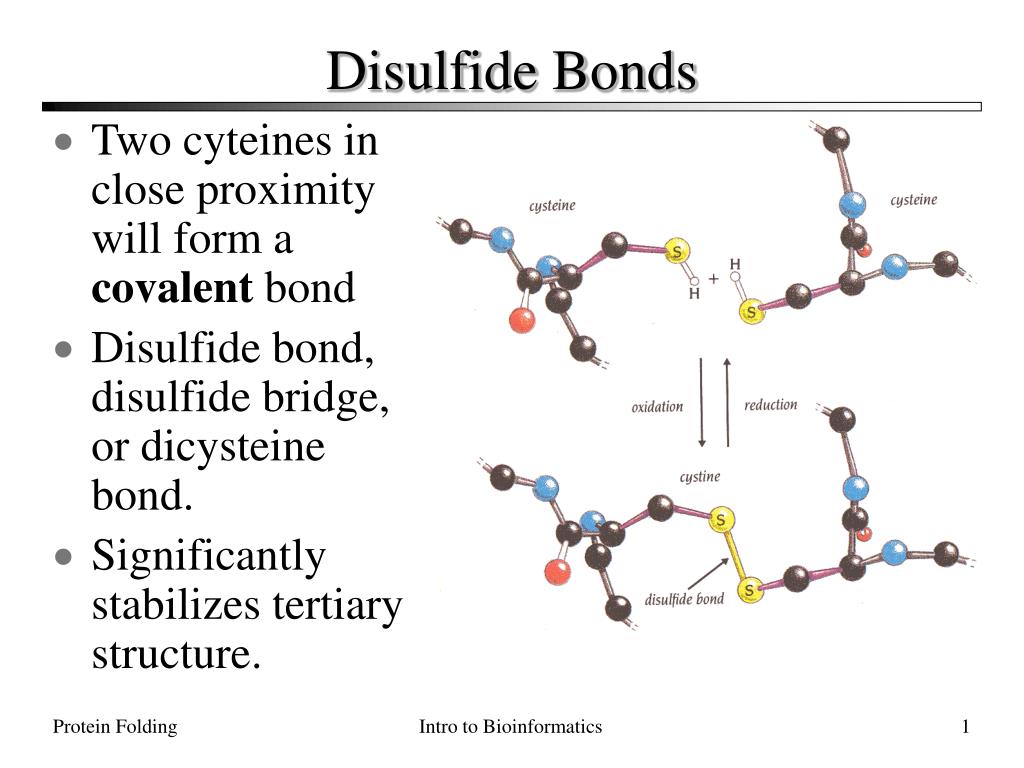
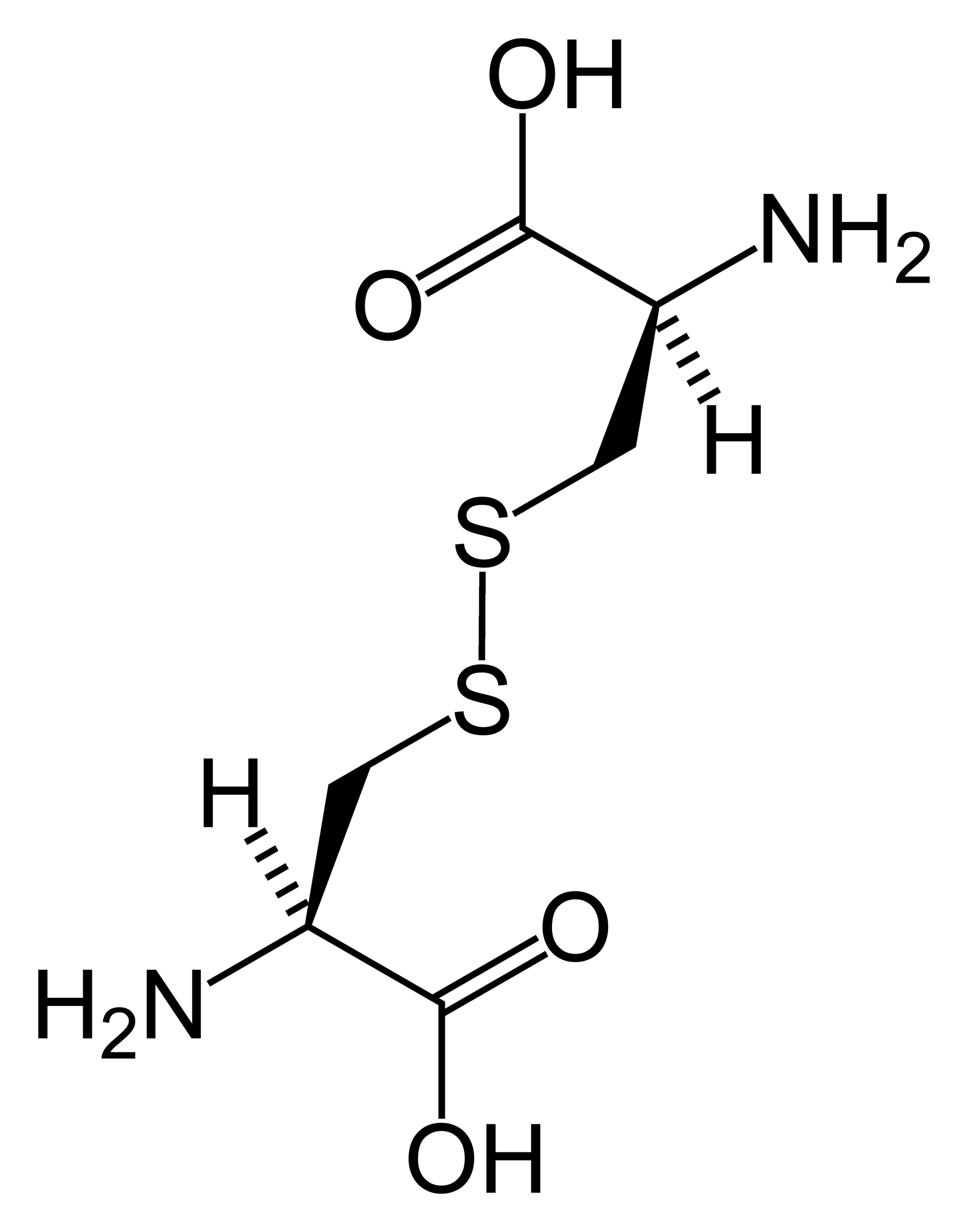
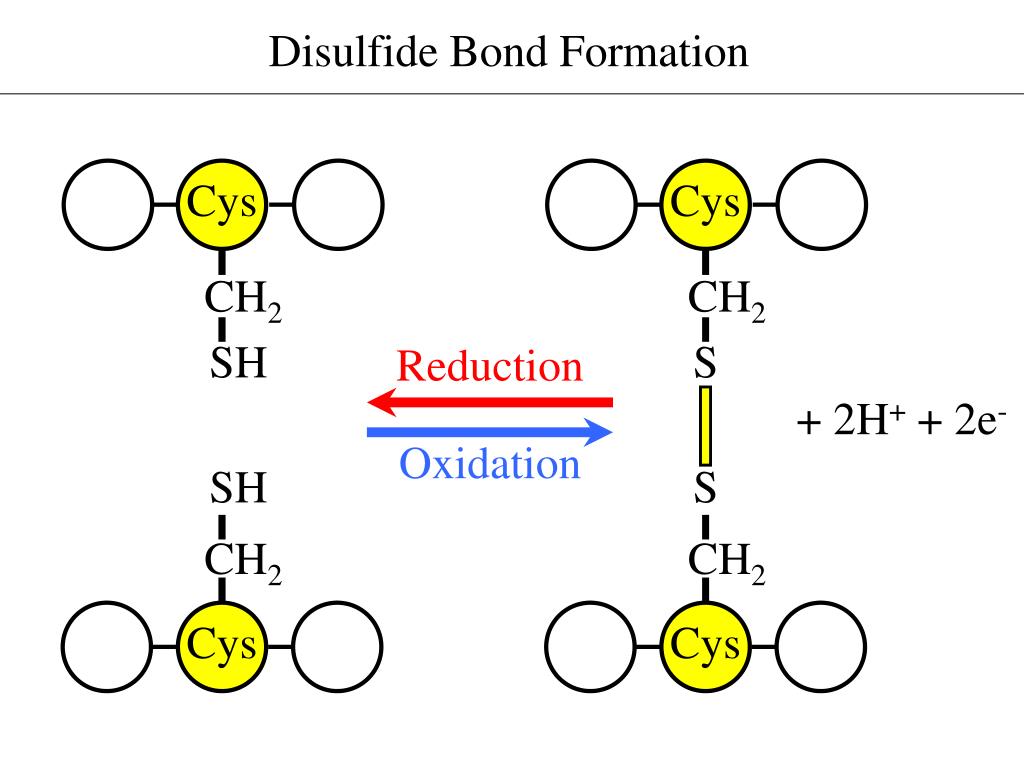
Where Do Disulfide Bonds Form
Where Do Disulfide Bonds Form - Disulfide bond formation generally occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum by oxidation. Web in bacteria, disulfide bonds in bioactive peptides and polypeptides of the secretory pathway are formed in the periplasm; Web conversely, in the case of the constant domain (c l) of the antibody light chain (figure 1.1.2), formation of its single disulfide bond accelerated folding up to. Ad provides disulfide linkers to conjugate various payloads.higher stability.call! Structurally, the disulfide linkage in a cystine displays a typical bond length of ~2.04 å ( chaney and steinrauf,. Examination of oxidation conditions 2. These bonds are formed between two sulfur atoms, typically found in cysteine residues. Web the critical roles of disulfide bonds in protein structure stabilization and redox regulation of protein activity are addressed. Disulfide bonds are an abundant feature of proteins across all domains of life that are important for structure, stability, and function. Disulfide bonds are essential to the structural stability of. Ad provides disulfide linkers to conjugate various payloads.higher stability.call! Most proteins synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum (er) in eukaryotic cells and in the periplasmic space in prokaryotes are stabilized by. Web the critical roles of disulfide bonds in protein structure stabilization and redox regulation of protein activity are addressed. Web stable disulfide bonds rarely form in the cytoplasm. It involves. Extracellular proteins often have several disulfide bonds, whereas. Web disulfide bond s play a crucial role in the stability and structure of proteins. These bonds are formed between two sulfur atoms, typically found in cysteine residues. Web 7 citations metrics abstract the folding of proteins that contain disulfide bonds is termed oxidative protein folding. Disulfide bonds are an abundant feature. Most proteins synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum (er) in eukaryotic cells and in the periplasmic space in prokaryotes are stabilized by. Structurally, the disulfide linkage in a cystine displays a typical bond length of ~2.04 å ( chaney and steinrauf,. Web the study by craig and dombkowski showed that almost all (90%) of disulfides in native proteins in the pdb. Disulfide bonds are essential to the structural stability of. Structurally, the disulfide linkage in a cystine displays a typical bond length of ~2.04 å ( chaney and steinrauf,. Web stable disulfide bonds rarely form in the cytoplasm. Ad provides disulfide linkers to conjugate various payloads.higher stability.call! Disulfide bond formation generally occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum by oxidation. Examination of oxidation conditions 2. Most proteins synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum (er) in eukaryotic cells and in the periplasmic space in prokaryotes are stabilized by. Web in bacteria, disulfide bonds in bioactive peptides and polypeptides of the secretory pathway are formed in the periplasm; Web nmr spectroscopy & prediction techniques. Web the study by craig and dombkowski showed that. Web 7 citations metrics abstract the folding of proteins that contain disulfide bonds is termed oxidative protein folding. Web nmr spectroscopy & prediction techniques. Structurally, the disulfide linkage in a cystine displays a typical bond length of ~2.04 å ( chaney and steinrauf,. These bonds are formed between two sulfur atoms, typically found in cysteine residues. Web disulfide bonds are. Ad provides disulfide linkers to conjugate various payloads.higher stability.call! Web in bacteria, disulfide bonds in bioactive peptides and polypeptides of the secretory pathway are formed in the periplasm; Web disulfide bonds in protein membranes are found in both bacteria and eukaryotes. Web disulfide bonds (bridges) form when cysteines far apart in the primary structure of the molecule end up near. Examination of oxidation conditions 2. Web stable disulfide bonds rarely form in the cytoplasm. Disulfide bonds are an abundant feature of proteins across all domains of life that are important for structure, stability, and function. The bacterial cytoplasm ( e °′= −0.27 v) is normally even more reducing than its eukaryotic counterpart ( e °′= −0.23 v) [ 2 ].. Structurally, the disulfide linkage in a cystine displays a typical bond length of ~2.04 å ( chaney and steinrauf,. Web disulfide bonds are formed by the oxidation of sulfhydryl groups between two cysteine side chains, resulting in a covalent bond, greatly increasing the stability of the protein. Web disulfide bonds in protein membranes are found in both bacteria and eukaryotes.. Most proteins synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum (er) in eukaryotic cells and in the periplasmic space in prokaryotes are stabilized by. Structurally, the disulfide linkage in a cystine displays a typical bond length of ~2.04 å ( chaney and steinrauf,. Web 7 citations metrics abstract the folding of proteins that contain disulfide bonds is termed oxidative protein folding. Web disulfide. Disulfide bonds are an abundant feature of proteins across all domains of life that are important for structure, stability, and function. Web where do disulfide bridges form? Web 7 citations metrics abstract the folding of proteins that contain disulfide bonds is termed oxidative protein folding. Disulfide bond formation generally occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum by oxidation. Web disulfide bonds (bridges) form when cysteines far apart in the primary structure of the molecule end up near each other in a folded polypeptide. Web the formation of disulfide bonds (dsbs) in proteins is an oxidative process that generates a covalent bond linking the sulfur atoms of two cysteine residues. Structurally, the disulfide linkage in a cystine displays a typical bond length of ~2.04 å ( chaney and steinrauf,. The bacterial cytoplasm ( e °′= −0.27 v) is normally even more reducing than its eukaryotic counterpart ( e °′= −0.23 v) [ 2 ]. Extracellular proteins often have several disulfide bonds, whereas. In eukaryotes, such (poly)peptides tend to acquire their. Web disulfide bond formation a. Ad provides disulfide linkers to conjugate various payloads.higher stability.call! These bonds are formed between two sulfur atoms, typically found in cysteine residues. It involves a chemical reaction resulting in the. Web nmr spectroscopy & prediction techniques. Web the study by craig and dombkowski showed that almost all (90%) of disulfides in native proteins in the pdb have an energy < 2.2 kcal/mol, so this metric. Web stable disulfide bonds rarely form in the cytoplasm. Web disulfide bonds are formed by the oxidation of sulfhydryl groups between two cysteine side chains, resulting in a covalent bond, greatly increasing the stability of the protein. Most proteins synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum (er) in eukaryotic cells and in the periplasmic space in prokaryotes are stabilized by. Disulfide bonds are essential to the structural stability of.PPT Disulfide Bonds PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID165240
PPT The role of disulfide bonds on the activity, stability and
Along came a spider Digital World Biology
LabXchange
Disulfide bond wikidoc
Disulfide Bond Formation in the Mammalian Endoplasmic Reticulum
DsbB pathway and screening basis. E. coli disulfide bond formation
Disulfide bond wikidoc
Disulfide Bond Formation in the Mammalian Endoplasmic Reticulum
PPT Making the right connections Disulfide Bond Formation in the
Related Post: