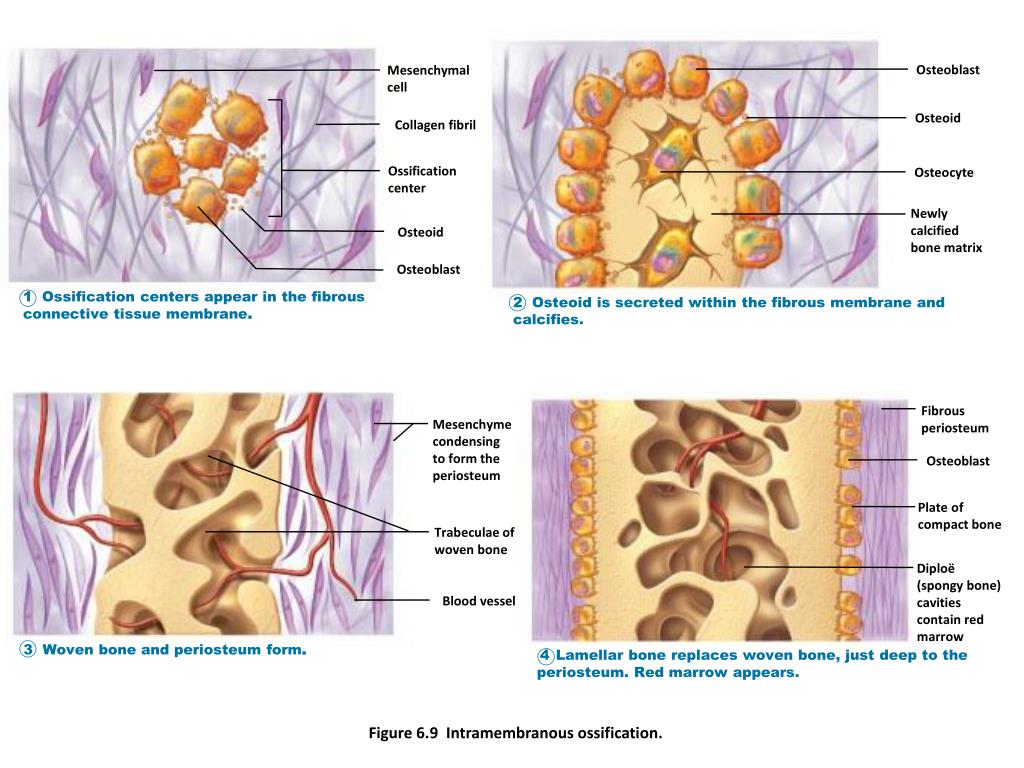
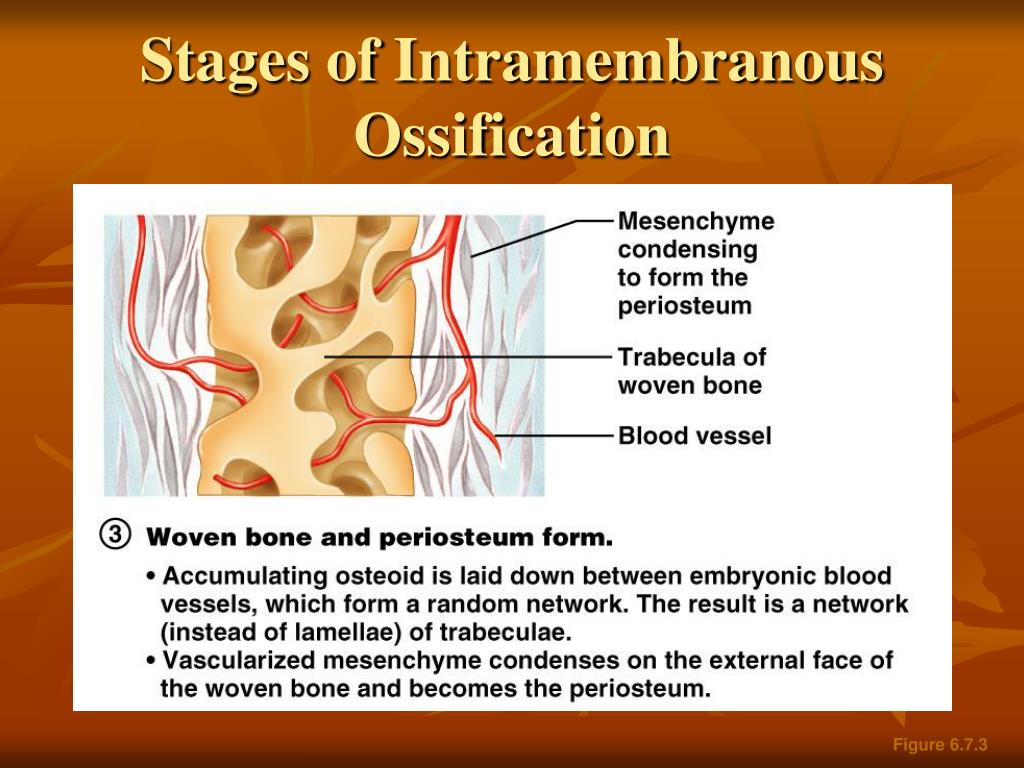
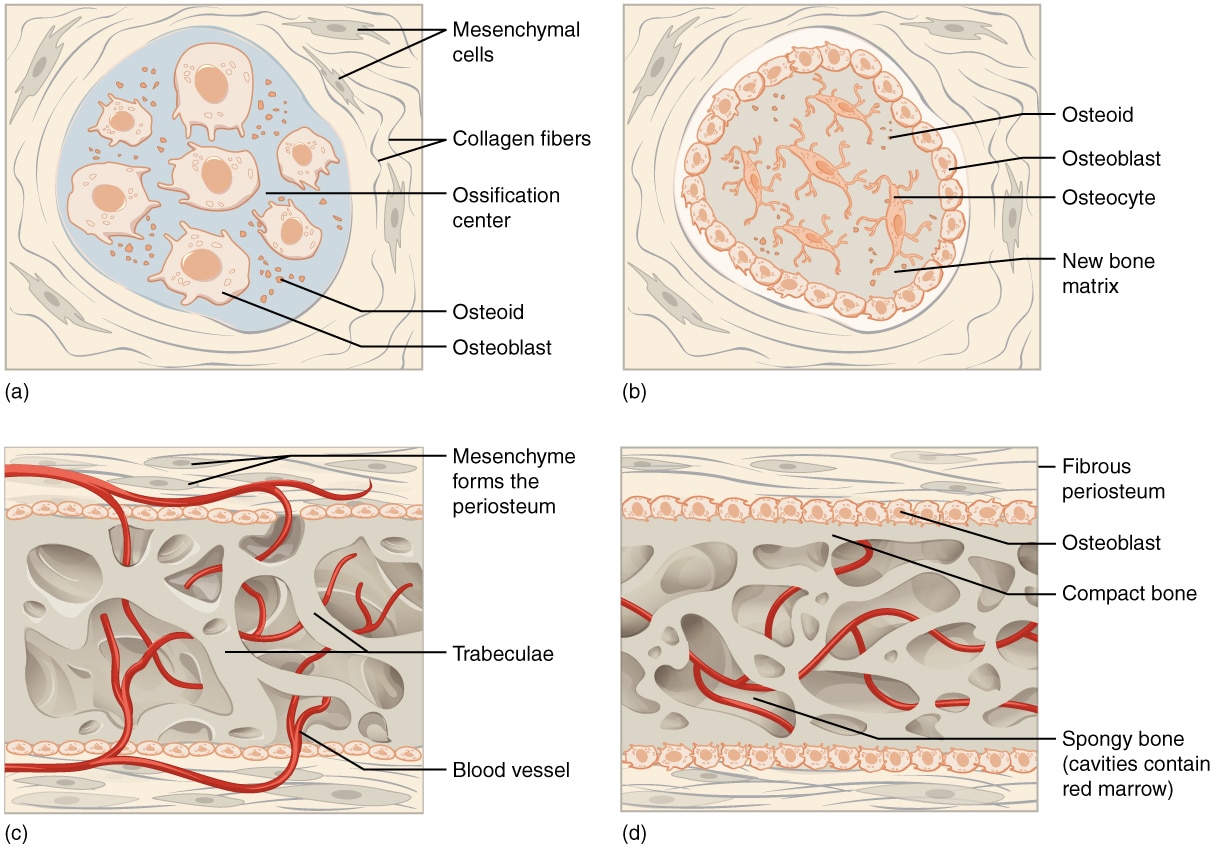
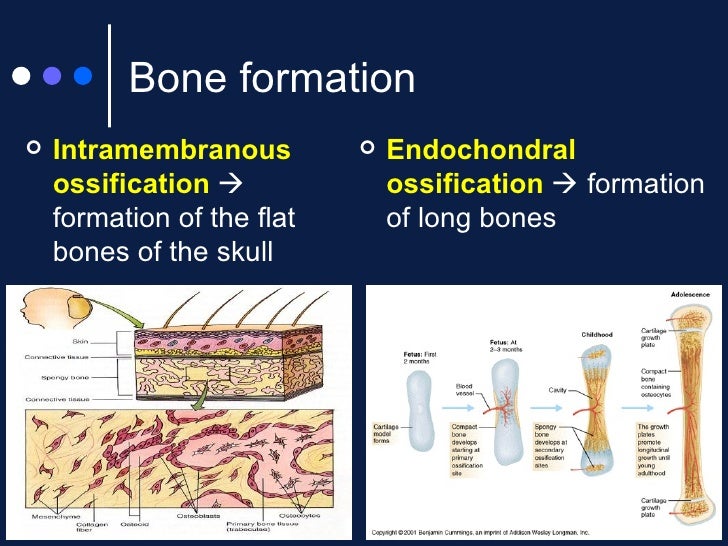
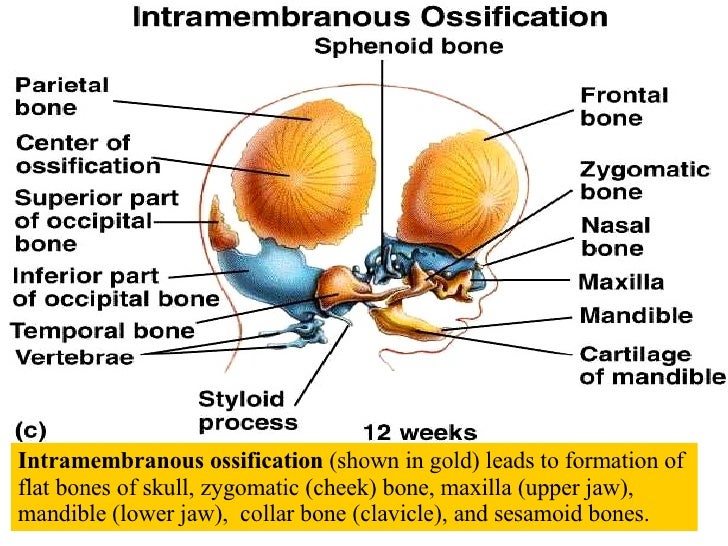
The Flat Bones Of The Cranium Form By Intramembranous Ossification
The Flat Bones Of The Cranium Form By Intramembranous Ossification - Web intramembranous ossification is one of the two essential processes during fetal development of the gnathostome (excluding chondrichthyans such as sharks) skeletal. Web during intramembranous ossification, compact and spongy bone develops directly from sheets of mesenchymal (undifferentiated) connective tissue.the flat bones. Which is not true about bone remodling. The interior of the cranium shows a multitude of details, reflecting the shapes of the softer structures that are in contact with the bones. Web the flat bones of the face, most of the cranial bones, and the clavicles (collarbones) are formed via intramembranous ossification. Explain the function of cartilage list the steps of intramembranous ossification list the steps of endochondral ossification explain the growth activity at the epiphyseal plate compare and contrast the processes of modeling and remodeling in the early stages of embryonic development, the embryo’s skeleton consists. Web the cranium is formed of one frontal bone, two parietal bones, one sphenoid, two temporal bones, one occipital bone, and one ethmoid. It occurs only at articular. The spongy bone found within a flat bone is called _____ diploe. Web the flat bones of the cranium form by intramembranous ossification. Intramembranous ossification is the process of bone development from fibrous membranes. Web terms in this set (131) the flat bones of the cranium form by intramembranous ossification. They have a flat shape, not rounded. Web the flat bones of the face, most of the cranial bones, and the clavicles (collarbones) are formed via intramembranous ossification. Web the flat bones of. They have a flat shape, not rounded. The interior of the cranium shows a multitude of details, reflecting the shapes of the softer structures that are in contact with the bones. Web flat bones, such as bones of the skull, that develop from sheetlike layers of connective tissue, are called ______. Web the flat bones of the cranium form by. Intramembranous ossification is the process of bone development from fibrous membranes. Flat bones are made up of a layer of spongy bone between two thin layers of compact bone. Web the flat bones of the face, most of the cranial bones, and the clavicles (collarbones) are formed via intramembranous ossification. The process begins when mesenchymal. Diagram showing stages of endochondral. Diagram showing stages of endochondral. It occurs only at articular. Web the flat bones of the face, most of the cranial bones, and the clavicles (collarbones) are formed via intramembranous ossification. Web the flat bones of the cranium form by intramembranous ossification. Web (january 2021) intramembranous ossification forms the flat bones of the skull, mandible and hip bone. Web the flat bones of the face, most of the cranial bones, and the clavicles (collarbones) are formed via intramembranous ossification. Diagram showing stages of endochondral. Web during intramembranous ossification, compact and spongy bone develops directly from sheets of mesenchymal (undifferentiated) connective tissue.the flat bones. The interior of the cranium shows a multitude of details, reflecting the shapes of the. Explain the function of cartilage list the steps of intramembranous ossification list the steps of endochondral ossification explain the growth activity at the epiphyseal plate compare and contrast the processes of modeling and remodeling in the early stages of embryonic development, the embryo’s skeleton consists. The interior of the cranium shows a multitude of details, reflecting the shapes of the. The spongy bone found within a flat bone is called _____ diploe. Web intramembranous ossification is one of the two essential processes during fetal development of the gnathostome (excluding chondrichthyans such as sharks) skeletal. Web the flat bones of the face, most of the cranial bones, and the clavicles (collarbones) are formed via intramembranous ossification. Intramembranous ossification is the process. Web terms in this set (131) the flat bones of the cranium form by intramembranous ossification. Explain the function of cartilage list the steps of intramembranous ossification list the steps of endochondral ossification explain the growth activity at the epiphyseal plate compare and contrast the processes of modeling and remodeling in the early stages of embryonic development, the embryo’s skeleton. Diagram showing stages of endochondral. Web the cranium is formed of one frontal bone, two parietal bones, one sphenoid, two temporal bones, one occipital bone, and one ethmoid. Web the flat bones of the face, most of the cranial bones, and the clavicles (collarbones) are formed via intramembranous ossification. Web (january 2021) intramembranous ossification forms the flat bones of the. Web the flat bones of the face, most of the cranial bones, and the clavicles (collarbones) are formed via intramembranous ossification. The interior of the cranium shows a multitude of details, reflecting the shapes of the softer structures that are in contact with the bones. Diagram showing stages of endochondral. Intramembranous ossification is the process of bone development from fibrous. Web intramembranous ossification directly converts the mesenchymal tissue to bone and forms the flat bones of the skull, clavicle, and most of the cranial bones. Web the flat bones of the cranium form by intramembranous ossification. Web the flat bones of the face, most of the cranial bones, and the clavicles (collarbones) are formed via intramembranous ossification. Web flat bones, such as bones of the skull, that develop from sheetlike layers of connective tissue, are called ______. Explain the function of cartilage list the steps of intramembranous ossification list the steps of endochondral ossification explain the growth activity at the epiphyseal plate compare and contrast the processes of modeling and remodeling in the early stages of embryonic development, the embryo’s skeleton consists. Web intramembranous ossification is one of the two essential processes during fetal development of the gnathostome (excluding chondrichthyans such as sharks) skeletal. Web the flat bones of the face, most of the cranial bones, and the clavicles (collarbones) are formed via intramembranous ossification. They have a flat shape, not rounded. Which is not true about bone remodling. Intramembranous ossification is the process of bone development from fibrous membranes. Web during intramembranous ossification, compact and spongy bone develops directly from sheets of mesenchymal (undifferentiated) connective tissue.the flat bones. Web the flat bones of the face, most of the cranial bones, and the clavicles (collarbones) are formed via intramembranous ossification. The process begins when mesenchymal. Web terms in this set (131) the flat bones of the cranium form by intramembranous ossification. Web the flat bones of the face, most of the cranial bones, and the clavicles (collarbones) are formed via intramembranous ossification. Flat bones are made up of a layer of spongy bone between two thin layers of compact bone. It occurs only at articular. Web the cranium is formed of one frontal bone, two parietal bones, one sphenoid, two temporal bones, one occipital bone, and one ethmoid. It is involved in the formation of the flat bones of. Web (january 2021) intramembranous ossification forms the flat bones of the skull, mandible and hip bone.PPT Bones and Skeletal Tissues PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Embryology Glossary Intramembranous vs Endochondral Draw It to Know It
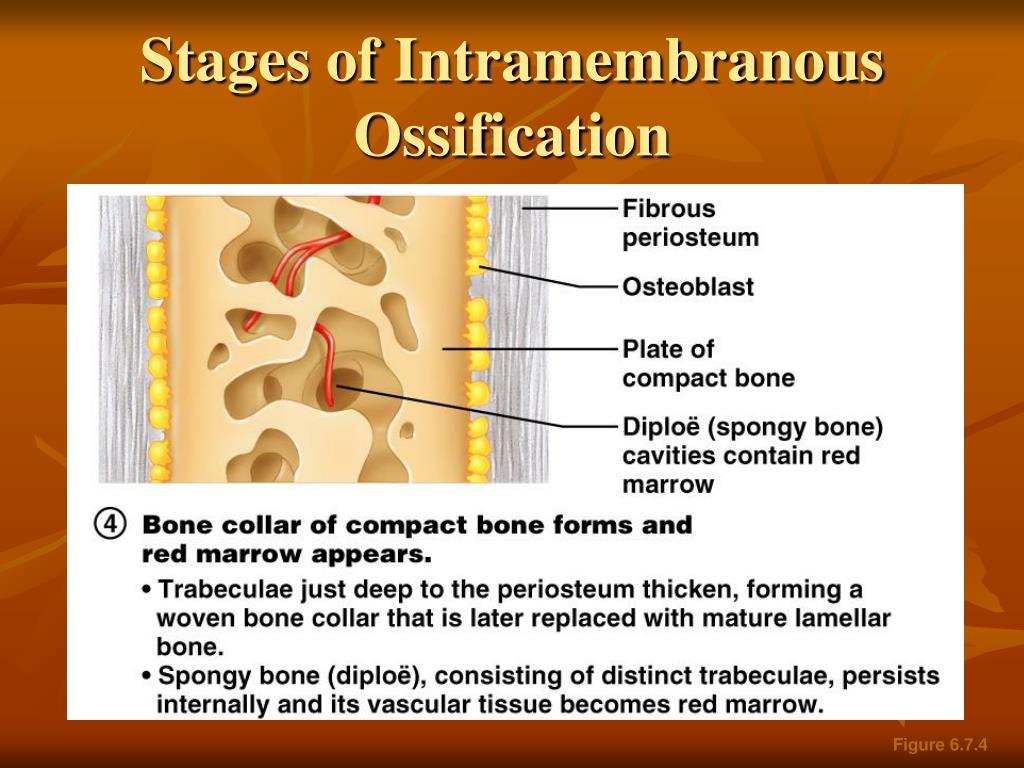
PPT Stages of Intramembranous Ossification PowerPoint Presentation
Bone Ossification Process Histology TeachMePhysiology
PPT SECTION 61 Introduction to the skeletal system PowerPoint
Presentation 15 Musculoskeletal System
03 Cartilage And Bone Connective Tissue
Intramembranous Ossification Diagram Quizlet
PPT Stages of Intramembranous Ossification PowerPoint Presentation
Intramembranous Ossification Formation of Bone Flat Bone Formation
Related Post: