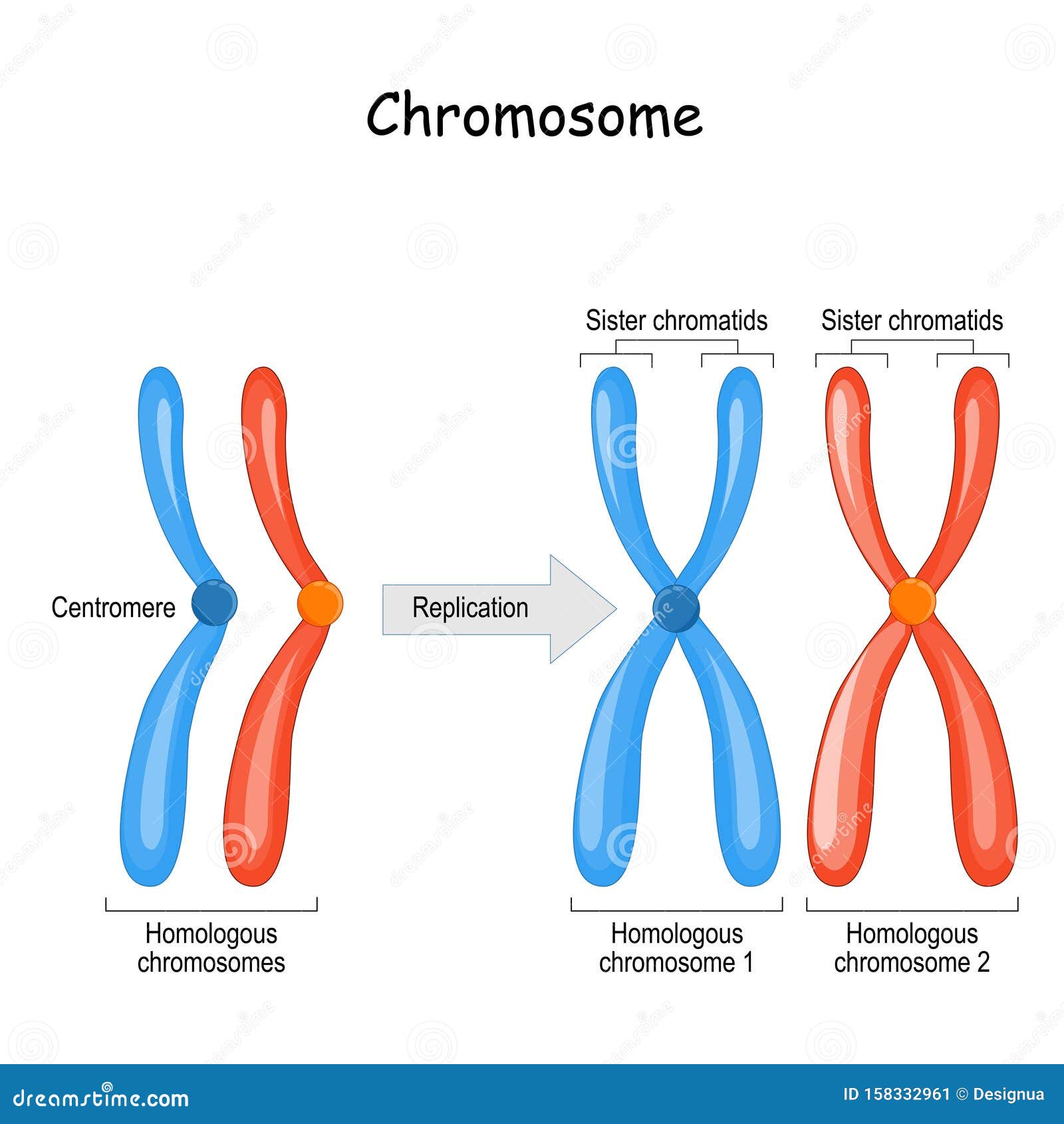
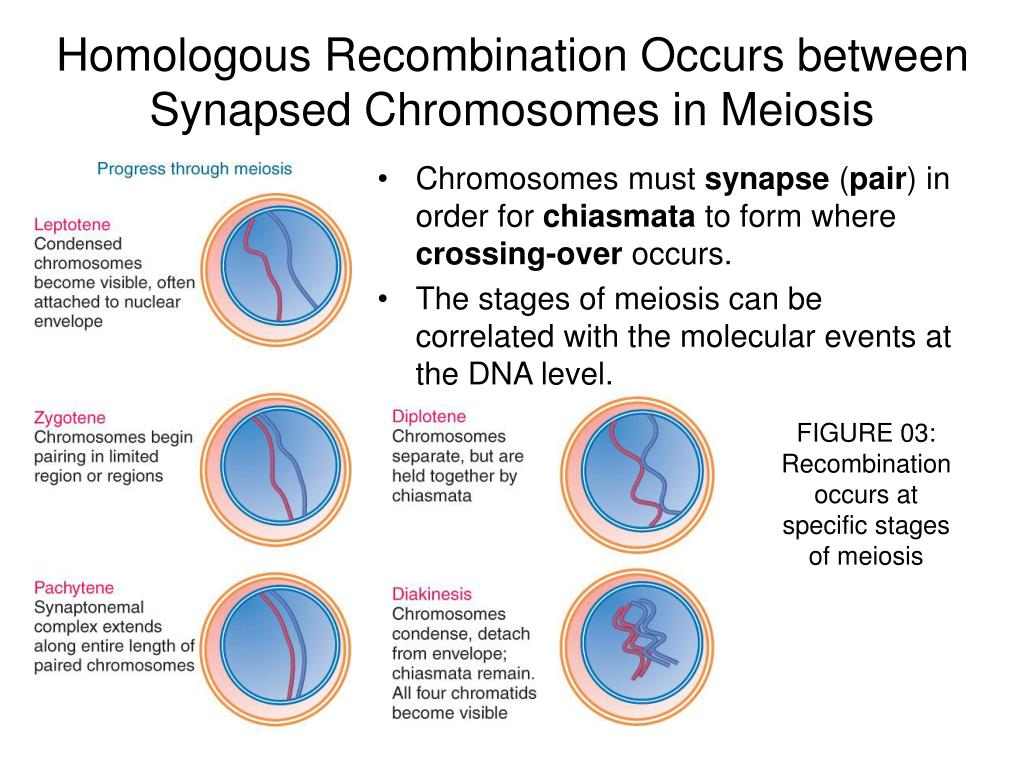
Homologous Chromosomes Pair And Form Synapses
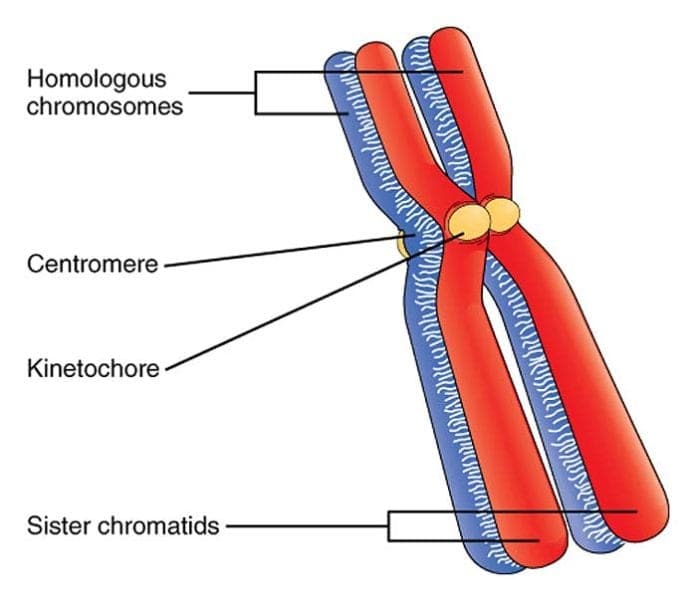
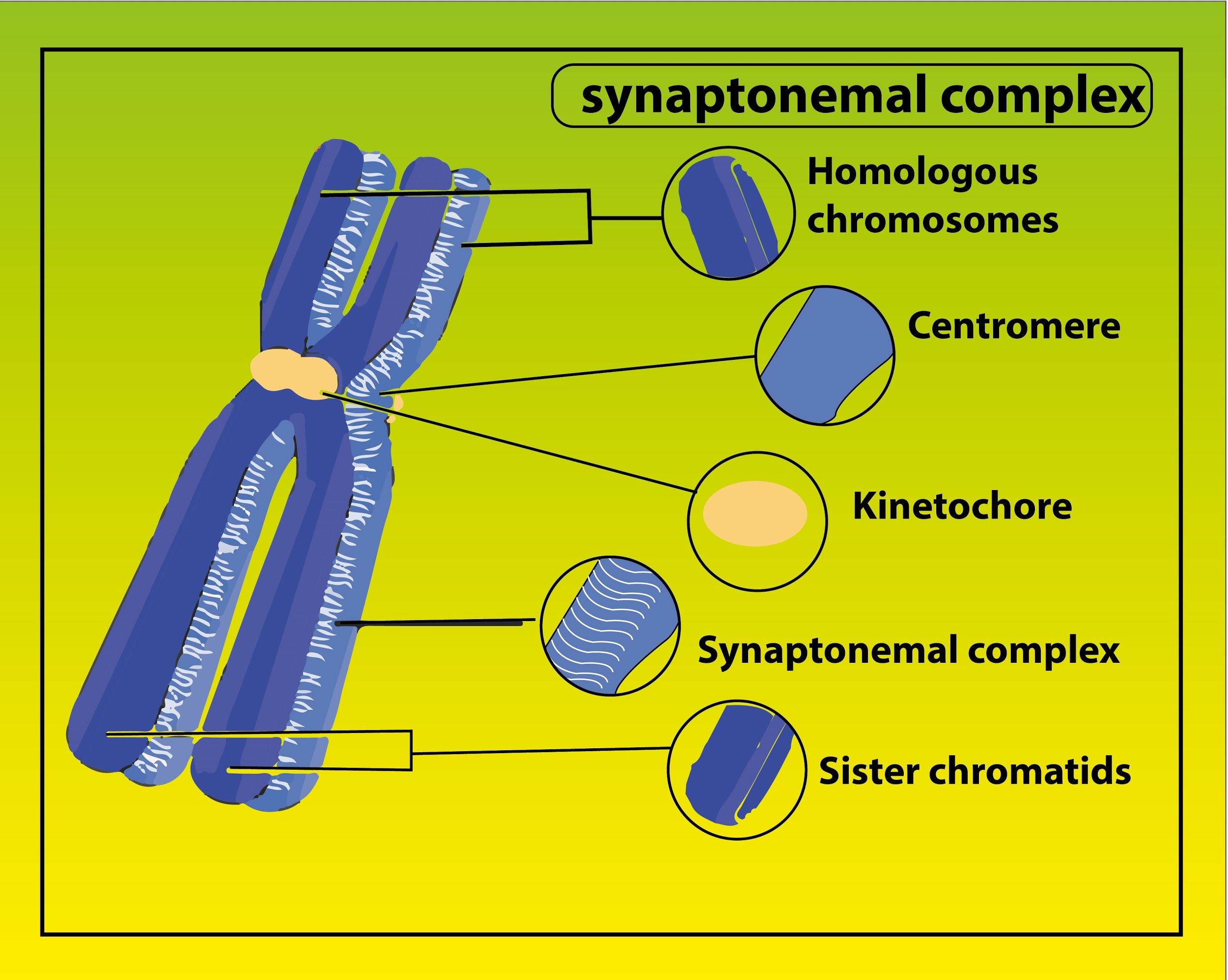
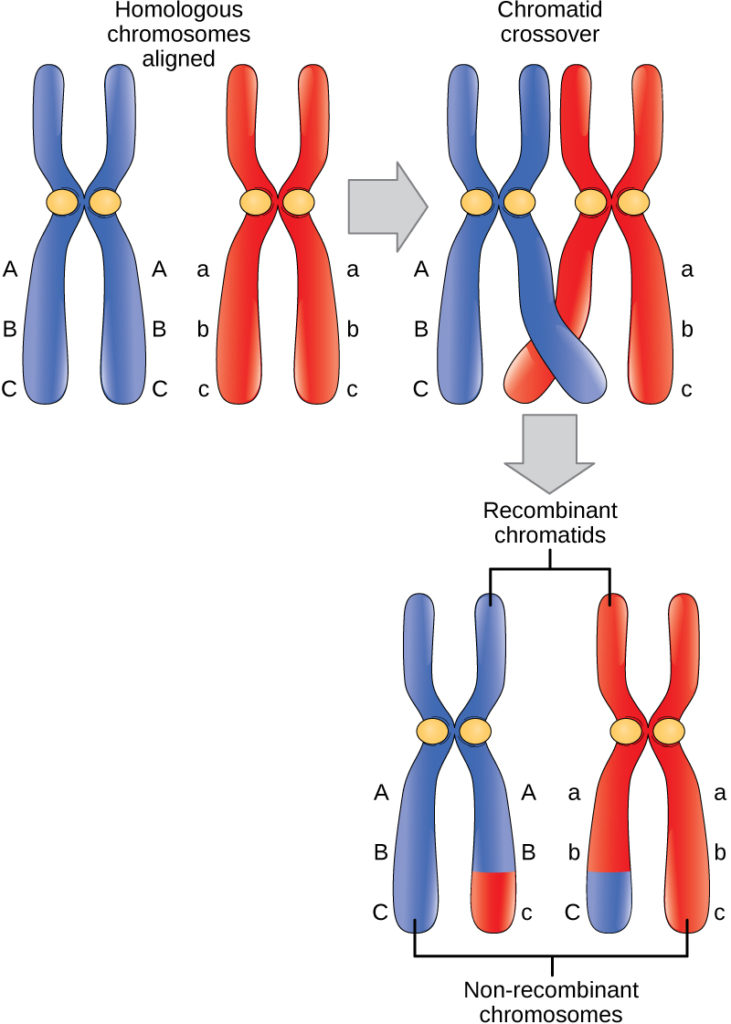
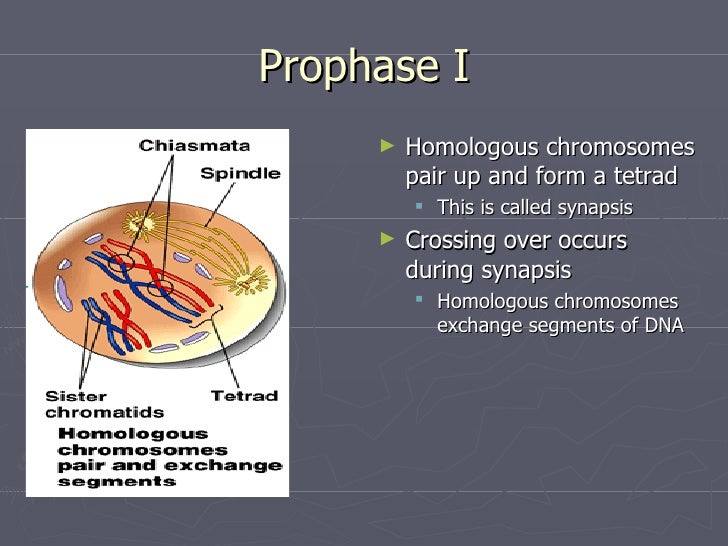
Homologous Chromosomes Pair And Form Synapses - During prophase i, homologous chromosomes pair and form. It is this step in meiosis that generates genetic diversity. Web when homologous chromosomes form pairs, it is called synapse. Synapsis holds pairs of homologous chromosomes together: Web in meiosis i, chromosomes in a diploid cell resegregate, producing four haploid daughter cells. Dna replication precedes the start of meiosis i. Web nuclear membrane breaks down and disintegrates replicated chromosomes condense and become visible homologous chromosomes synapse (pair up) to form. Synapsis is the pairing of two chromosomes that occurs during meiosis. The chromosomes are bound tightly together and in perfect alignment by a. Spindle fibers move homologous chromosomes to opposite sides. Web figure 11.2 early in prophase i, homologous chromosomes come together to form a synapse. Tetrads align at metaphase plate. To achieve haploidy, two divisions are necessary. Web name the stage of meiosis 1 where each of the following occurs: Spindle fibers move homologous chromosomes to opposite sides. When homologous chromosomes synapse, their ends are first attached to the nuclear envelope. Web homologous chromosomes pair up and form a tetrad. Web figure 11.2 early in prophase i, homologous chromosomes come together to form a synapse. Spindle fibers move homologous chromosomes to opposite sides. Early in prophase i, homologous chromosomes come together to form a synapse. Web name each pair of homologous chromosomes. Synapsis is the pairing of two chromosomes that occurs during meiosis. It is this step in meiosis that generates genetic diversity. When homologous chromosomes synapse, their ends are first attached to the nuclear envelope. Web homologous chromosomes pair up and form a tetrad. Web when homologous chromosomes form pairs, it is called synapse. Web homologous chromosomes pair and form synapses. Synapsis takes place during prophase i of meiosis. Web name the stage of meiosis 1 where each of the following occurs: Homologous chromosomes pair and form synapses. Tetrads align at metaphase plate. Early in prophase i, homologous chromosomes come together to form a synapse. The chromosomes are bound tightly together and in perfect alignment by a. Web when homologous chromosomes form pairs, it is called synapse. It is this step in meiosis that generates genetic diversity. When homologous chromosomes synapse, their ends are first attached to the nuclear envelope. Web in meiosis i, chromosomes in a diploid cell resegregate, producing four haploid daughter cells. Web homologous chromosomes pair and form synapses. Synapsis takes place during prophase i of meiosis. The paired chromosomes are called bivalents. Web we would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. It is this step in meiosis that generates genetic diversity. Web nuclear membrane breaks down and disintegrates replicated chromosomes condense and become visible homologous chromosomes synapse (pair up) to form. Dna replication precedes the start of meiosis i. Paired chromosomes (bivalents) align at metaphase. Web we would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Homologous chromosomes pair and form synapses, a step unique to meiosis. It is this step in meiosis that generates genetic diversity. Web nuclear membrane breaks down and disintegrates replicated chromosomes condense and become visible homologous chromosomes synapse (pair up) to form. Web therefore, when. The chromosomes are bound tightly together and in perfect alignment by a. Synapsis is the pairing of two chromosomes that occurs during meiosis. To achieve haploidy, two divisions are necessary. Tetrads align at metaphase plate. Homologous chromosomes pair and form synapses. Synapsis takes place during prophase i of meiosis. During prophase i, homologous chromosomes pair and form. Web in meiosis i, chromosomes in a diploid cell resegregate, producing four haploid daughter cells. Web we would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Web nuclear membrane breaks down and disintegrates replicated chromosomes condense and become visible. The chromosomes are bound tightly together and in perfect alignment by a. Dna replication precedes the start of meiosis i. Spindle fibers move homologous chromosomes to opposite sides. Name the stage of prophase at which it takes place. Web we would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Web homologous chromosomes pair up and form a tetrad. Web nuclear membrane breaks down and disintegrates replicated chromosomes condense and become visible homologous chromosomes synapse (pair up) to form. Homologous chromosomes pair and form synapses. Web we would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. When do these two divisions occur? The paired chromosomes are called bivalents. Web therefore, when two chromosomes containing the relatively same structure exist (e.g., maternal chromosome 15 and paternal chromosome 15), they are able to pair together. When homologous chromosomes synapse, their ends are first attached to the nuclear envelope. Synapsis takes place during prophase i of meiosis. Synapsis holds pairs of homologous chromosomes together: Web figure 11.2 early in prophase i, homologous chromosomes come together to form a synapse. Paired chromosomes (bivalents) align at metaphase plate. Web in meiosis i, chromosomes in a diploid cell resegregate, producing four haploid daughter cells. Homologous chromosomes pair and form synapses, a step unique to meiosis. To achieve haploidy, two divisions are necessary.What Is Synapsis? Definition and Function
What Is A Homologous Chromosome? Biology Explorer
What develops between the homologous chromosomes during zygotene.(a
Meiosis I Biology for Majors I
Homologous pairing and the role of pairing centers in meiosis Journal
Copy of meiosis2010
Difference between Homologous Chromosomes, a Pair of Homologous
Meiosis Biology for Majors I
The complex formed by a pair of synapsed homologous chromosomes is called
PPT Objectives of DNA PowerPoint Presentation, free
Related Post:
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-1048828128-157a76170f1e4ca8841bf66f0cc042e6.jpg)