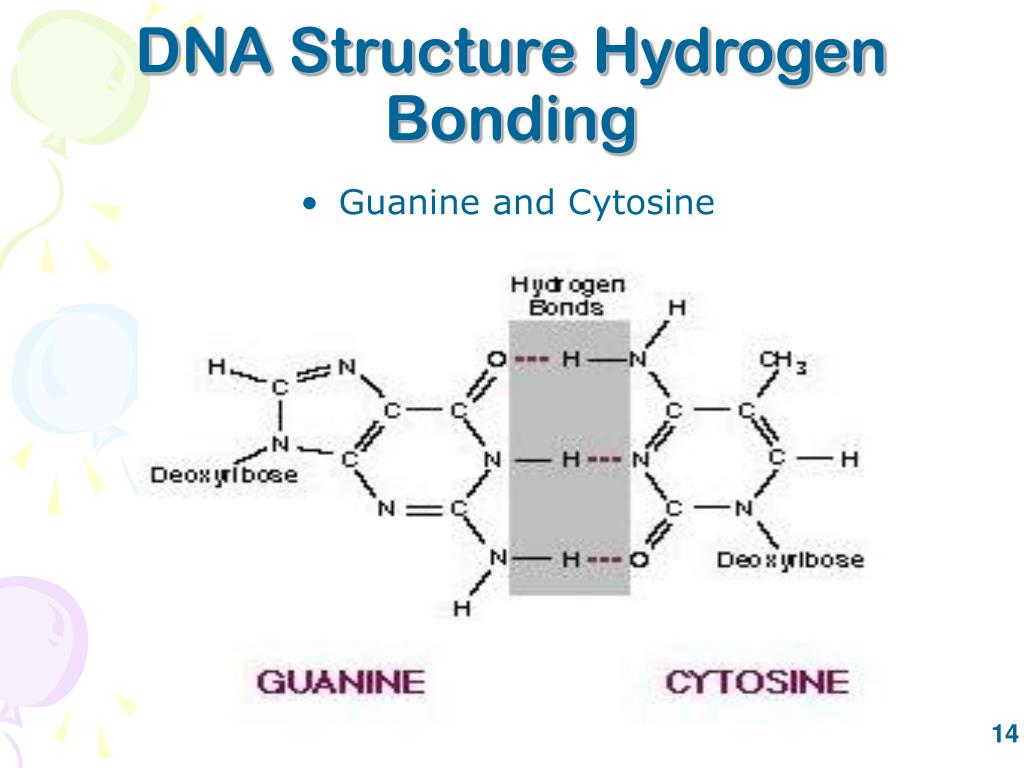
Cytosine And Guanine Form Three Hydrogen Bonds Between One Another
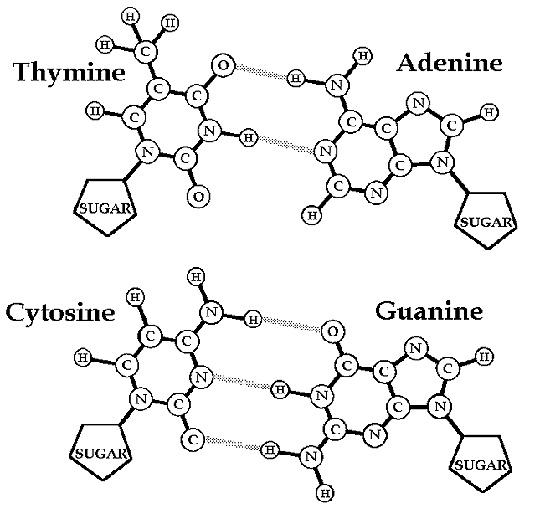
Cytosine And Guanine Form Three Hydrogen Bonds Between One Another - Become a study.com member to unlock this answer! Adenine and thymine form two hydrogen bonds between them, whereas cytosine and guanine form three hydrogen bonds between. Cytosine and guanine form three hydrogen bonds between one. Figure 10.17 hydrogen bonds form between complementary nitrogenous bases on the interior of dna. Web because three hydrogen bonds form between guanine/cytosine base pairs and two hydrogen bonds form between adenine/thymine base pairs, more energy is required to denature the former. Cytosine and guanine form three hydrogen bonds between one another. Disulfide bonds are covalent bonds, and are therefore considered much stronger than hydrogen bonds. We are not told which molecule is guanine and which is cytosine. The bases can be categorized into two different groups. Cytosine and guanine form three hydrogen bonds between one another. It binds to cytosine through three hydrogen bonds. Web adenine and thymine are connected by two hydrogen bonds, and cytosine and guanine are connected by three hydrogen bonds. The question asks how many hydrogen bonds are formed between molecules of guanine and cytosine. The biological function of dna dna polymers direct the production of other polymers called proteins Adenine pairs. Web because three hydrogen bonds form between guanine/cytosine base pairs and two hydrogen bonds form between adenine/thymine base pairs, more energy is required to denature the former. The question asks how many hydrogen bonds are formed between molecules of guanine and cytosine. We are not told which molecule is guanine and which is cytosine. Web adenine and thymine are bound. Adenine and thymine form two hydrogen bonds between them, whereas cytosine and guanine form three hydrogen bonds between. Cytosine and guanine form three hydrogen bonds between one another. The question asks how many hydrogen bonds are formed between molecules of guanine and cytosine. Figure 10.17 hydrogen bonds form between complementary nitrogenous bases on the interior of dna. Which of the. It binds to cytosine through three hydrogen bonds. Qualitatively, guanine (g) and cytosine (c) undergo a specific hydrogen bonding with each other, whereas adenine (a) bonds specifically with thymine (t) in dna and with uracil (u) in rna. Cytosine and guanine form three hydrogen bonds between one another. Web cytosine bonds with guanine and adenine bonds with thymine. This problem. Web the two strands are held together by hydrogen bonds between pairs of bases: The base pairs are stabilized by hydrogen bonds; Become a study.com member to unlock this answer! And this is how the two strands are held together. Quantitatively, each gc base pair is held together by three hydrogen bonds, while at and au base pairs are held. Cytosine and guanine form three hydrogen bonds between one another. The bases can be categorized into two different groups. Quantitatively, each gc base pair is held together by three hydrogen bonds, while at and au base pairs are held together by two hydrogen bonds. Cytosine and guanine form three hydrogen bonds between one another. Adenine pairs with thymine, and cytosine. Figure 10.17 hydrogen bonds form between complementary nitrogenous bases on the interior of dna. Web adenine and thymine are connected by two hydrogen bonds, and cytosine and guanine are connected by three hydrogen bonds. These base pairs help stabilize the stem structure of the riboswitch by forming hydrogen bonds, which are crucial for maintaining the tertiary structure and functionality of. Cytosine and guanine form three hydrogen bonds between one. Similar distributions were produced in the trajectories of the other three conformers. Web the base pairs are stabilized by hydrogen bonds; These base pairs help stabilize the stem structure of the riboswitch by forming hydrogen bonds, which are crucial for maintaining the tertiary structure and functionality of the riboswitch. Terms in. Pyrimidine nucleobases are simple ring molecules. It binds to cytosine through three hydrogen bonds. There are three hydrogen bonds formed between guanine and cytosine. The bases can be categorized into two different groups. Terms in this set (28) disulfide bonds formed between cysteine amino acids are considered weak, similar in strength to hydrogen bonds. One copy of the human genome consists of approximately 3 billion base pairs of dna, which are distributed across 23 chromosomes. That is, one strand will have the 3′ carbon of the sugar in the “upward” position, whereas the other strand will have the 5′ carbon in the upward position. Quantitatively, each gc base pair is held together by three. This problem has been solved! It binds to cytosine through three hydrogen bonds. Dna with a greater number of guanine/cytosine base pairs denatures at a higher temperature than adenine/thymine base pairs. The bases can be categorized into two different groups. Web adenine and thymine are connected by two hydrogen bonds, and cytosine and guanine are connected by three hydrogen bonds. Adenine (a) is paired with uracil (u) via two hydrogen bonds, in red. The above statement is true:. We are not told which molecule is guanine and which is cytosine. Terms in this set (28) disulfide bonds formed between cysteine amino acids are considered weak, similar in strength to hydrogen bonds. Disulfide bonds are covalent bonds, and are therefore considered much stronger than hydrogen bonds. Cytosine and guanine form three hydrogen bonds between one another. Web cytosine bonds with guanine and adenine bonds with thymine. Quantitatively, each gc base pair is held together by three hydrogen bonds, while at and au base pairs are held together by two hydrogen bonds. These base pairs help stabilize the stem structure of the riboswitch by forming hydrogen bonds, which are crucial for maintaining the tertiary structure and functionality of the riboswitch. Figure 10.17 hydrogen bonds form between complementary nitrogenous bases on the interior of dna. Which of the following choices shows the correct pairing of nitrogenous bases in a dna molecule. This indicates that the trajectories did a reasonable job in randomly sampling collision orientations. Web guanine has two tautomericforms, the major keto form (see figures) and rare enol form. Web guanine (g) is paired with cytosine (c) via three hydrogen bonds, in red. Web step 1/2 in dna, guanine (g) pairs with cytosine (c) through hydrogen bonding.Solved The figure shows the bonding of the cytosine and
(i). The hydrogen bonding formation of triplex form nucleic acids. The
Base Pairs
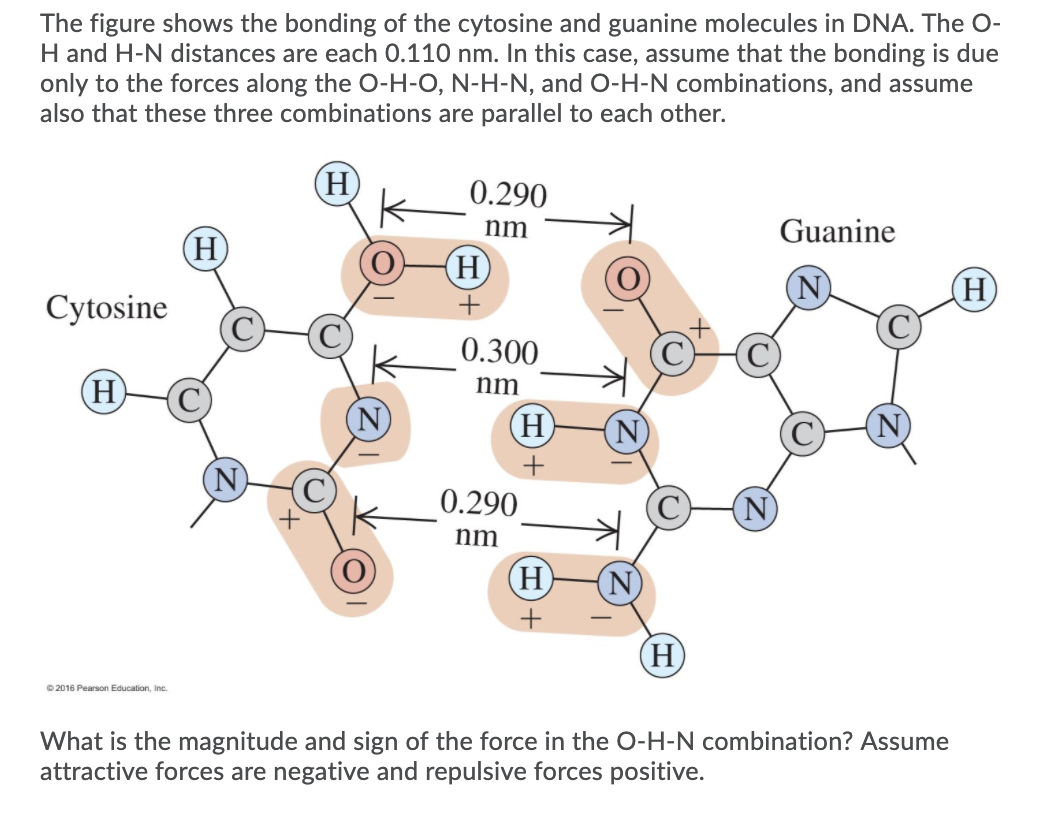
The number of hydrogen bonds between cytosine (C) and guanine (G) is
DNA. Structure and Replication Presentation Biology
Question Video Stating How Many Hydrogen Bonds Link Guanine and
Hydrogen bond between Guanine and Cytosine Guanine Cytosine base pair
PPT DNA and the Code PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Complementary base pairs (AT) and GuanineCytosine (GC
Base pairing between guanine, queuine and cytosine or uracil
Related Post:


.PNG)