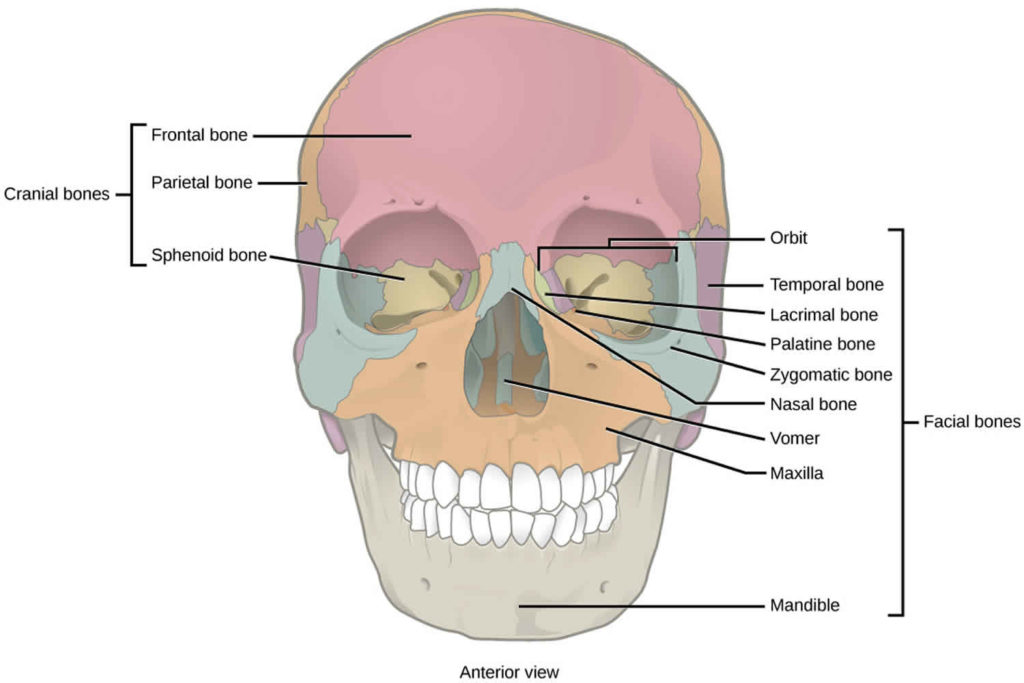
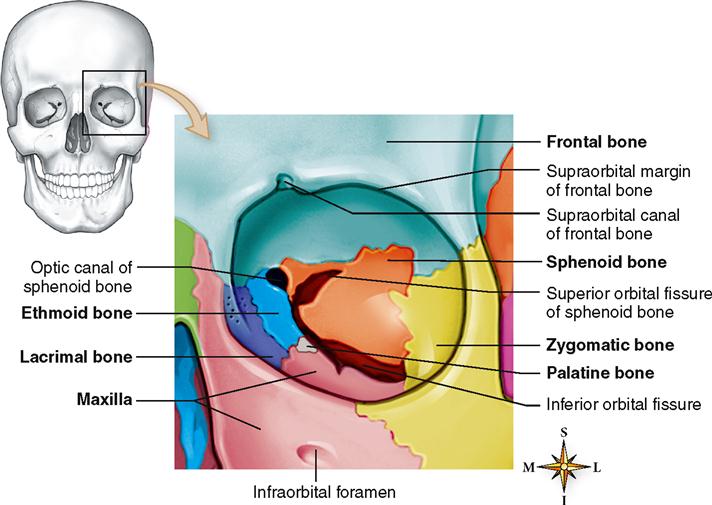
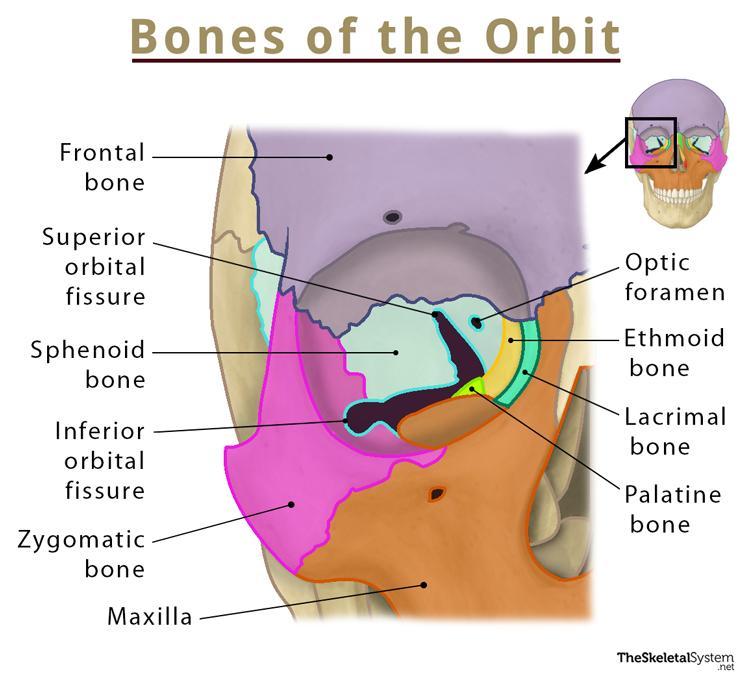
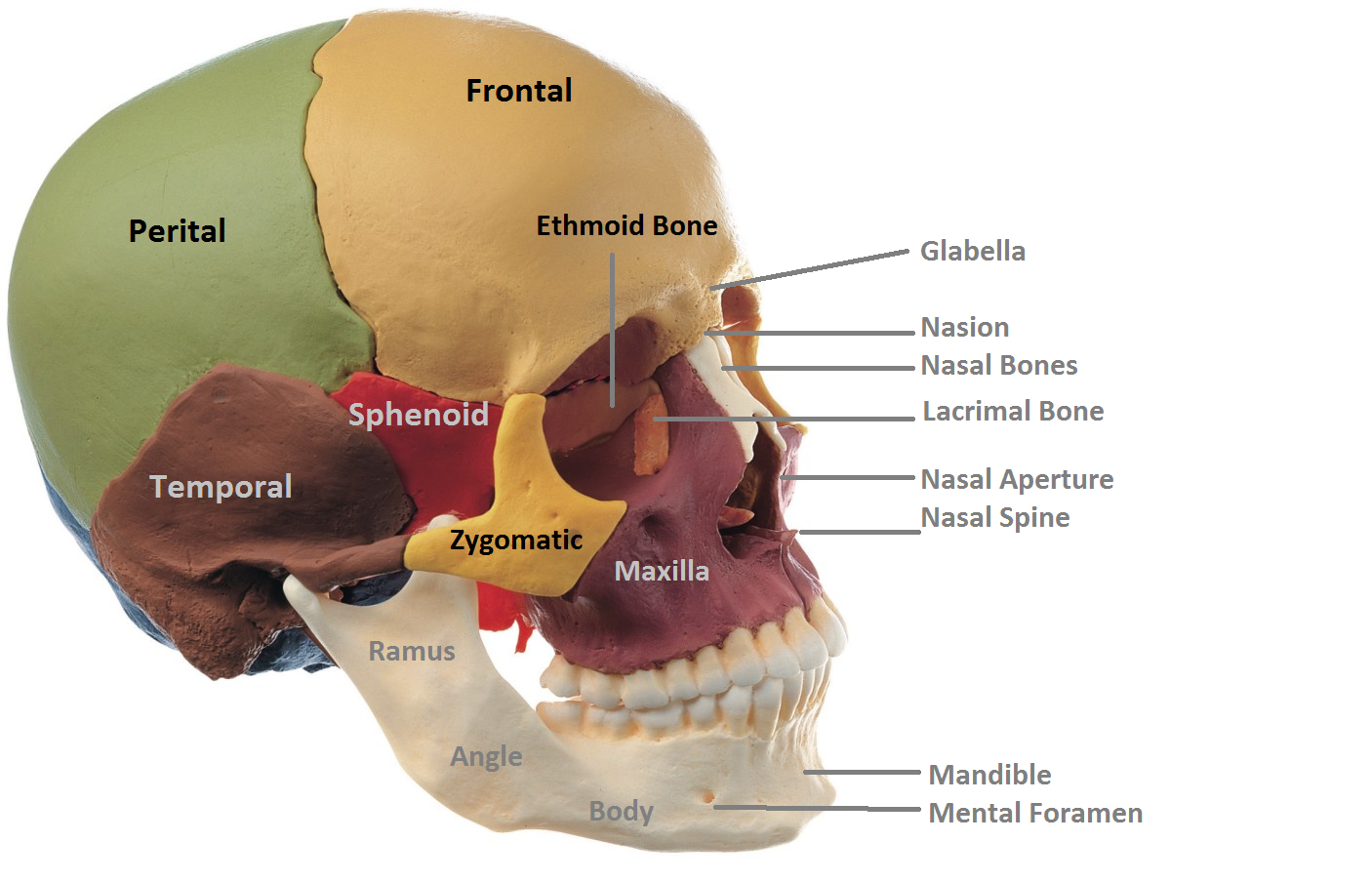
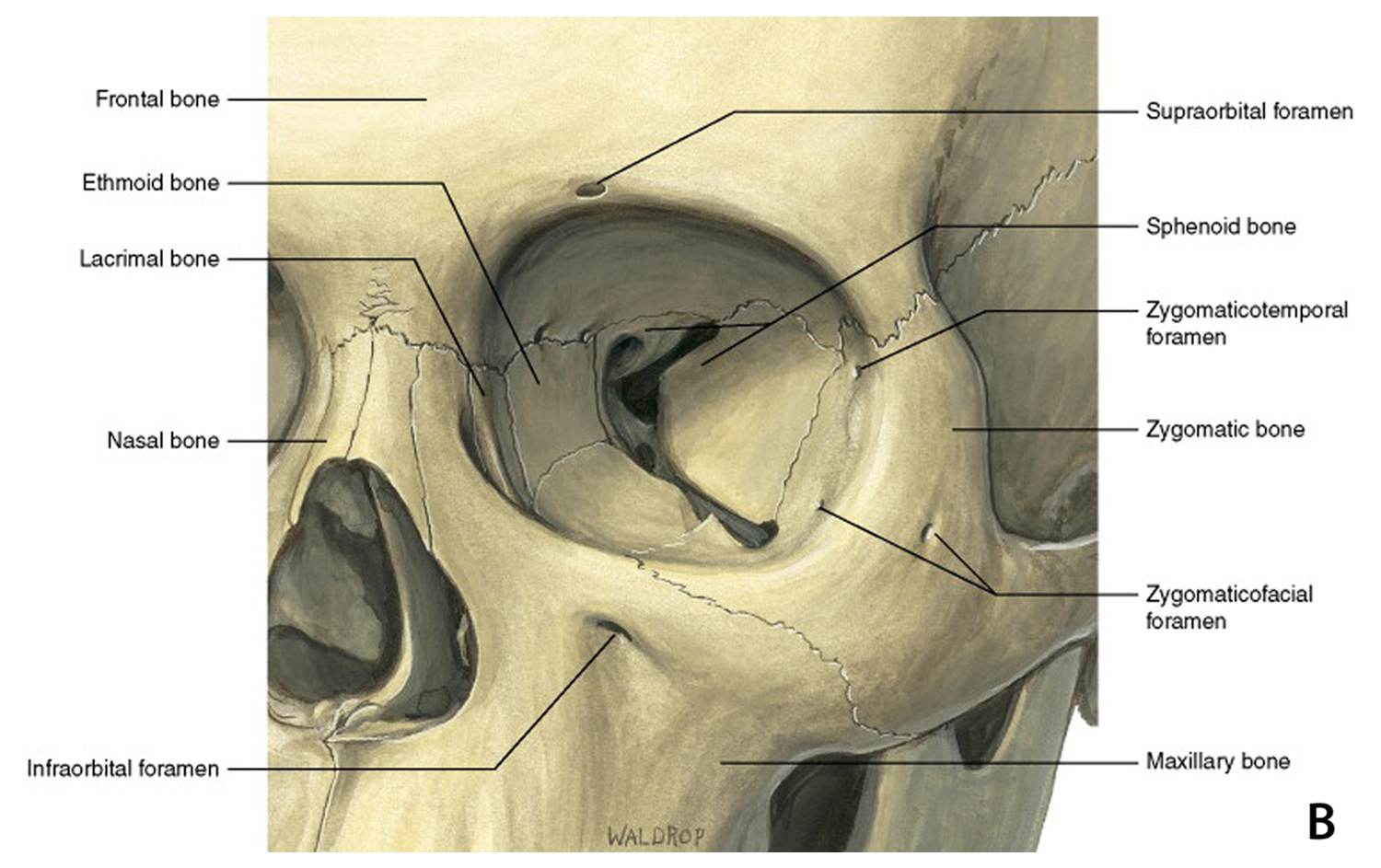
Which Bone Does Not Help Form The Orbital Cavity
Which Bone Does Not Help Form The Orbital Cavity - Web the medial orbital wall consists of four bones, the frontal process of the maxillary bone: Web most important facial bone since most others are articulating with it. Web the lateral portions of the ethmoid bone are located between the orbit and upper nasal cavity, and thus form the lateral nasal cavity wall and a portion of the medial orbit wall. Helps form the 3 main. Web palatine bone (os palatinum) the palatine bone is a paired bone located between the maxillae and the pterygoid process of the sphenoid bone. Web the sphenoid bone is one of the seven bones that make up the orbit (the space that holds the eyeball), and helps make up the floor of the middle cranial fossa,. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like how many bones comprise the skull?, the ______ is not an integral bone of the skull and is not. The lacrimal bone, the orbital plate of the ethmoid bone, and the lesser. Web the orbit, which protects, supports, and maximizes the function of the eye, is shaped like a quadrilateral pyramid, with its base in plane with the orbital rim. Web the eye does not rest on the orbital floor but is held up (in fact, closer to the roof) by the suspensory ligament. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like how many bones comprise the skull?, the ______ is not an integral bone of the skull and is not. Helps form the 3 main. Web the eye does not rest on the orbital floor but is held up (in fact, closer to the roof) by the suspensory ligament. Foramina learning. Web most important facial bone since most others are articulating with it. Web the medial orbital wall consists of four bones, the frontal process of the maxillary bone: Web which bone does not help form the orbital cavity? Web the anterior skull consists of the facial bones and provides the bony support for the eyes, teeth and structures of the. Web the quadrangular orbital plate of the ethmoid separates the orbit from the nasal cavity and it articulates superiorly with the medial edge of the orbital plate of the. The frontal, sphenoid, zygomatic, ethmoid, lacrimal, palatine and maxilla bones. Articulates solidly with each other below the bony nasal septum to form palatine bone. Web the lateral portions of the ethmoid. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like how many bones comprise the skull?, the ______ is not an integral bone of the skull and is not. Helps form the 3 main. Web palatine bone (os palatinum) the palatine bone is a paired bone located between the maxillae and the pterygoid process of the sphenoid bone. Foramina learning. Articulates solidly with each other below the bony nasal septum to form palatine bone. Web the eye does not rest on the orbital floor but is held up (in fact, closer to the roof) by the suspensory ligament. Web there are seven orbital bones that make up this structure: Web the quadrangular orbital plate of the ethmoid separates the orbit. Web most important facial bone since most others are articulating with it. The lacrimal bone, the orbital plate of the ethmoid bone, and the lesser. Web the anterior skull consists of the facial bones and provides the bony support for the eyes, teeth and structures of the face and provides openings for eating and breathing. Foramina learning objectives locate the. The frontal, sphenoid, zygomatic, ethmoid, lacrimal, palatine and maxilla bones. The lacrimal bone, the orbital plate of the ethmoid bone, and the lesser. Web the lateral portions of the ethmoid bone are located between the orbit and upper nasal cavity, and thus form the lateral nasal cavity wall and a portion of the medial orbit wall. Web the orbit, which. Foramina learning objectives locate the orbits in the skull the orbit, or eye socket, is the cavity located in the skull in which the eye and its associated. Web the eye does not rest on the orbital floor but is held up (in fact, closer to the roof) by the suspensory ligament. Web the anterior skull consists of the facial. Web the orbit, which protects, supports, and maximizes the function of the eye, is shaped like a quadrilateral pyramid, with its base in plane with the orbital rim. Web the orbital cavity contains the globe, nerves, vessels, lacrimal gland, extraocular muscles, tendons, the trochlea, as well as fat and other connective tissue. Web the anterior skull consists of the facial. Web 7 of the cranial and facial bones contribute to the formation of the orbital cavities, with 3 being cranial bones and the other 4 being facial bones: Articulates solidly with each other below the bony nasal septum to form palatine bone. Web there are seven orbital bones that make up this structure: Web palatine bone (os palatinum) the palatine. Web palatine bone (os palatinum) the palatine bone is a paired bone located between the maxillae and the pterygoid process of the sphenoid bone. Web the anterior skull consists of the facial bones and provides the bony support for the eyes, teeth and structures of the face and provides openings for eating and breathing. Web by definition, the orbit (bony orbit or orbital cavity) is a skeletal cavity comprised of seven bones situated within the skull. Web most important facial bone since most others are articulating with it. Web the medial orbital wall consists of four bones, the frontal process of the maxillary bone: Articulates solidly with each other below the bony nasal septum to form palatine bone. The frontal, sphenoid, zygomatic, ethmoid, lacrimal, palatine and maxilla bones. Web the sphenoid bone is one of the seven bones that make up the orbit (the space that holds the eyeball), and helps make up the floor of the middle cranial fossa,. Web the eye does not rest on the orbital floor but is held up (in fact, closer to the roof) by the suspensory ligament. Web which bone does not help form the orbital cavity? The cavity surrounds and provides mechanical protection for the eye and soft tissue structures related to it. Web the lateral portions of the ethmoid bone are located between the orbit and upper nasal cavity, and thus form the lateral nasal cavity wall and a portion of the medial orbit wall. Web 7 of the cranial and facial bones contribute to the formation of the orbital cavities, with 3 being cranial bones and the other 4 being facial bones: Web there are seven orbital bones that make up this structure: It helps form the walls of the eye socket, or orbital cavity, as well as. Web the orbit, which protects, supports, and maximizes the function of the eye, is shaped like a quadrilateral pyramid, with its base in plane with the orbital rim. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like how many bones comprise the skull?, the ______ is not an integral bone of the skull and is not. The lacrimal bone, the orbital plate of the ethmoid bone, and the lesser. As a result, the whole maxilla can be removed with the. Helps form the 3 main.Orbital floor fracture causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment & prognosis
The Bony Orbit Borders Contents Fractures TeachMeAnatomy
right orbit bones Анатомия
Skeletal System Basicmedical Key
Bones of the Orbit Names, Location, Anatomy, & Pictures
1 Bones forming the orbit Download Scientific Diagram
Bones of the orbit Diagram Quizlet
Orbital Roof — Ophthalmology Review
Anatomy Made Easy Anterior View of Skull
What Is The Orbit In Anatomy Anatomical Charts & Posters
Related Post: