Which Bonds Form In The Reaction Shown In The Diagram
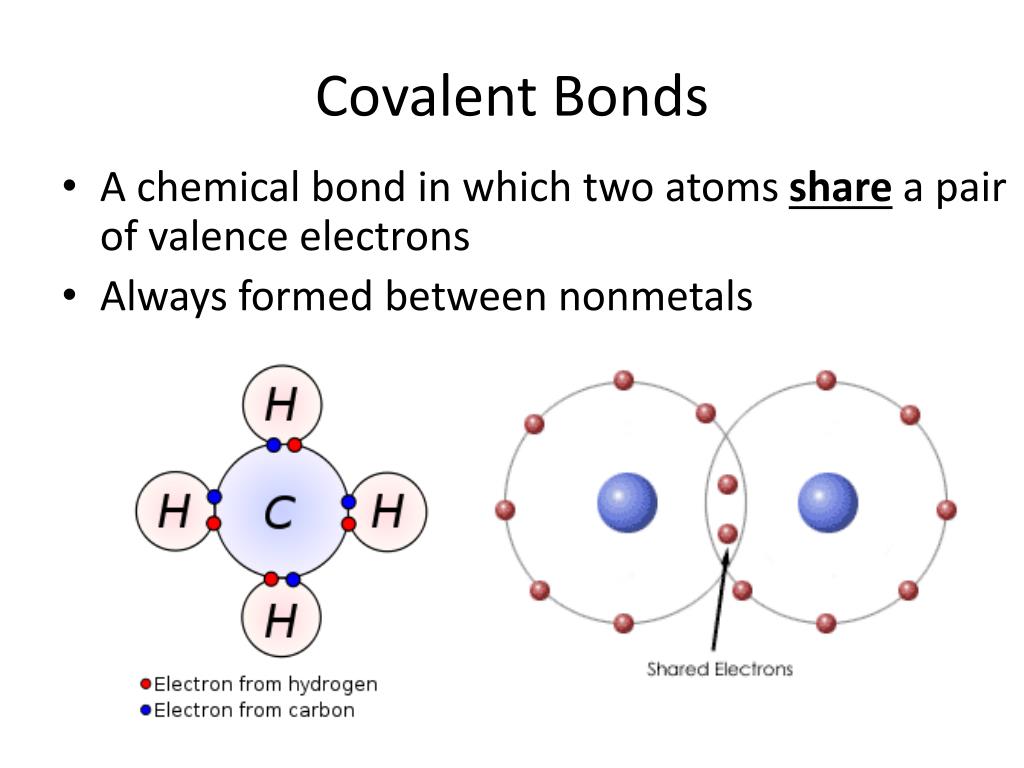
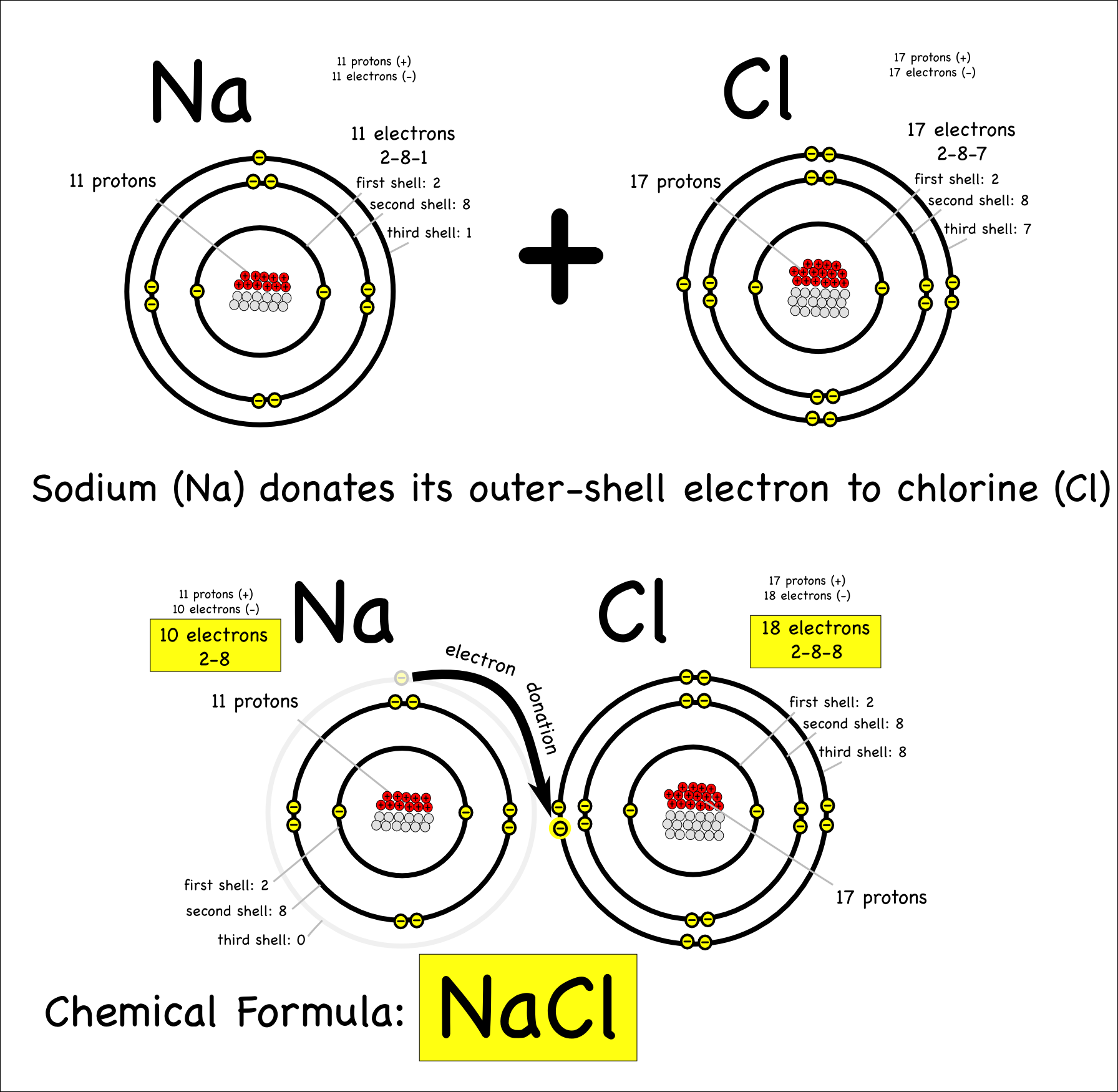
Which Bonds Form In The Reaction Shown In The Diagram - Web or shown graphically: With these average bond energies involved: As we can observe in this reaction, that the ch4 is reacting with 2 moles of oxygen to produce co2 gas and water molecule is released. It occurs between molecules when hydrogen is covalently bound to a strongly electronegative. And the rule of thumb is when chemical bonds are formed, heat is released, and when chemical bonds are broken, heat is absorbed. molecules inherently want to stay together, so. Covalent bonding is where atoms share electrons more or less. Web so, there is 1 o=o bond in o2. Web hydrogen bonding is an intermolecular interaction, i.e. Web which bonds form in the reaction shown in the diagram structure and bonding tables of redemption values for united states savings notes for the months of physical. Web chemical bonds involve only the outermost or valence electrons of atoms. Web to illustrate further, consider the two major types of chemical bonds: As we can observe in this reaction, that the ch4 is reacting with 2 moles of oxygen to produce co2 gas and water molecule is released. Whether a reaction is endothermic or. Web examples of chemical bonds. Web using the mo diagrams shown in figure 8.37, we can. With these average bond energies involved: Covalent bonding is where atoms share electrons more or less. Covalent bonds and ionic bonds. As we can observe in this reaction, that the ch4 is reacting with 2 moles of oxygen to produce co2 gas and water molecule is released. Which bonds form in the reaction shown in the diagram? Which bonds form in the reaction shown in the diagram? Covalent bonding is where atoms share electrons more or less. The two main types of bonds are covalent bonds and ionic bonds. In covalent bonds, two atoms share pairs of electrons, while in ionic bonds,. Web chemical bonds involve only the outermost or valence electrons of atoms. Web in any chemical reaction, chemical bonds are either broken or formed. Web the type of bonding shown in the diagram is a covalent bond.covalent. Using the example of the simplest element, hydrogen, its two atoms on approaching. In covalent bonds, two atoms share pairs of electrons, while in ionic bonds,. Web the number of bonds that an atom can. Web examples of chemical bonds. Which bonds form in the reaction shown in the diagram? Whether a reaction is endothermic or. It occurs between molecules when hydrogen is covalently bound to a strongly electronegative. Web which bonds form in the reaction shown in the diagram structure and bonding tables of redemption values for united states savings notes for the months. As we can observe in this reaction, that the ch4 is reacting with 2 moles of oxygen to produce co2 gas and water molecule is released. Terms in this set (22) which of the following best describes the formation of the bond shown in figure 1 ?. Covalent bonding is where atoms share electrons more or less. The two main. Energy is released when new bonds form. Covalent bonds and ionic bonds. Using the example of the simplest element, hydrogen, its two atoms on approaching. Web or shown graphically: And the rule of thumb is when chemical bonds are formed, heat is released, and when chemical bonds are broken, heat is absorbed. molecules inherently want to stay together, so. Energy is released when new bonds form. Web in any chemical reaction, chemical bonds are either broken or formed. Web we have in this case, the reaction; Web examples of chemical bonds. Web so, there is 1 o=o bond in o2. Web to illustrate further, consider the two major types of chemical bonds: Web hydrogen bonding is an intermolecular interaction, i.e. Web which bonds form in the reaction shown in the diagram structure and bonding tables of redemption values for united states savings notes for the months of physical. Energy is released when new bonds form. And the rule of thumb. Whether a reaction is endothermic or. Web so, there is 1 o=o bond in o2. In this case, we have the following bonds being formed in the process of the reaction; Energy is released when new bonds form. Covalent bonds and ionic bonds. In this case, we have the following bonds being formed in the process of the reaction; This is especially true of the. And the rule of thumb is when chemical bonds are formed, heat is released, and when chemical bonds are broken, heat is absorbed. molecules inherently want to stay together, so. Web the number of bonds that an atom can form can often be predicted from the number of electrons needed to reach an octet (eight valence electrons); Whether a reaction is endothermic or. Covalent bonding is where atoms share electrons more or less. It occurs between molecules when hydrogen is covalently bound to a strongly electronegative. Web using the mo diagrams shown in figure 8.37, we can add in the electrons and determine the molecular electron configuration and bond order for each of the diatomic molecules. With these average bond energies involved: The two main types of bonds are covalent bonds and ionic bonds. Web which bonds form in the reaction shown in the diagram structure and bonding tables of redemption values for united states savings notes for the months of physical. Illustrate covalent bond formation with lewis electron dot diagrams. Web to illustrate further, consider the two major types of chemical bonds: As we can observe in this reaction, that the ch4 is reacting with 2 moles of oxygen to produce co2 gas and water molecule is released. Energy is released when new bonds form. Web at the very top of the energy barrier, the reaction is at its transition state (ts), which is the point at which the bonds are in the process of breaking and forming. Web the type of bonding shown in the diagram is a covalent bond.covalent. Web in any chemical reaction, chemical bonds are either broken or formed. Web we have in this case, the reaction; Web chemical bonds involve only the outermost or valence electrons of atoms.chemical bonding Ionic and covalent compounds Britannica
PPT Covalent Bonds PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6647183
Covalent bonding in an oxygen molecule. Chemistry Activities, Gcse
covalent bond Definition, Properties, Examples, & Facts Britannica
CH150 Chapter 4 Covalent Bonds and Molecular Compounds Chemistry
Bonding A Level Notes
Introducing Covalent Bonding Montessori Muddle
Energy Changes and Formations of Chemical Bonds SPM Chemistry
How does a polar bond differ from a covalent bond
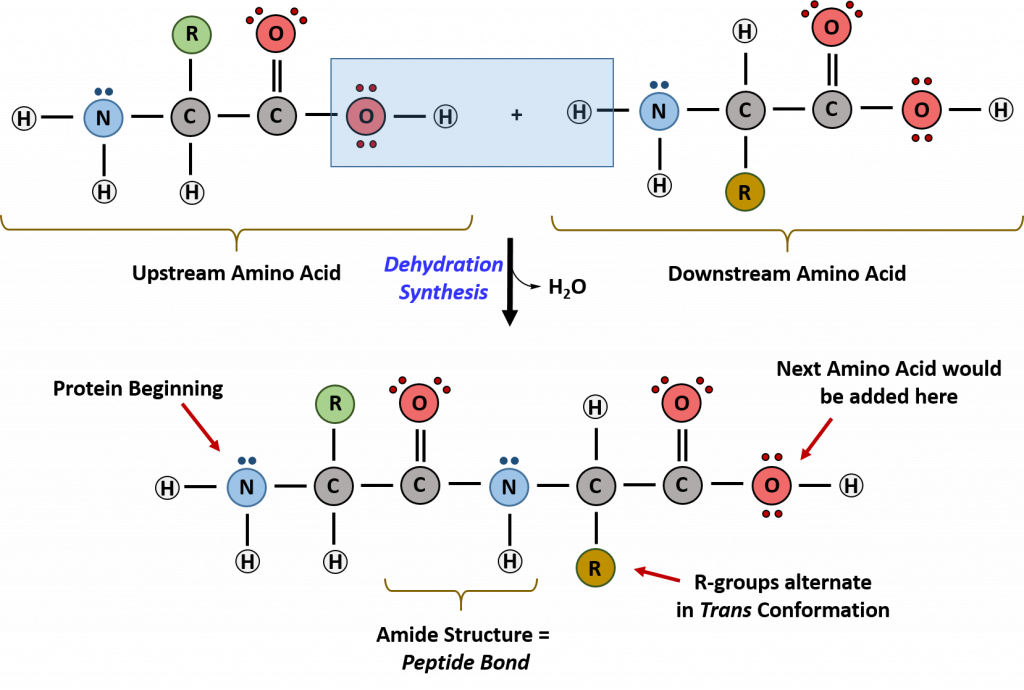
CH103 Chapter 8 The Major Macromolecules Chemistry
Related Post: