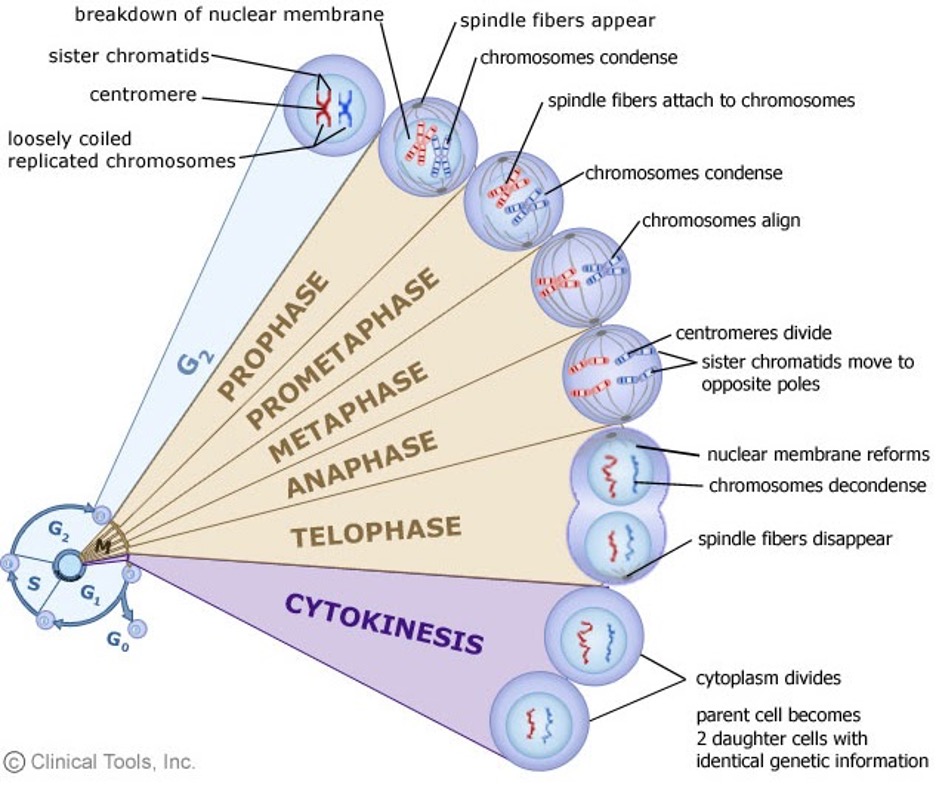
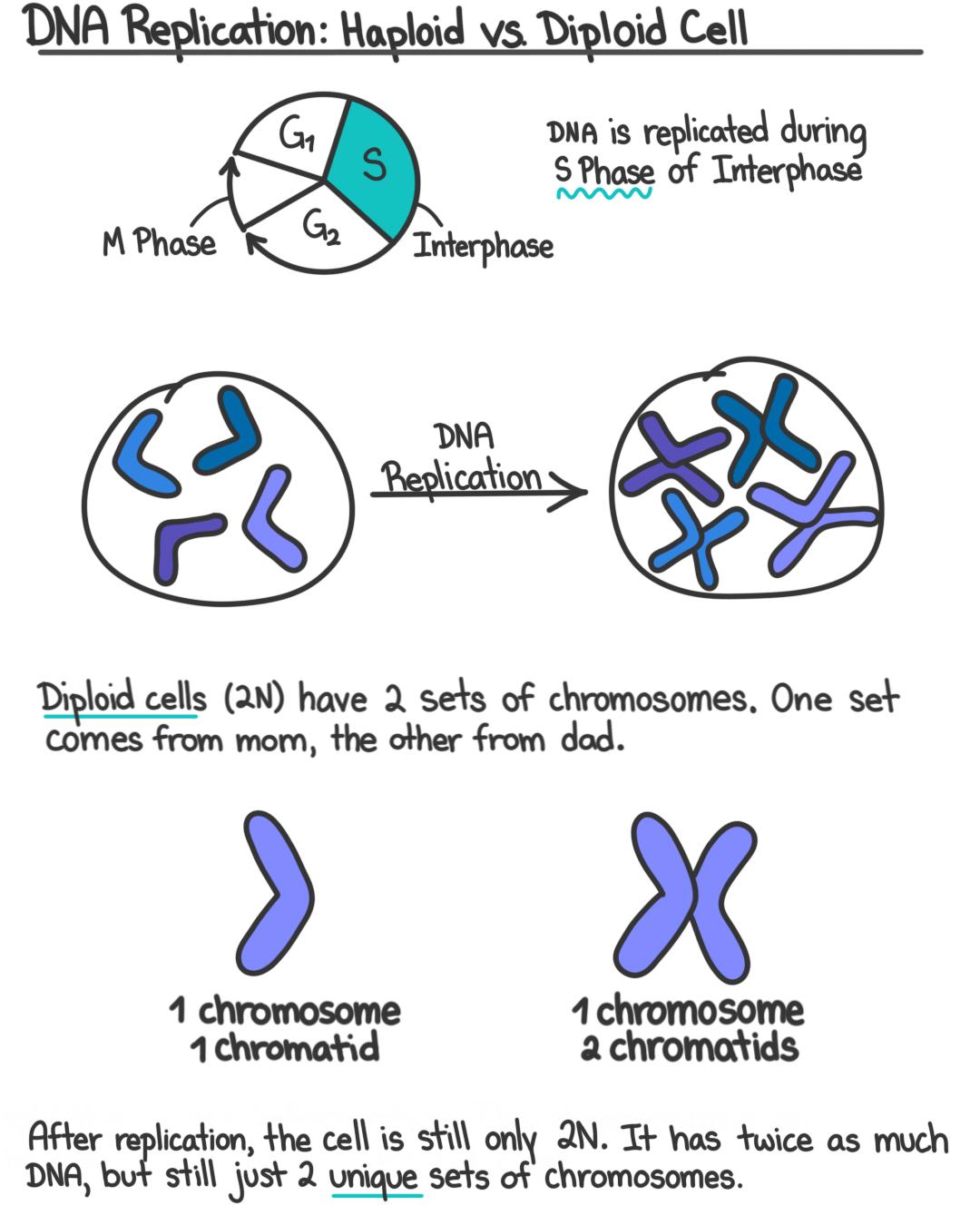
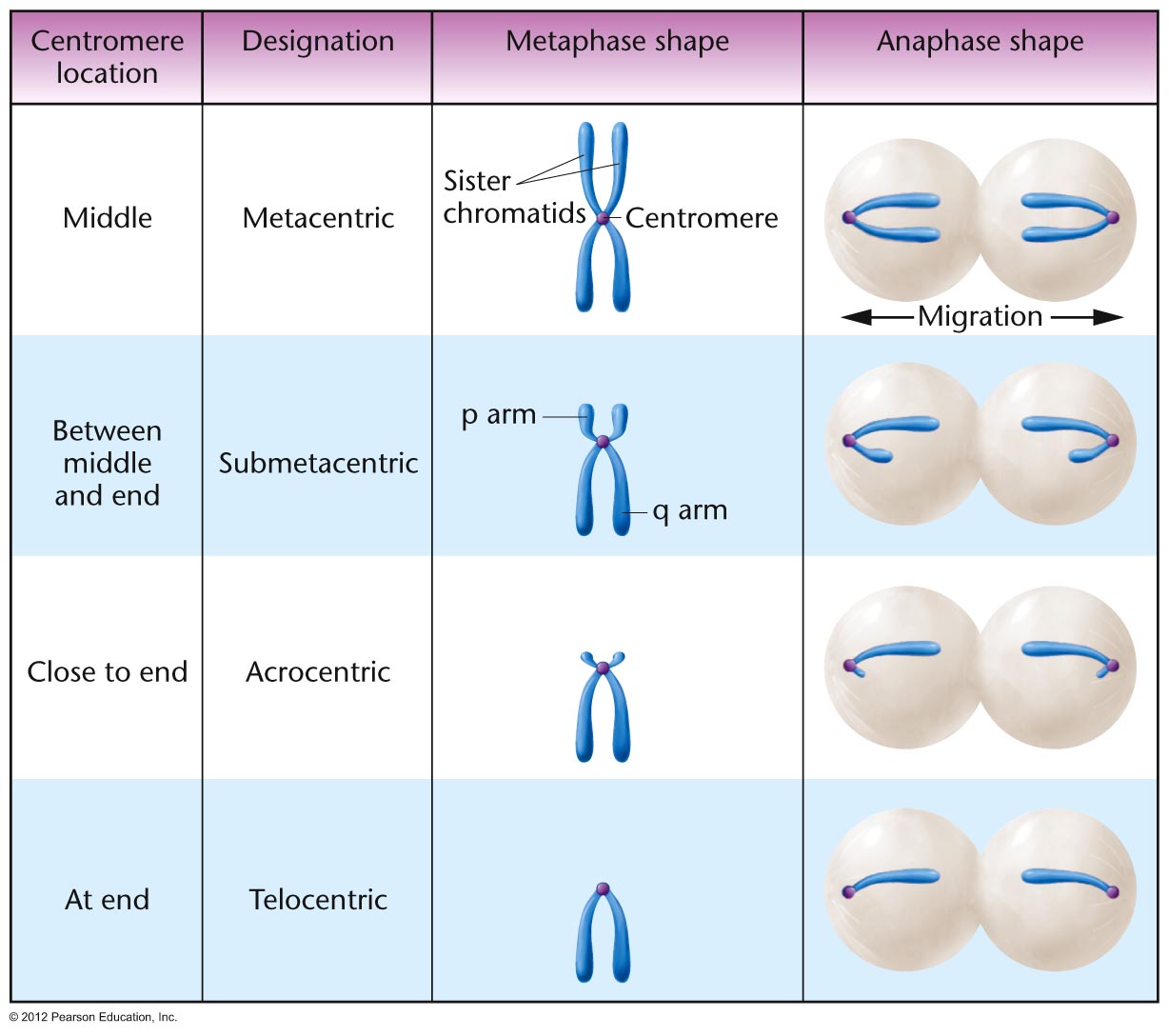
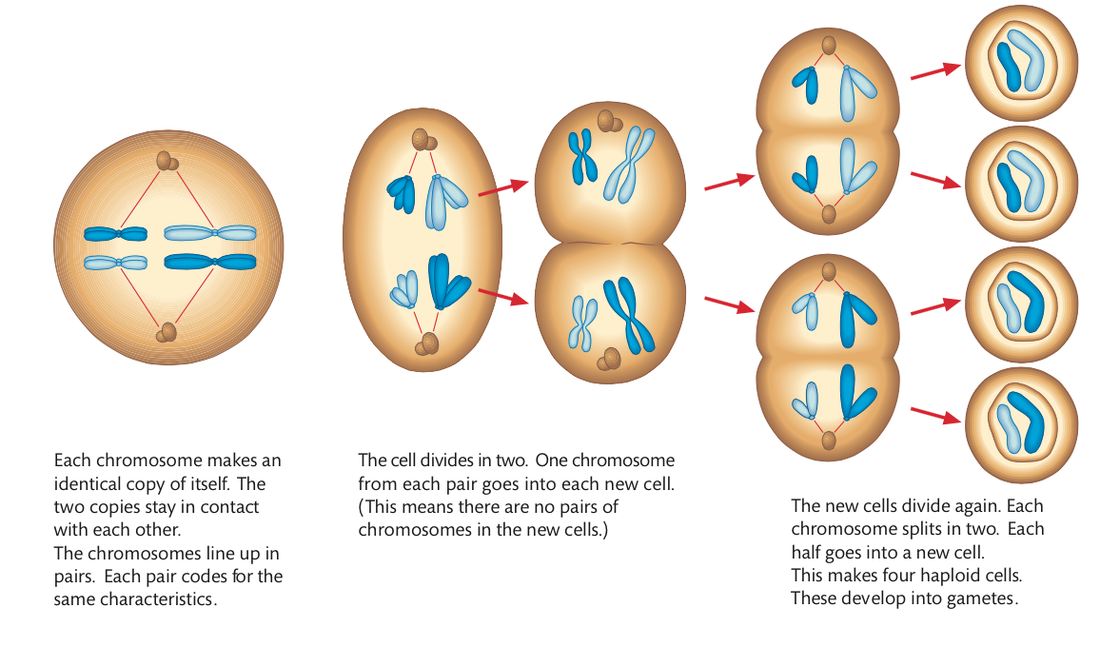
During S Phase Chromosomes Are Converted To What Form
During S Phase Chromosomes Are Converted To What Form - Web as the two daughter dna strands are produced from the chromosomal dna during s phase, these daughter strands recruit additional histones and other proteins to form the. The cell synthesizes a complete copy of the dna in its nucleus. Web chromosomes condense and become visible by light microscopy as eukaryotic cells enter mitosis or meiosis. Web during the interphase (s phase) of cell division, eukaryote chromosomes present in the nucleus are replicated, and two identical copies of each chromosome are. Web a) gametes receive one copy of each member of each pair of homologous chromosomes. The cell cycle encompasses the whole life of a cell from birth through to its death. Cohesion between sister chromatids is established. Contributions from histone deposition, dna replication and the cell division cycle. Web after chromosome condensation, the chromosomes condense to form compact structures (still made up of two chromatids). A normal diploid somatic cell with a 2n complement of dna at the. It is the time from the formation of a cell from its parent cell until its division into its daughter cells. An important part of the cell cycle is cell division, the process whereby a cell is replicated to form either two daughter cells, through the. During s phase of the eukaryotic cell division cycle, newly. A normal diploid somatic. The events of s phase are intimately linked to chromosome structure. Web in the s phase (synthesis phase), dna replication results in the formation of two identical copies of each chromosome—sister chromatids—that are firmly attached at the. Finally, the g 2 phase, also called the second gap. Web during the interphase (s phase) of cell division, eukaryote chromosomes present in. Web chromosomes condense and become visible by light microscopy as eukaryotic cells enter mitosis or meiosis. It is the time from the formation of a cell from its parent cell until its division into its daughter cells. Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Web during the interphase (s phase) of cell division, eukaryote chromosomes present in the nucleus are replicated, and. Web s phase is the period of wholesale dna synthesis during which the cell replicates its genetic content; This is done by enzymes called dna polymerases. Finally, the g 2 phase, also called the second gap. Events that occur prior to. Web in the s phase (synthesis phase), dna replication results in the formation of two identical copies of each. An important part of the cell cycle is cell division, the process whereby a cell is replicated to form either two daughter cells, through the. Web when expressed during s phase, 2cscc1 nc can generate cds but not when expressed only transiently during the previous g2/m phase. Finally, the g 2 phase, also called the second gap. This is done. The cell synthesizes a complete copy of the dna in its nucleus. An important part of the cell cycle is cell division, the process whereby a cell is replicated to form either two daughter cells, through the. Web in the s phase (synthesis phase), dna replication results in the formation of two identical copies of each chromosome—sister chromatids—that are firmly. It is the time from the formation of a cell from its parent cell until its division into its daughter cells. Web s phase is the period of wholesale dna synthesis during which the cell replicates its genetic content; Web the s phase is the second phase of interphase, during which the dna of the chromosomes is replicated. Web a). B) each gamete receives one member of each pair of homologous. Events that occur prior to. An important part of the cell cycle is cell division, the process whereby a cell is replicated to form either two daughter cells, through the. Web after chromosome condensation, the chromosomes condense to form compact structures (still made up of two chromatids). Prophase, metaphase,. Events that occur prior to. It is the time from the formation of a cell from its parent cell until its division into its daughter cells. Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Web as the two daughter dna strands are produced from the chromosomal dna during s phase, these daughter strands recruit additional histones and other proteins to form the. Web. Web a) gametes receive one copy of each member of each pair of homologous chromosomes. Contributions from histone deposition, dna replication and the cell division cycle. Web s phase is the period of wholesale dna synthesis during which the cell replicates its genetic content; Web after chromosome condensation, the chromosomes condense to form compact structures (still made up of two. Web when expressed during s phase, 2cscc1 nc can generate cds but not when expressed only transiently during the previous g2/m phase. It is the time from the formation of a cell from its parent cell until its division into its daughter cells. B) each gamete receives one member of each pair of homologous. Web chromatin assembly during s phase: The cell grows larger and organelles are copied. Some textbooks list five, breaking prophase into an early phase (called prophase) and a. Web s phase is the period of wholesale dna synthesis during which the cell replicates its genetic content; Web a) gametes receive one copy of each member of each pair of homologous chromosomes. The cell cycle encompasses the whole life of a cell from birth through to its death. The cell synthesizes a complete copy of the dna in its nucleus. Web as the two daughter dna strands are produced from the chromosomal dna during s phase, these daughter strands recruit additional histones and other proteins to form the. An important part of the cell cycle is cell division, the process whereby a cell is replicated to form either two daughter cells, through the. Web during the interphase (s phase) of cell division, eukaryote chromosomes present in the nucleus are replicated, and two identical copies of each chromosome are. Cohesion between sister chromatids is established. Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Web after chromosome condensation, the chromosomes condense to form compact structures (still made up of two chromatids). Web the s phase is the second phase of interphase, during which the dna of the chromosomes is replicated. Web mitosis consists of four basic phases: The events of s phase are intimately linked to chromosome structure. During interphase (g1 + s + g2), chromosomes are fully or partially.Cell cycle NC DNA Day Blog
What does the nucleus look like in S phase of Meiosis? Biology Stack
S Phase (Interphase) — Overview & Diagrams Expii
Mitotic chromosome segregation. Chromosomes are duplicated during S
Cell Division
Cell Division Types, Stages & Processes Plantlet
Linkage and (Part 1) Chromosomal Theory, Linkage
Chromosome Diagrams 101 Diagrams
cell cycle Chromosomal structures in S phase and Prophase Biology
3.3 Meiosis Biology 2016
Related Post: