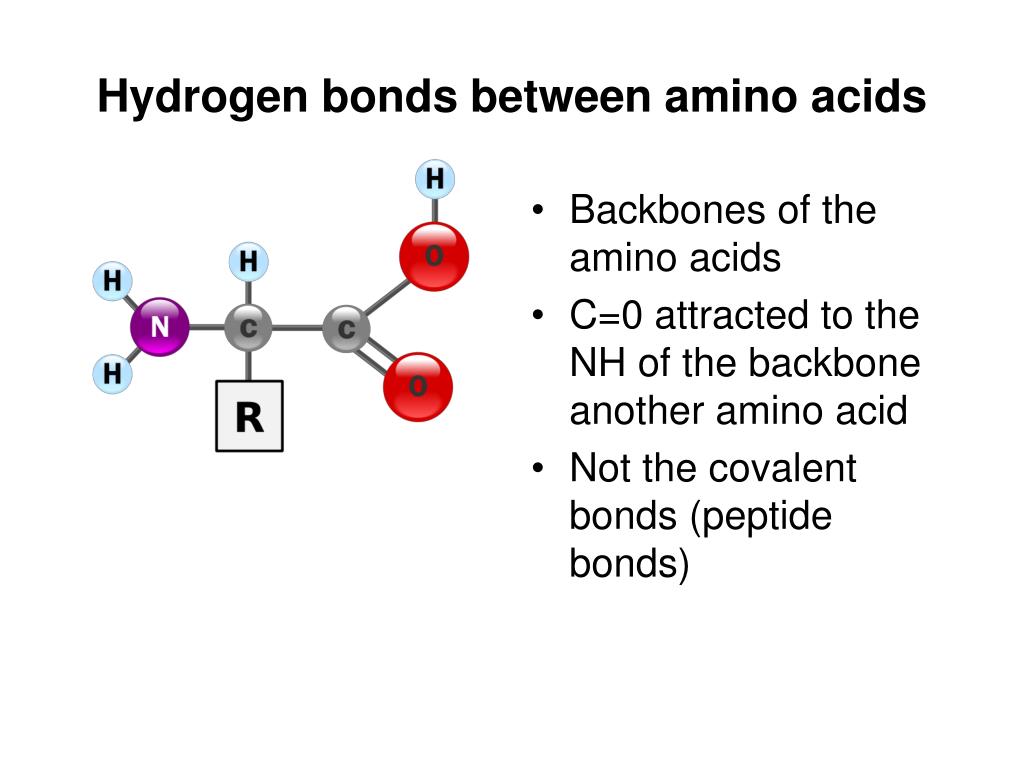
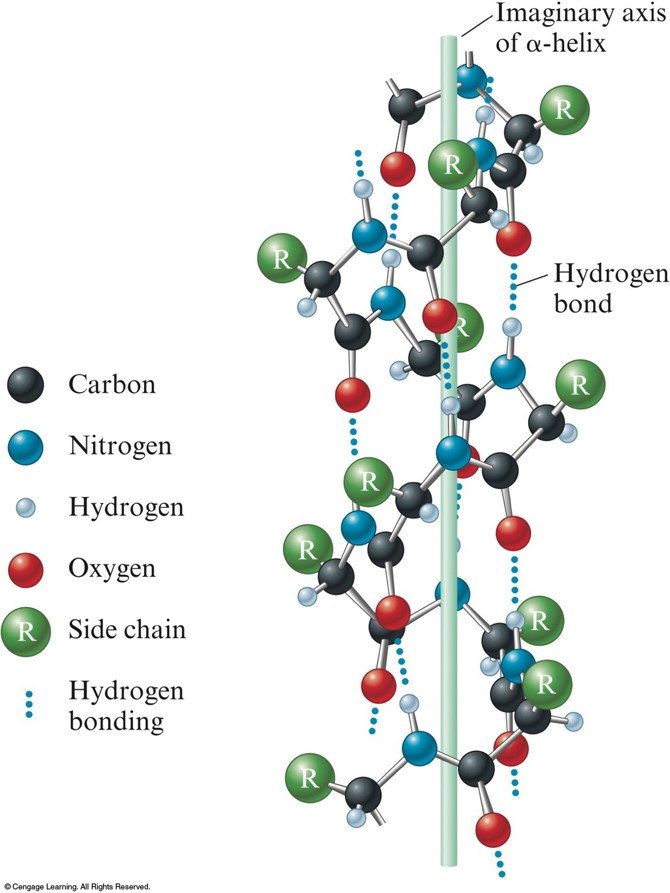
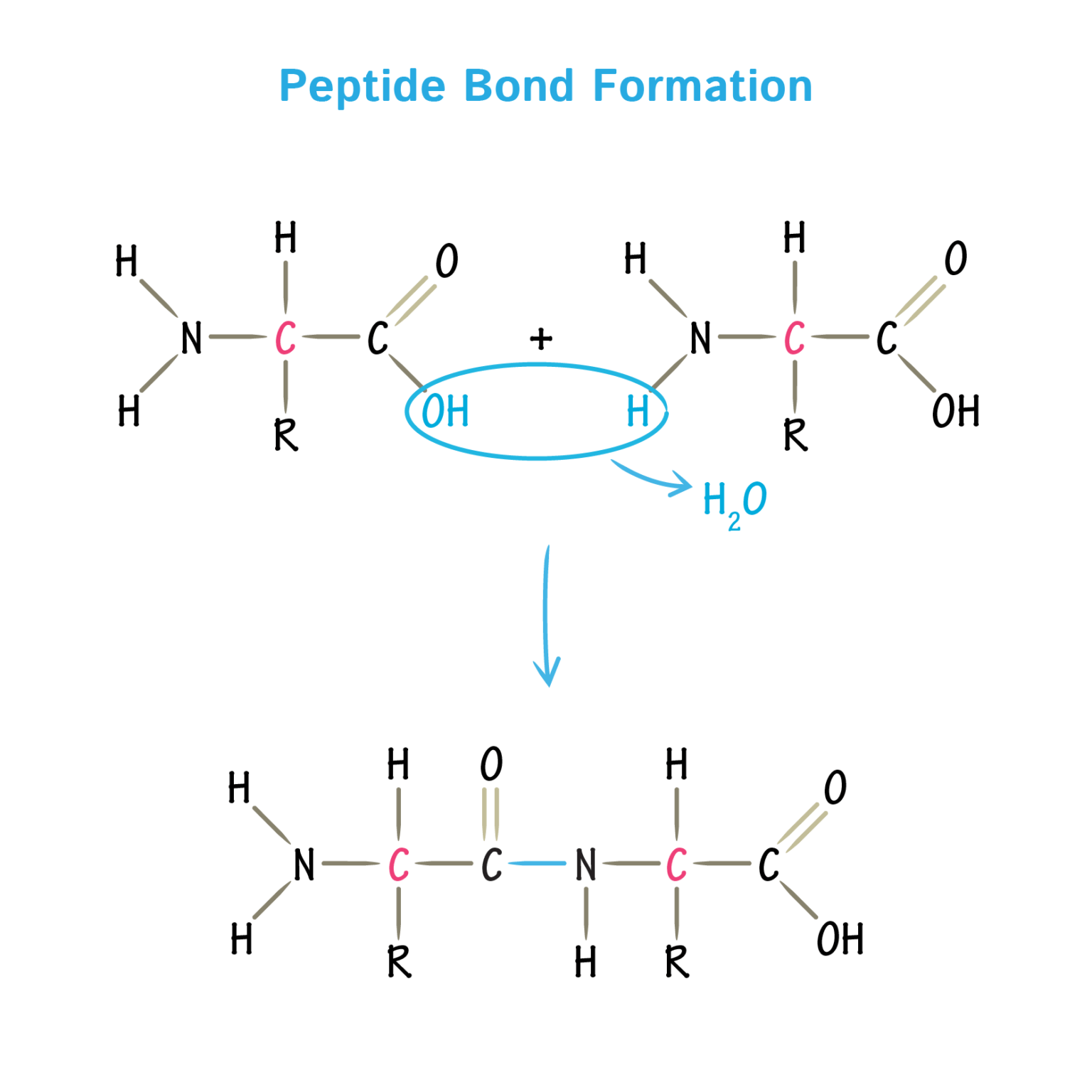
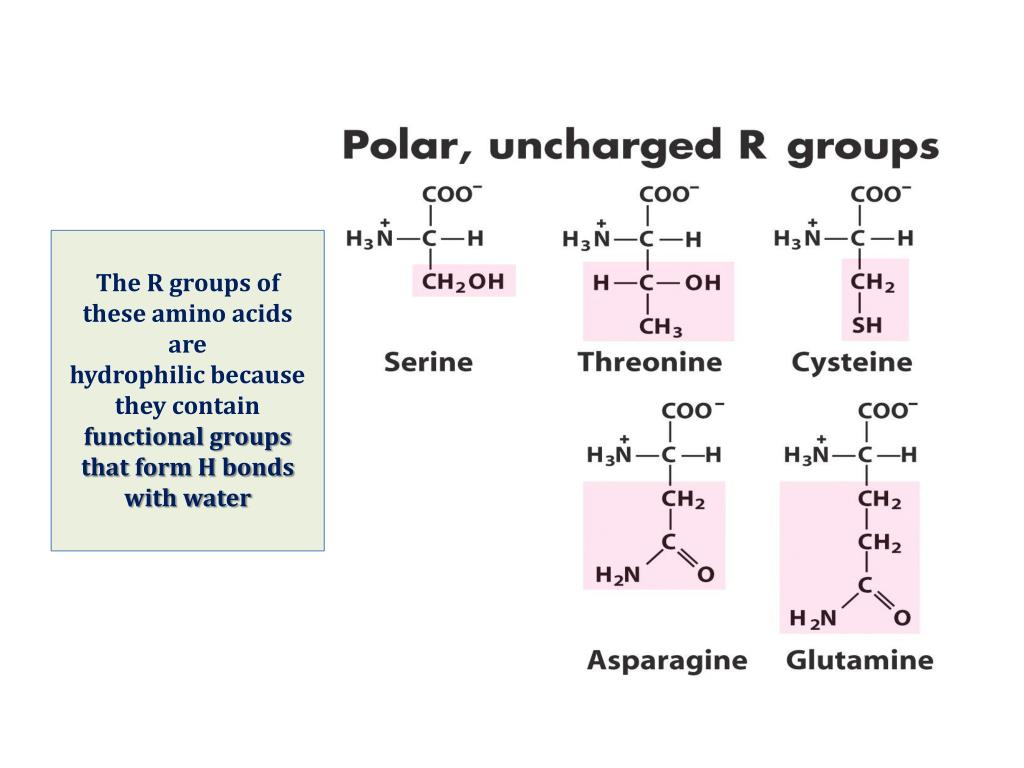
What Amino Acids Can Form Hydrogen Bonds
What Amino Acids Can Form Hydrogen Bonds - For this problem, draw all hydrogen atoms explicitly. Their solubility depends on the size and nature of the side chain. They do not ionize in normal conditions, a prominent exception being the catalytic serine in serine proteases. Web hydrogen bonding, interaction involving a hydrogen atom located between a pair of other atoms having a high affinity for electrons; Please explain why that is the correct answer. This link provides an nh group that can form a hydrogen bond to a suitable acceptor atom and an oxygen atom, which. One atom of the pair (the. A few biologically important derivatives of the standard amino acids are shown in the figure below. Hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, and van der waals. These involve atoms in the polypeptide backbone, as well as atoms in the amino acid side chains. Examples of amino acids include glycine and threonine. Amino acids share a basic structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha (α) carbon, bonded to an amino group ( nh 2 ), a carboxyl group ( cooh ), and a hydrogen atom. The 4 structural levels of proteins. Hydrogen bonding and ionic bonding (figure 1).. Part a draw the dipeptide that results when a peptide bond is formed between the two glycine molecules shown here. Acidic amino acids the two amino acids in this group are aspartic acid and glutamic acid. Web lots of amino acids contain groups in the side chains which have a hydrogen atom attached to either an oxygen or a nitrogen. Web the polar, uncharged amino acids serine (ser, s), threonine (thr, t), asparagine (asn, n) and glutamine (gln, q) readily form hydrogen bonds with water and other amino acids. Web lots of amino acids contain groups in the side chains which have a hydrogen atom attached to either an oxygen or a nitrogen atom. Web which amino acids can form. Tertiary structure is stabilized by a combination of forces, including. Web there are 20 types of amino acids commonly found in proteins. Examples of amino acids include glycine and threonine. Hydrophobic side chains interact with each other via weak van der. This link provides an nh group that can form a hydrogen bond to a suitable acceptor atom and an. Hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, and van der waals. Web which amino acids can form hydrogen bonds. Web amino acids are crystalline solids which usually are water soluble and only sparingly dissoluble in organic solvents. The amino acids lysine, arginine, and histidine have side chains with charged basic groups. Their other properties varying for each particular amino acid. Web lots of amino acids contain groups in the side chains which have a hydrogen atom attached to either an oxygen or a nitrogen atom. Hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, and van der waals. Web amino acids can be linked by a condensation reaction in which an ―oh is lost from the carboxyl group of one amino acid along with a. This is an example of severe perturbation, and is not. Web 1 day agoscience biochemistry proteins are made from chains of amino acids. Which amino acids are involved in turns and kinks?. C) aspartic acid and lysine. What amino acid participated in disulfide bonds? (figure 1) draw it as it would. Web which amino acids can form hydrogen bonds. Their solubility depends on the size and nature of the side chain. Web the polar, uncharged amino acids serine (ser, s), threonine (thr, t), asparagine (asn, n) and glutamine (gln, q) readily form hydrogen bonds with water and other amino acids. Amino acids share a. They do not ionize in normal conditions, a prominent exception being the catalytic serine in serine proteases. Please explain why that is the correct answer. Example of salt bridge between amino acids glutamic acid and lysine demonstrating electrostatic interaction and hydrogen bonding. Web the polar, uncharged amino acids serine (ser, s), threonine (thr, t), asparagine (asn, n) and glutamine (gln,. A) arginine and glutamic acid. Hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, and van der waals. These involve atoms in the polypeptide backbone, as well as atoms in the amino acid side chains. Web which amino acids can form hydrogen bonds. Amino acids share a basic structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha (α) carbon, bonded to. Tertiary structure is stabilized by a combination of forces, including. Web which pair of amino acids can form hydrogen bonds between their r groups? For this problem, draw all hydrogen atoms explicitly. The weak bonds are of three types: Web the folding of a protein chain is, however, further constrained by many different sets of weak noncovalent bonds that form between one part of the chain and another. Amino acids share a basic structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha (α) carbon, bonded to an amino group ( nh 2 ), a carboxyl group ( cooh ), and a hydrogen atom. These residues typically form the hydrophobic core of proteins, which. What amino acid participated in disulfide bonds? (figure 1) draw it as it would. The forces in secondary structure primarily involve hydrogen bonds. For example, the amino acid serine contains an. They do not ionize in normal conditions, a prominent exception being the catalytic serine in serine proteases. A few biologically important derivatives of the standard amino acids are shown in the figure below. Acidic amino acids the two amino acids in this group are aspartic acid and glutamic acid. The 4 structural levels of proteins. Web an important feature of the structure of proteins (which are polypeptides, or polymers formed from amino acids) is the existence of the peptide link, the group ―co―nh―, which appears between each pair of adjacent amino acids. Ion pairing is one of the most important noncovalent forces in chemistry, in. Web hydrogen bonding, interaction involving a hydrogen atom located between a pair of other atoms having a high affinity for electrons; Example of salt bridge between amino acids glutamic acid and lysine demonstrating electrostatic interaction and hydrogen bonding. Hydrophobic side chains interact with each other via weak van der.PPT Inner Life of a Cell PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
Two amino acids are joined together by
PPT Proteins PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1828850
organic chemistry Which atoms in a given amino acid are able to form
amino acids salt bridge vs hydrogen bond Chemistry Stack Exchange
Chapter 22 Presentation
(a) Hydrogen bonding patterns that describe the αand πconfigurations
Amino acids physical, chemical properties and peptide bond
PPT Introduction to Amino Acids of Medical Importance PowerPoint
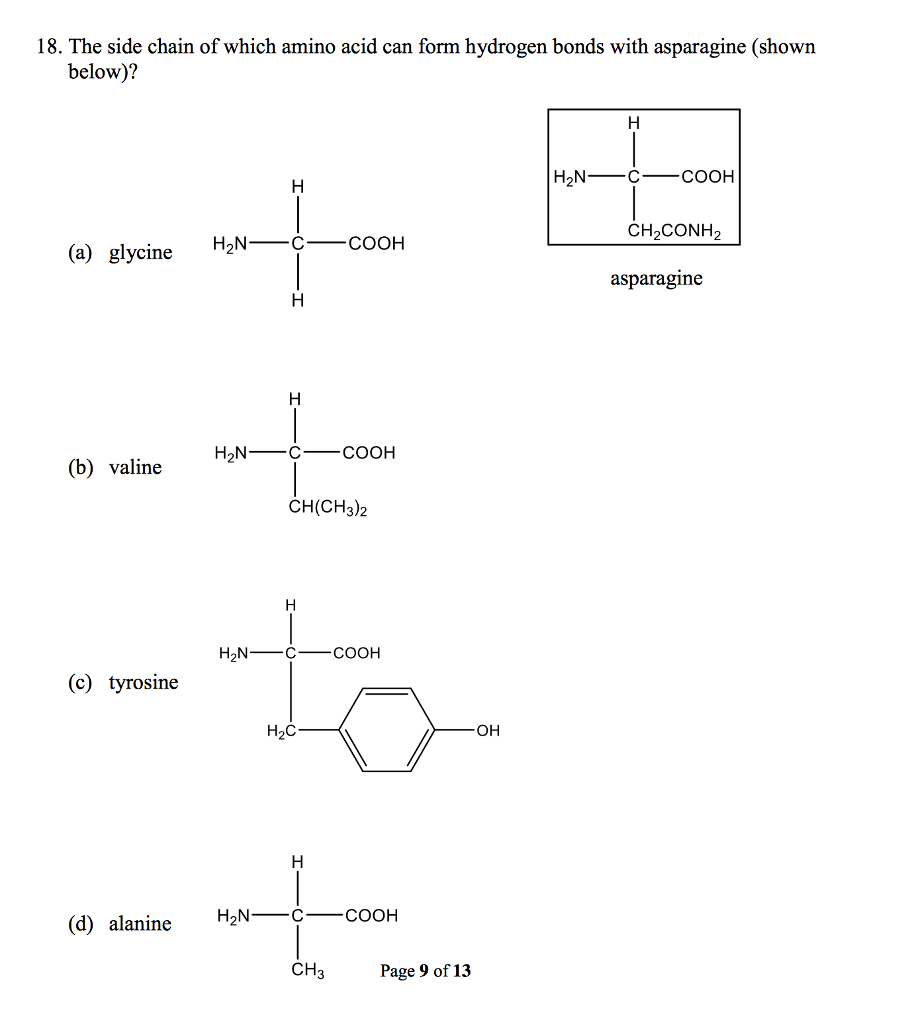
Solved 18. The side chain of which amino acid can form
Related Post: