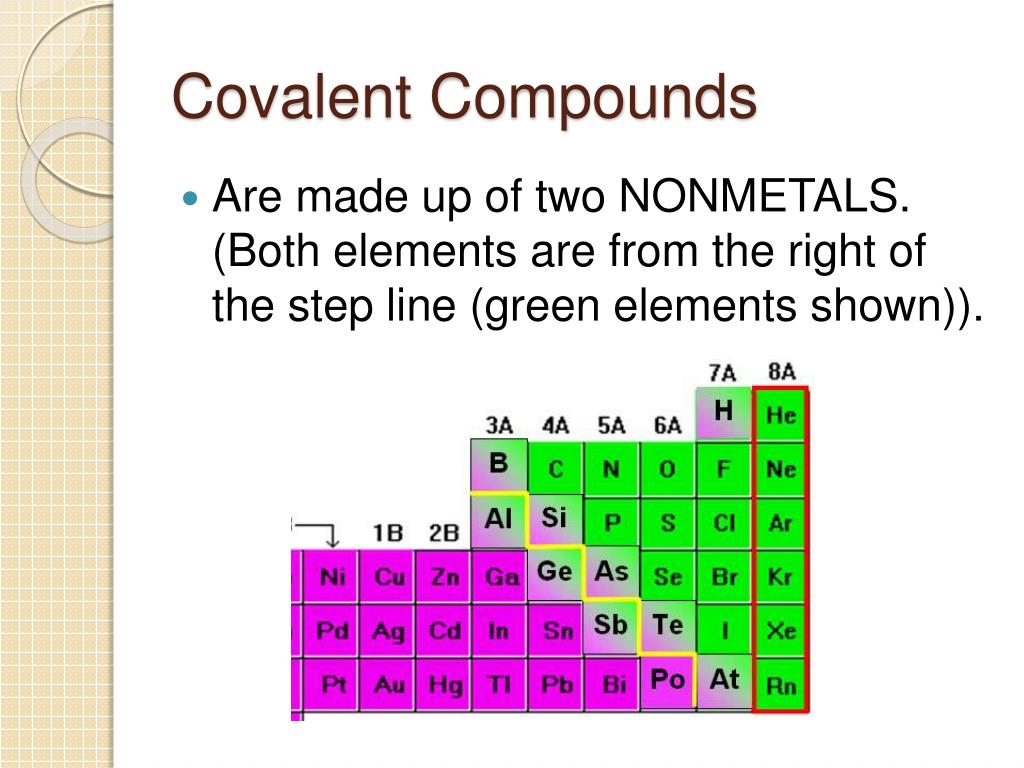
PPT Covalent Compounds PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
CH150 Chapter 4 Covalent Bonds and Molecular Compounds Chemistry
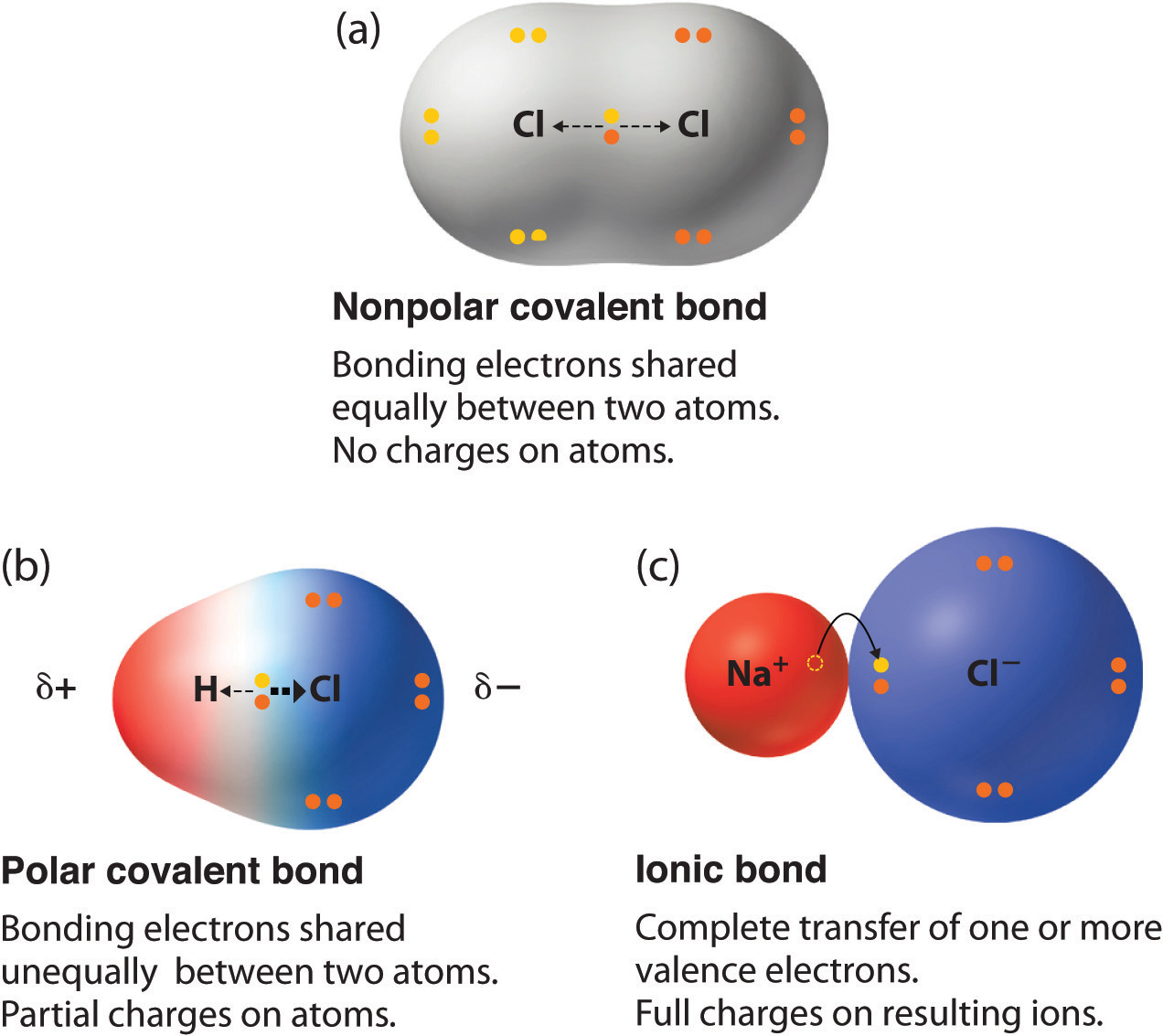
Chapter 5.6 Properties of Polar Covalent Bonds Chemistry LibreTexts
Examples of Covalent Bonds Several Examples of Covalent (molecular
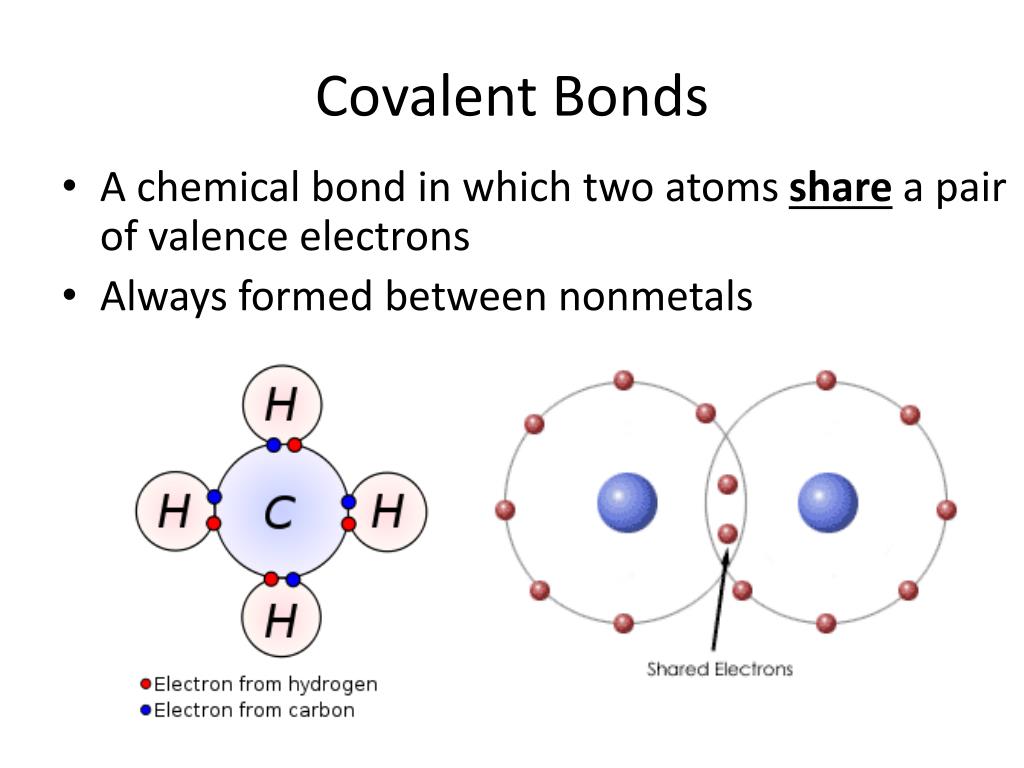
PPT Covalent Bonds PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6647183
The top panel in this figure shows two hydrogen atoms sharing two
covalent bond Definition, Properties, Examples, & Facts Britannica
Covalent Bonds The Basics of Chemical Bonding
Covalent Bonding (Biology) — Definition & Role Expii
Related Post: