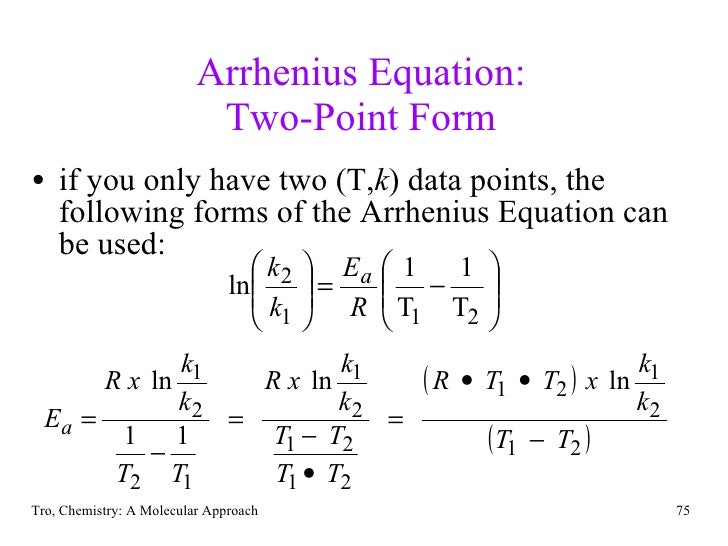
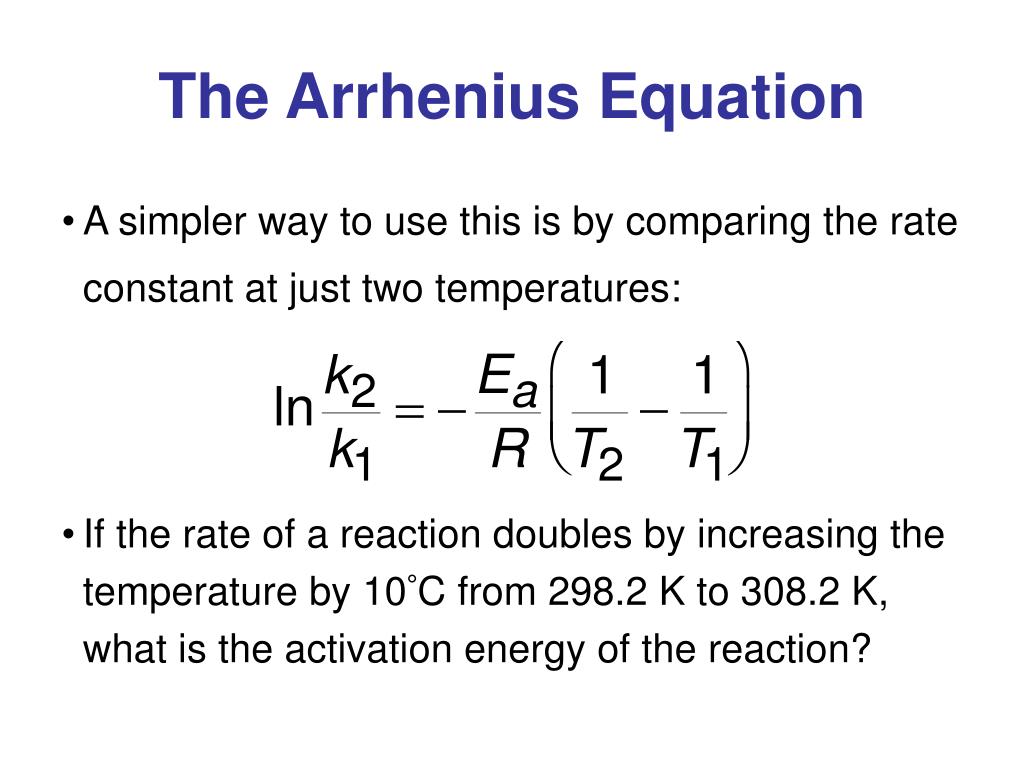
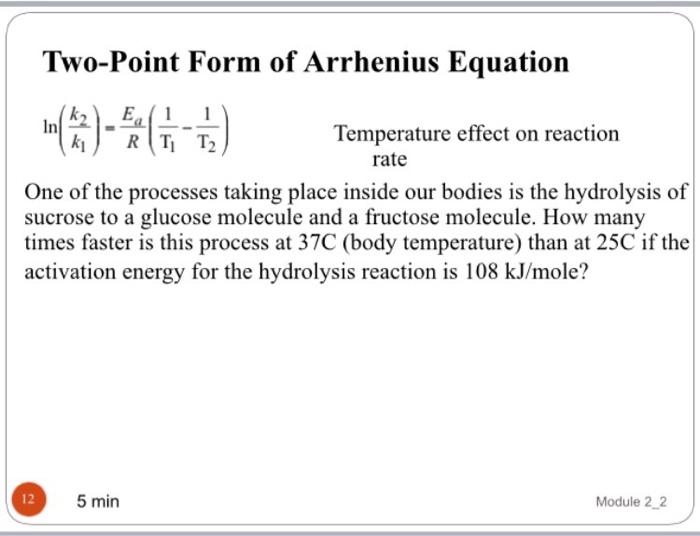
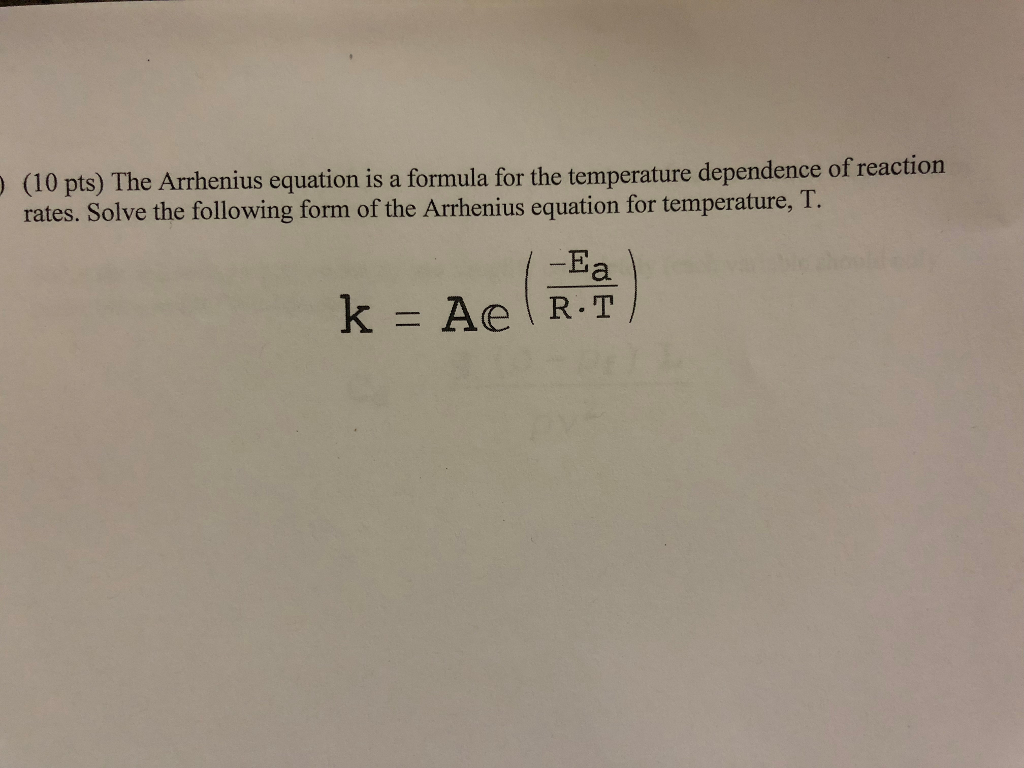Two Point Form Of Arrhenius Equation
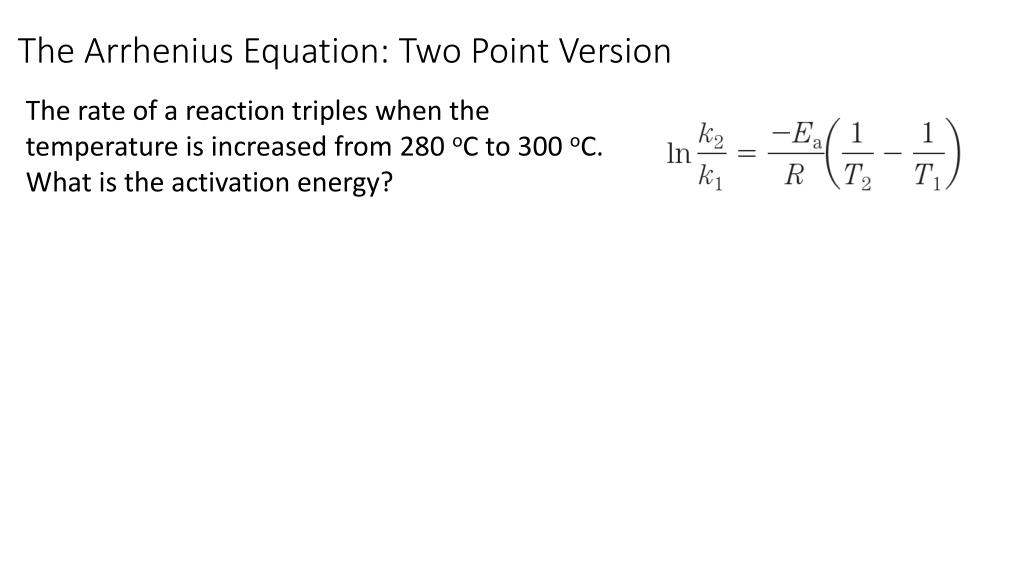
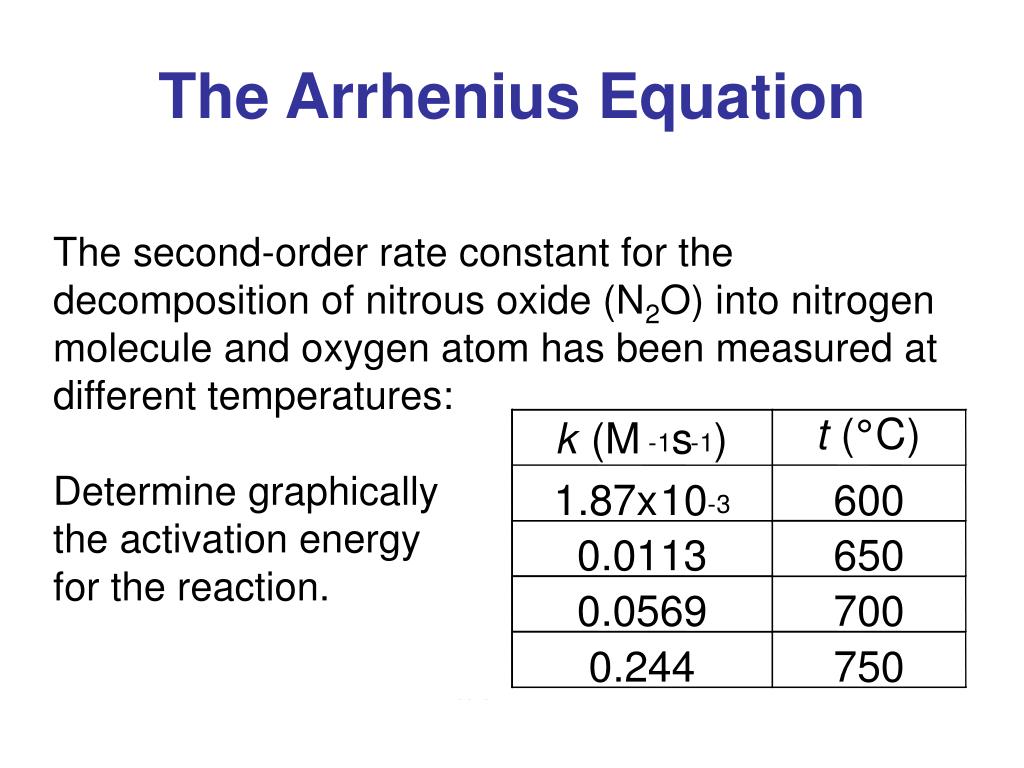
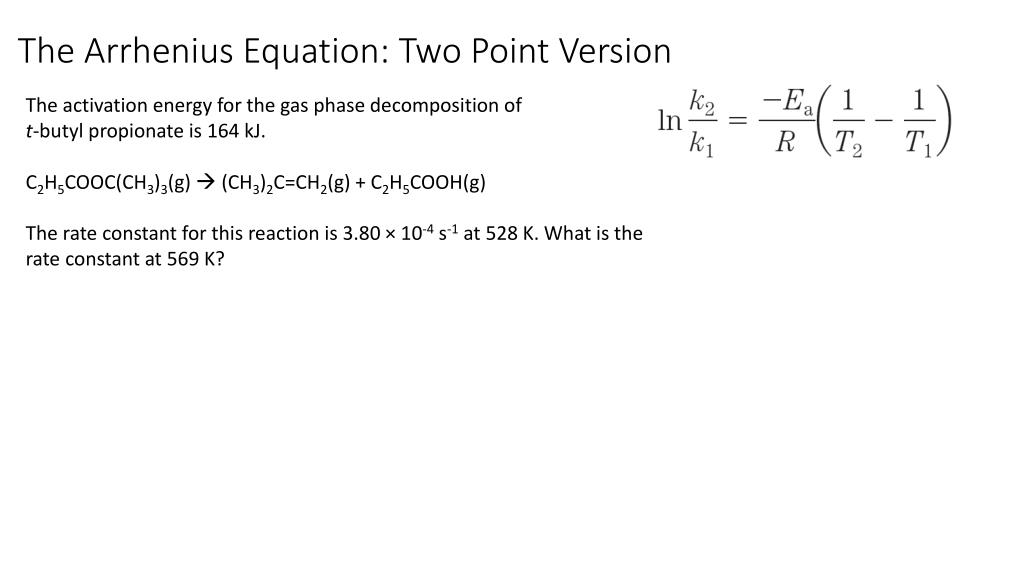
Two Point Form Of Arrhenius Equation - Now here we're going to say that the higher the reaction temperature this causes an increase in the rate constant k. Web k = ae − ea rt. Web the arrhenius equation (equation \ref{eq1}) can be rearranged to deal with specific situations. The various symbols represent the following: Subtracting equation (i) from the equation (ii), we get. The activation energy equation using the arrhenius formula is: This is a constant which comes from the ideal gas law, p v = n r t, which relates the pressure, volume and temperature of a particular number of moles of gas. Web now the two point form of the iranians equation shows how changing the temperature can impact the rate constant which uses the variable que. Lnk = ln(ae − ea / rt) = lna + ln(e − ea / rt) = (− ea r)(1 t) + lna. A reaction has a rate constant of 0.000122 si at 27°c and 0.228 at 77°c. 131 kj/mole) end of chapter 12 practice #65a, 67 temperature and reaction rates. Web co ( g) + o 2 ( g) co 2 ( g) + o ( g) although there are many different possible orientations the two molecules can have relative to each other, consider the two presented in figure 12.13. Using equation (2), suppose that at two. Complete the two point form of the arrhenius equation: The various symbols represent the following: Web the arrhenius equation (equation \ref{eq1}) can be rearranged to deal with specific situations. Web two point arrhenius equation. Web now the two point form of the iranians equation shows how changing the temperature can impact the rate constant which uses the variable que. Calculate the value for the arrhenius energy of activation, ea, for reaction 1, below. Web the activation energy can also be calculated directly given two known temperatures and a rate constant at each temperature. A reaction has a rate constant of 0.000122 si at 27°c and 0.228 at 77°c. Web there are two common forms of the arrhenius equation. Web. This is a constant which comes from the ideal gas law, p v = n r t, which relates the pressure, volume and temperature of a particular number of moles of gas. Substracting equation (4) from equation (3) results in rerrangement of equation (5) and solving for e a yields Subtracting equation (i) from the equation (ii), we get. Web. You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. Temperature, t, measured in kelvin. Web the arrhenius equation, k = ae − ea / rt. Web two point arrhenius equation. Web the arrhenius equation (equation \ref{eq1}) can be rearranged to deal with specific situations. Subtracting equation (i) from the equation (ii), we get. You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. Now here we're going to say that the higher the reaction temperature this causes an increase in the rate constant k. Web how to use arrhenius equation in a sentence. The various symbols represent the. You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. Web the arrhenius equation, k = ae − ea / rt. The various symbols represent the following: Web two point arrhenius equation. This is a constant which comes from the ideal gas law, p v = n r t, which relates the pressure, volume. Can be visualized as the frequency of correctly oriented collisions between reactant particles). Temperature, t, measured in kelvin. The equations are essentially the same, but the units are different. Web this is shown mathematically in the arrhenius equation: Amanda balcerzak's chemistry headquarters 320 subscribers subscribe 721 views 2 years ago. Web two point arrhenius equation. 4 example arrhenius equation example 2 3m 4 comments mark as completed was this helpful? Amanda balcerzak's chemistry headquarters 320 subscribers subscribe 721 views 2 years ago. Web if we know the rate constants at two temperatures, then the activation energy can. 9.72 x 1010) work through example 12.11 and then attempt the following problem. Web the arrhenius equation, k = ae − ea / rt. In the first case, the oxygen side of the carbon monoxide molecule collides with the oxygen molecule. An equation describing the mathematical relationship between temperature and the rate of a chemical reaction… see the full definition 131 kj/mole) end of chapter 12 practice #65a, 67 temperature and reaction rates.. Determine the e, for this reaction. At two different temperatures t 1 and t 2, the corresponding values of rate constants k 1 and k 2 are known respectively then, we can write as: 9.72 x 1010) work through example 12.11 and then attempt the following problem. Ln k 2 k 1 = e a r ( 1 t 1 − 1. The various symbols represent the following: Using equation (2), suppose that at two different temperatures t 1 and t 2, reaction rate constants k 1 and k 2: The equations are essentially the same, but the units are different. Web the arrhenius equation (equation \ref{eq1}) can be rearranged to deal with specific situations. Can be visualized as the frequency of correctly oriented collisions between reactant particles). Web there are two common forms of the arrhenius equation. You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. Web now the two point form of the iranians equation shows how changing the temperature can impact the rate constant which uses the variable que. This is a constant which comes from the ideal gas law, p v = n r t, which relates the pressure, volume and temperature of a particular number of moles of gas. Temperature, t, measured in kelvin. Substracting equation (4) from equation (3) results in rerrangement of equation (5) and solving for e a yields A reaction has a rate constant of 0.000122 si at 27°c and 0.228 at 77°c. 131 kj/mole) end of chapter 12 practice #65a, 67 temperature and reaction rates. Web the activation energy can also be calculated directly given two known temperatures and a rate constant at each temperature. Web k = ae − ea rt. Web if we know the rate constants at two temperatures, then the activation energy can.Solved he Arrhenius equation is a formula for the
PPT Section 14.5 Activation Energy and Temperature PowerPoint
PPT The Arrhenius Equation PowerPoint Presentation, free download
PPT Section 14.5 Activation Energy and Temperature PowerPoint
Arrhenius Equation 2 data points to solve for k2 or Ea YouTube
Chapter13 chemical
Two point arrhenius equation, Easy derivation, 3 application
PPT The Arrhenius Equation PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Solved TwoPoint Form Of Arrhenius Equation In N2. Temper...
I Need Help With For Practice 14.8. I'm Not Sure H...
Related Post: