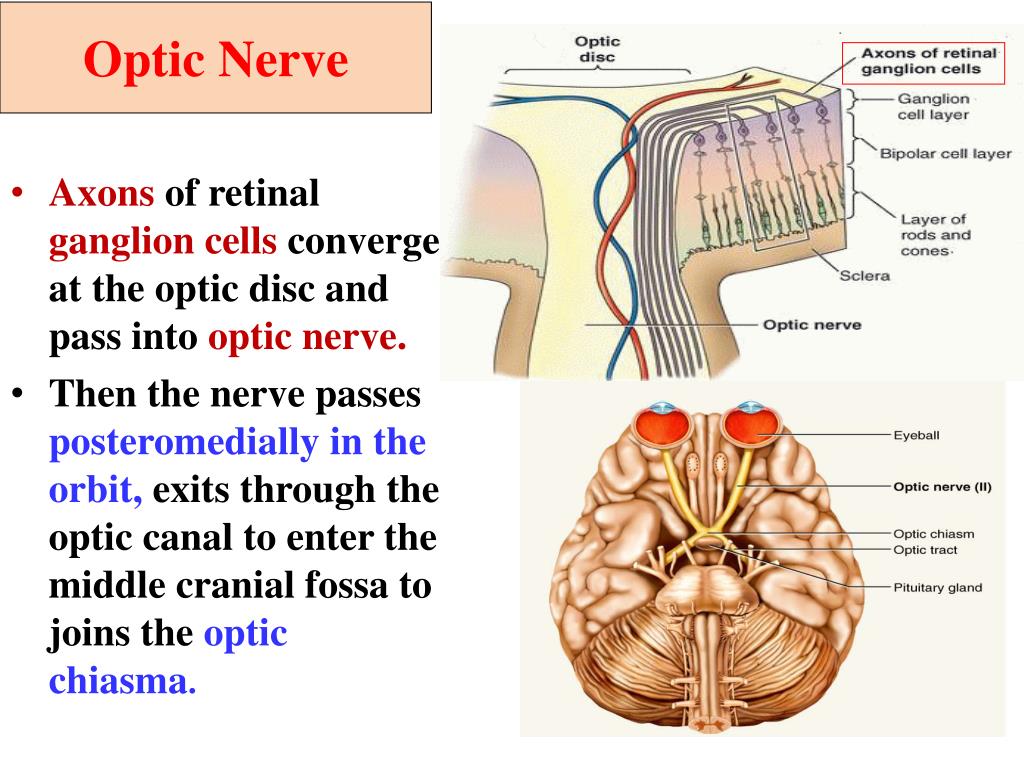
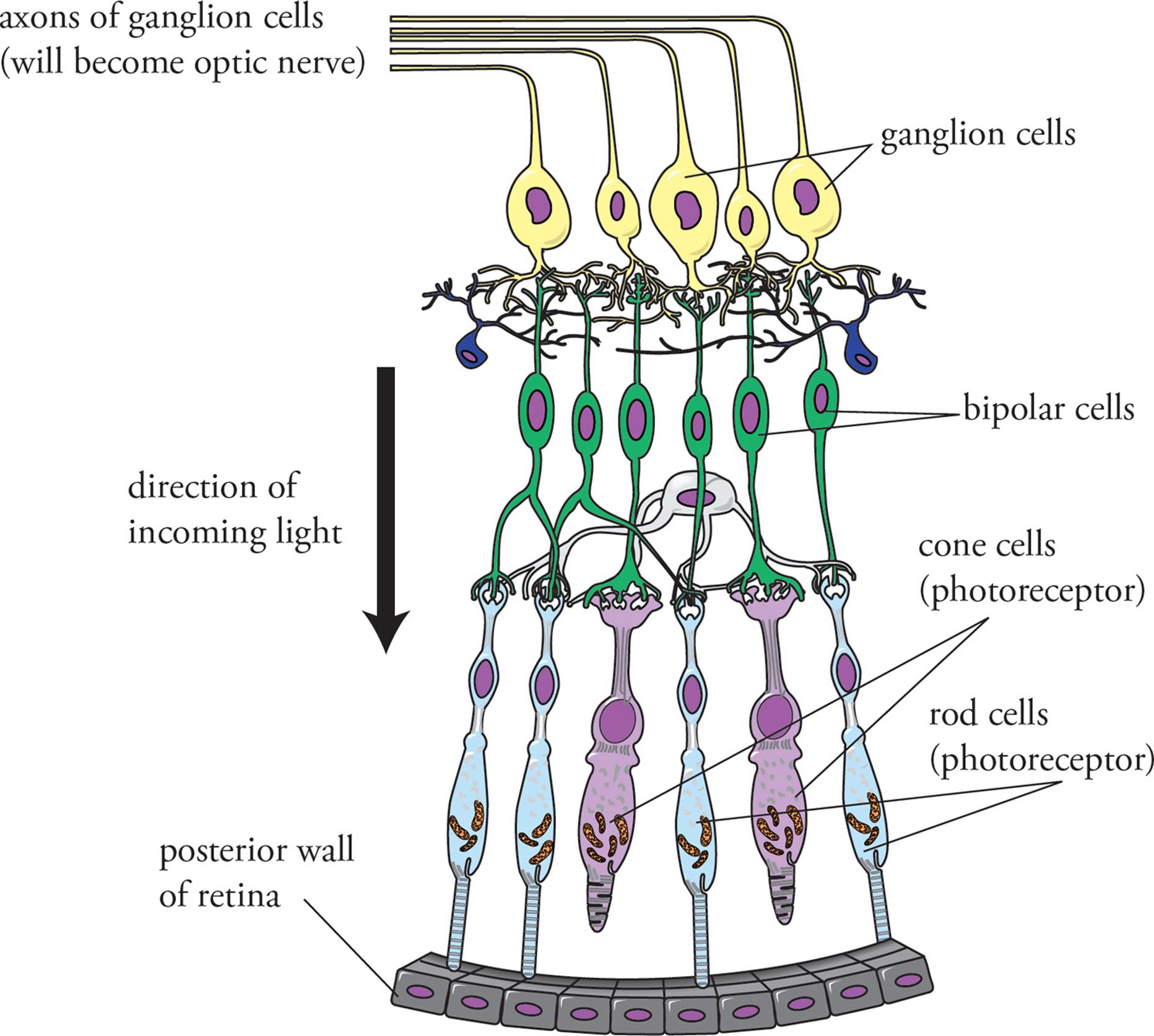
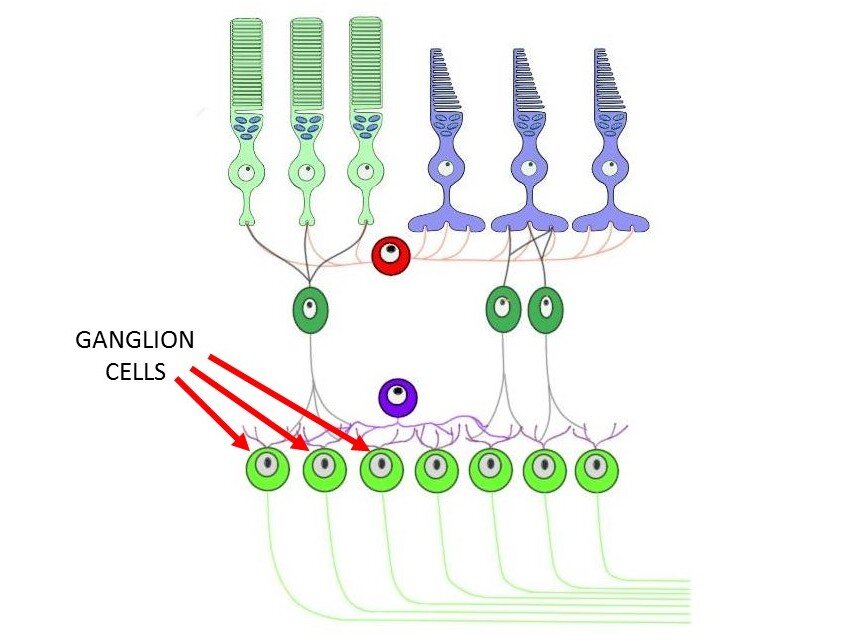
The Axons Of Ganglion Cells Converge To Form
The Axons Of Ganglion Cells Converge To Form - What structure do they form? Web the axons of ganglion cells converge to form. Brain (thalamus) where this nerve. Web where do nerve fibers converge in the eye? Web central projections of retinal ganglion cells. Web axons of ganglion cells pass through the optic nerve, optic chiasm, and optic tract. Web the prelaminar glial tissue offers structural support to the axons of the ganglion cells as they make the perpendicular bend from the retina to form the optic. It receives visual information from photoreceptors via two intermediate neuron types: A retinal ganglion cell (rgc) is a type of neuron located near the inner surface (the ganglion cell layer) of the retina of the eye. Ganglion cells receive inputs from bipolar cells and amacrine cells. They converge at the optic disc/blind spot + they leave as the optic nerve (291) students also viewed. Web optic nerve, chiasm, and tract. Web central projections of retinal ganglion cells. Ganglion cells receive inputs from bipolar cells and amacrine cells. Web the axons of ganglion cells converge to form. Brain (thalamus) where this nerve. C) the pigment epithelium is so dark in the blind spot that light cannot be perceived. Web retinal ganglion cell (rgc) axons converge on the optic disc to form an optic nerve. Sensory receptors in utricle and saccule for monitering the position of the head and equilibrium. Web the axons of the ganglion cells form. It receives visual information from photoreceptors via two intermediate neuron types: Web the axons of retinal ganglion cells converge to form the optic nerve, which exits through the back of the eye and carries the visual information to the brain. Sensory receptors in utricle and saccule for monitering the position of the head and equilibrium. Web optic nerve, chiasm, and. Axons of retinal ganglion cells conveying input from all areas of the retina converge at the optic disc, where they penetrate the choroid and. The receptor cells and the bipolar cells of the retina respond to. Brain (thalamus) where this nerve. Retina amacrine cells, particularly narrow field cells, are important for creating functional subunits within the ganglion cell layer and. Web central projections of retinal ganglion cells. A retinal ganglion cell (rgc) is a type of neuron located near the inner surface (the ganglion cell layer) of the retina of the eye. They converge at the optic disc/blind spot + they leave as the optic nerve (291) students also viewed. It receives visual information from photoreceptors via two intermediate neuron. Web the axons from ganglion cells converge to form the optic nerve, which establishes the area of no vision called the: Web central projections of retinal ganglion cells. A retinal ganglion cell (rgc) is a type of neuron located near the inner surface (the ganglion cell layer) of the retina of the eye. The optic disc represents the beginning of. What structure do they form? Web the axons of ganglion cells converge to form the ___ ___, which carries the visual information to the ___. Retina amacrine cells, particularly narrow field cells, are important for creating functional subunits within the ganglion cell layer and ma… The fourth neuronal elements are found in the lateral geniculate body; Web the axons of. Web the prelaminar glial tissue offers structural support to the axons of the ganglion cells as they make the perpendicular bend from the retina to form the optic. It receives visual information from photoreceptors via two intermediate neuron types: Web axons of ganglion cells pass through the optic nerve, optic chiasm, and optic tract. Web the axons of ganglion cells. Bipolar cells and retina amacrine cells. Web the ganglion cell axons form the optic nerve after they leave the eye. Ganglion cells receive inputs from bipolar cells and amacrine cells. A retinal ganglion cell (rgc) is a type of neuron located near the inner surface (the ganglion cell layer) of the retina of the eye. Axons converge to form optic. Web the ganglion cell axons of the optic nerve carry visual signals from the retina to the brain. Web optic nerve, chiasm, and tract. Web the axons from ganglion cells converge to form the optic nerve, which establishes the area of no vision called the: Web retinal ganglion cell (rgc) axons converge on the optic disc to form an optic. Web axons of ganglion cells pass through the optic nerve, optic chiasm, and optic tract. The receptor cells and the bipolar cells of the retina respond to. Web central projections of retinal ganglion cells. Web the axons of retinal ganglion cells converge to form the optic nerve, which exits through the back of the eye and carries the visual information to the brain. Retina amacrine cells, particularly narrow field cells, are important for creating functional subunits within the ganglion cell layer and ma… Web the ganglion cell axons form the optic nerve after they leave the eye. Bipolar cells and retina amacrine cells. Axons of retinal ganglion cells conveying input from all areas of the retina converge at the optic disc, where they penetrate the choroid and. Web the ganglion cell axons of the optic nerve carry visual signals from the retina to the brain. Web the axons of ganglion cells converge to form a) the optic nerve b) olfactory bulb c) bipolar cells d) basilar membrane e) auditory nerve c if we could stop our eyes from. Any neuron whose cell body is located within a ganglion. The fourth neuronal elements are found in the lateral geniculate body; A neuron of the retina of the eye whose cell body lies in the ganglion cell layer. Web where do nerve fibers converge in the eye? Ganglion cells receive inputs from bipolar cells and amacrine cells. It receives visual information from photoreceptors via two intermediate neuron types: Web the prelaminar glial tissue offers structural support to the axons of the ganglion cells as they make the perpendicular bend from the retina to form the optic. The optic disc represents the beginning of the optic nerve and is the point where the axons of retinal. Web the axons of ganglion cells converge to form the ___ ___, which carries the visual information to the ___. Web b) the axons of the ganglion cells converge in one spot to form the optic nerve.PPT Cranial nerves II,III, IV,VI and Visual Pathway PowerPoint
The OpticNerve Head and Proposed Events Leading to Retinal
The Nervous and Endocrine Systems MCAT Biology and Biochemistry
Ganglion cell definition — Neuroscientifically Challenged
What are Ganglion Cells? (with pictures)
The Retinal Ganglion Cell Transportome Identifies Proteins Transported
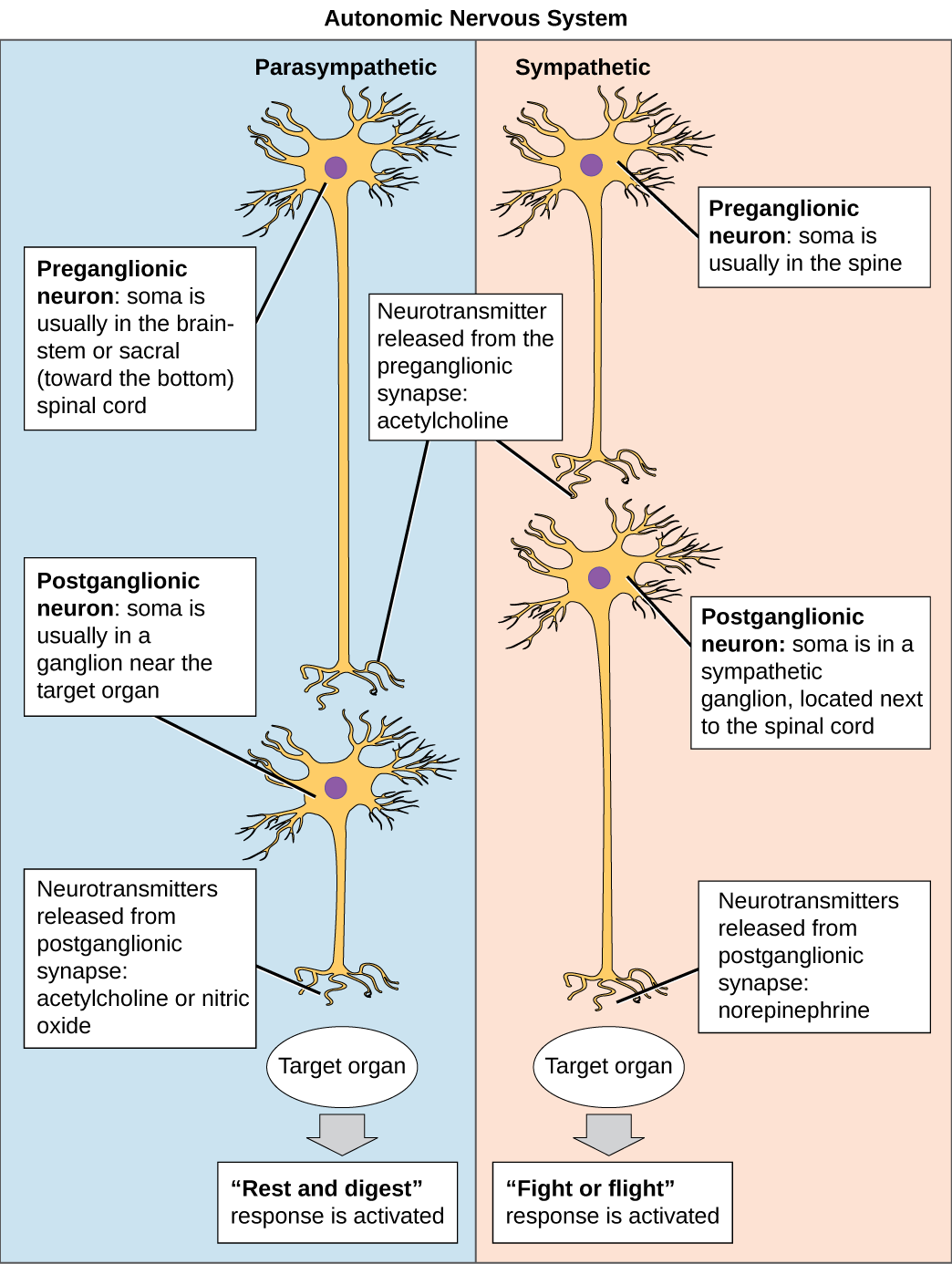
4.2 Autonomic Nervous System Basics Nursing Pharmacology
Illustration of retinal neuronal network and ganglion cell model. (A
Figure 5 from The Structure and Plasticity of the Proximal Axon of
Why Retinal Ganglion Cells Are Important in Vision Magazine
Related Post: