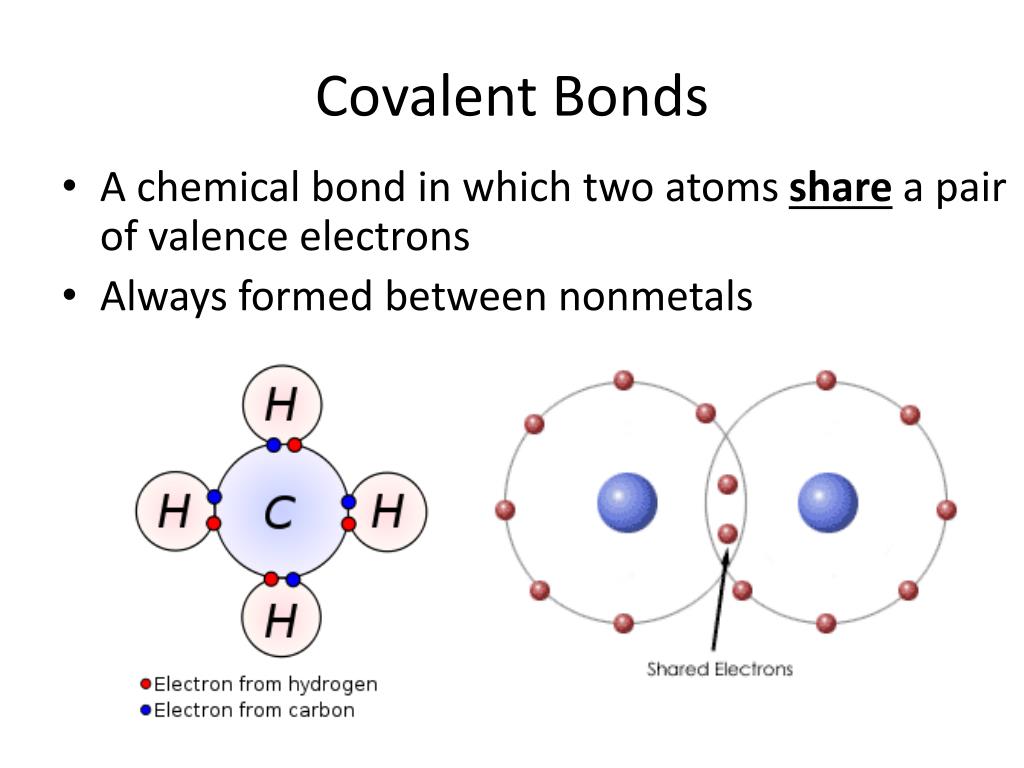
What Type Of Elements Form Covalent Bonds
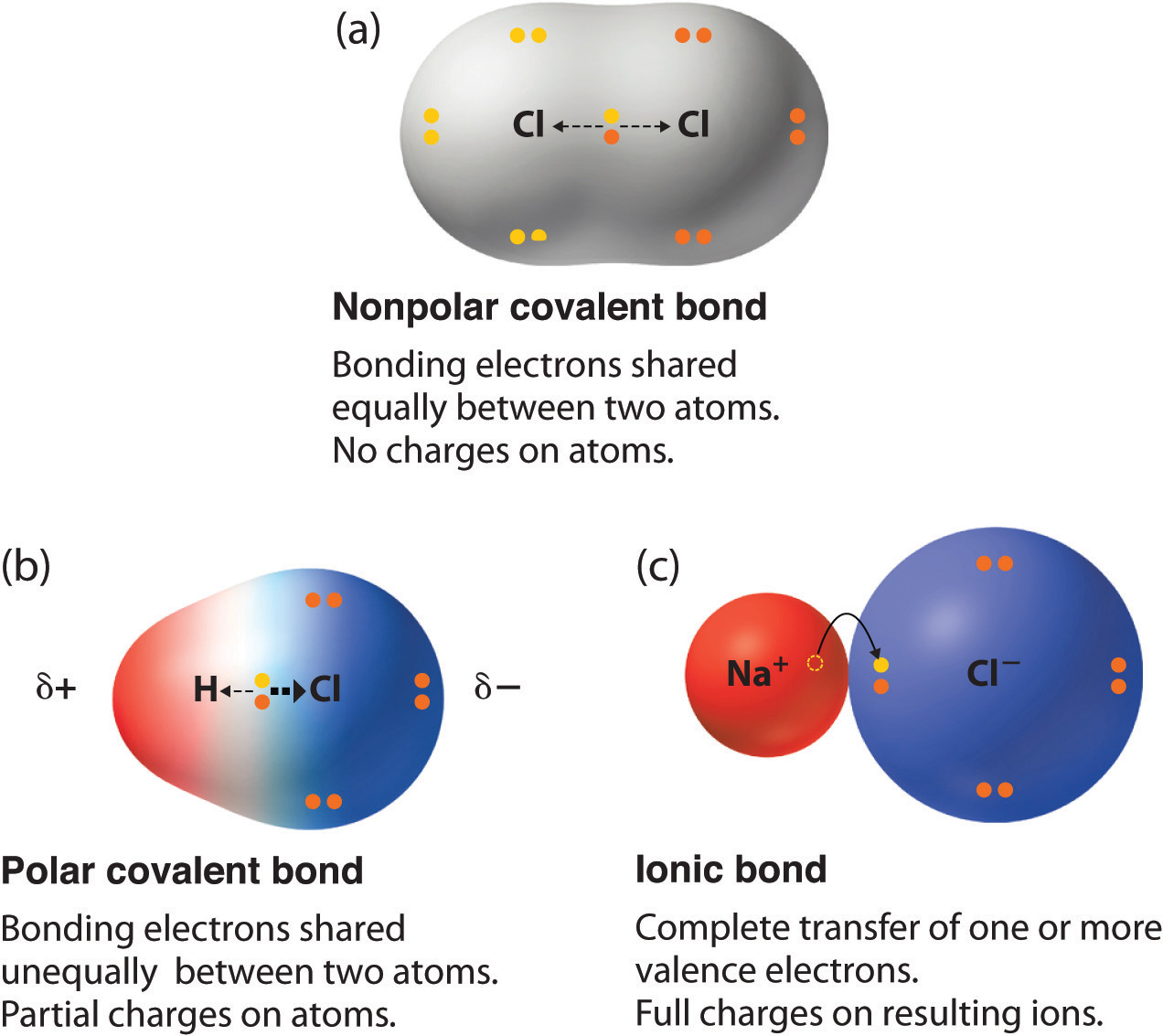
What Type Of Elements Form Covalent Bonds - Web a covalent bond is formed between two atoms by sharing electrons. Web we would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. A triple bond is formed when three pairs of electrons are shared between the two participating atoms. As the atoms collide with each other, some of the energy involved in the collision is usually released to the. The number of bonds an element forms in a covalent compound is determined by the number of electrons it. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms, when they share electrons, is known as covalent bonding. Bonding between a metal and a nonmetal is often ionic. Web there are two types of covalent bonds: It is a type of chemical. Web there are two types of covalent bonds: This type of covalent bond. Some compounds contain both covalent and ionic bonds. A triple bond is formed when three pairs of electrons are shared between the two participating atoms. The potential energy of two separate hydrogen atoms (right) decreases as. As the atoms collide with each other, some of the energy involved in the collision is usually released to the. Web bonds between two nonmetals are generally covalent; These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs. Some compounds contain both covalent and ionic bonds. Ionic bonding is the complete transfer of valence electron (s) between atoms. Boron commonly makes only three covalent bonds, resulting in only six. Some compounds contain both covalent and ionic bonds. Web as a general rule, covalent bonds are formed between elements lying toward the right in the periodic table (i.e., the nonmetals). Web covalent bonds single and multiple covalent bonds metallic bonds drawing lewis diagrams predicting bond type (metals vs. A. Web the most common examples are the covalent compounds of beryllium and boron. A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms. The potential energy of two separate hydrogen. Energy is always released when bonds are made. Web there are two types of covalent bonds: Web covalent bonds single and multiple covalent bonds metallic bonds drawing lewis diagrams predicting bond type (metals vs. A triple bond is formed when three pairs of electrons are shared between the two participating atoms. As the atoms collide with each other, some of the energy involved in the collision is usually released to the. Web the bond length is. A molecular approach (tro) 9: It is a type of chemical. Web a covalent bond is formed between two atoms by sharing electrons. Is determined by the distance at which the lowest potential energy is achieved. For example, beryllium can form two covalent bonds, resulting in only four electrons in its valence shell: A molecular approach (tro) 9: Boron commonly makes only three covalent bonds, resulting in only six. For example, beryllium can form two covalent bonds, resulting in only four electrons in its valence shell: Web a covalent bond is formed between two atoms by sharing electrons. Web double bonds triple bond. As the atoms collide with each other, some of the energy involved in the collision is usually released to the. A triple bond is formed when three pairs of electrons are shared between the two participating atoms. Web we would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. This type of covalent bond. Web double. A molecular approach (tro) 9: A triple bond is formed when three pairs of electrons are shared between the two participating atoms. Bonding between a metal and a nonmetal is often ionic. As the atoms collide with each other, some of the energy involved in the collision is usually released to the. Is determined by the distance at which the. Ionic bonding is the complete transfer of valence electron (s) between atoms. Web ionic and covalent bonds introduction. Boron commonly makes only three covalent bonds, resulting in only six. Energy is always released when bonds are made. Web bookshelves general chemistry map: A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms. Web the bond length is determined by the distance at which the lowest potential energy is achieved. The potential energy of two separate hydrogen atoms (right) decreases as. A molecular approach (tro) 9: Covalent bonding and simple molecular compounds Web bookshelves general chemistry map: A triple bond is formed when three pairs of electrons are shared between the two participating atoms. Some compounds contain both covalent and ionic bonds. Boron commonly makes only three covalent bonds, resulting in only six. Bonding between a metal and a nonmetal is often ionic. Web the most common examples are the covalent compounds of beryllium and boron. Web bonds between two nonmetals are generally covalent; Web in general, covalent bonds form between nonmetals, ionic bonds form between metals and nonmetals, and metallic bonds form between metals. Is determined by the distance at which the lowest potential energy is achieved. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms, when they share electrons, is known as covalent bonding. Web there are two types of covalent bonds: As the atoms collide with each other, some of the energy involved in the collision is usually released to the. Ionic bonding is the complete transfer of valence electron (s) between atoms. It is a type of chemical. For example, beryllium can form two covalent bonds, resulting in only four electrons in its valence shell:Examples of Covalent Bonds Several Examples of Covalent (molecular
PPT Covalent Bonds PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6647183
Covalent Bonding (Biology) — Definition & Role Expii
Covalent Bonds The Basics of Chemical Bonding
chemical bonding Definition, Types, & Examples Britannica
covalent bond Definition, Properties, Examples, & Facts Britannica
CH150 Chapter 4 Covalent Bonds and Molecular Compounds Chemistry
Covalent Bond Definition, Types, and Examples
Covalent Bond Biology Dictionary
Chapter 5.6 Properties of Polar Covalent Bonds Chemistry LibreTexts
Related Post: