Cos In Complex Form
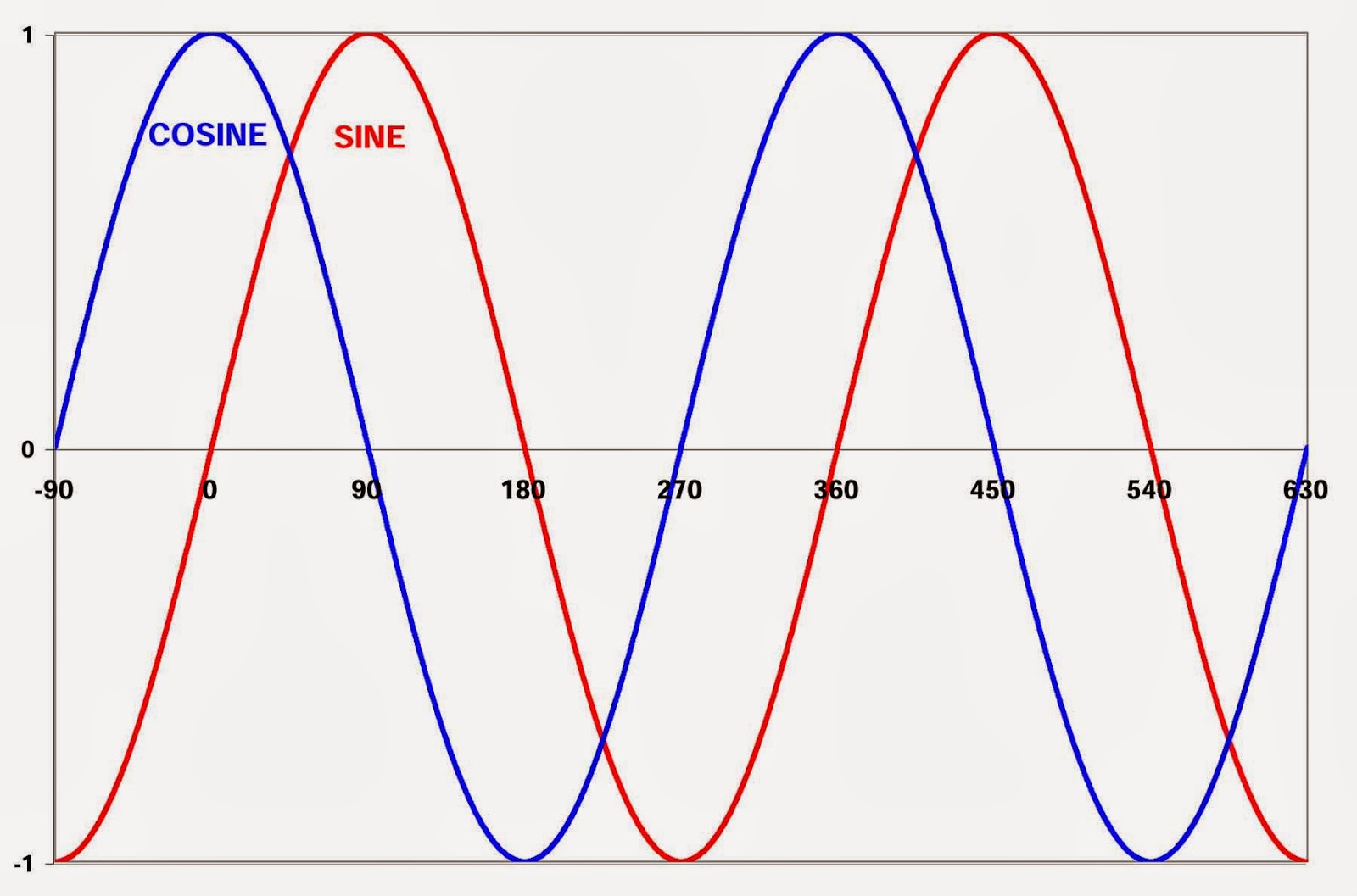
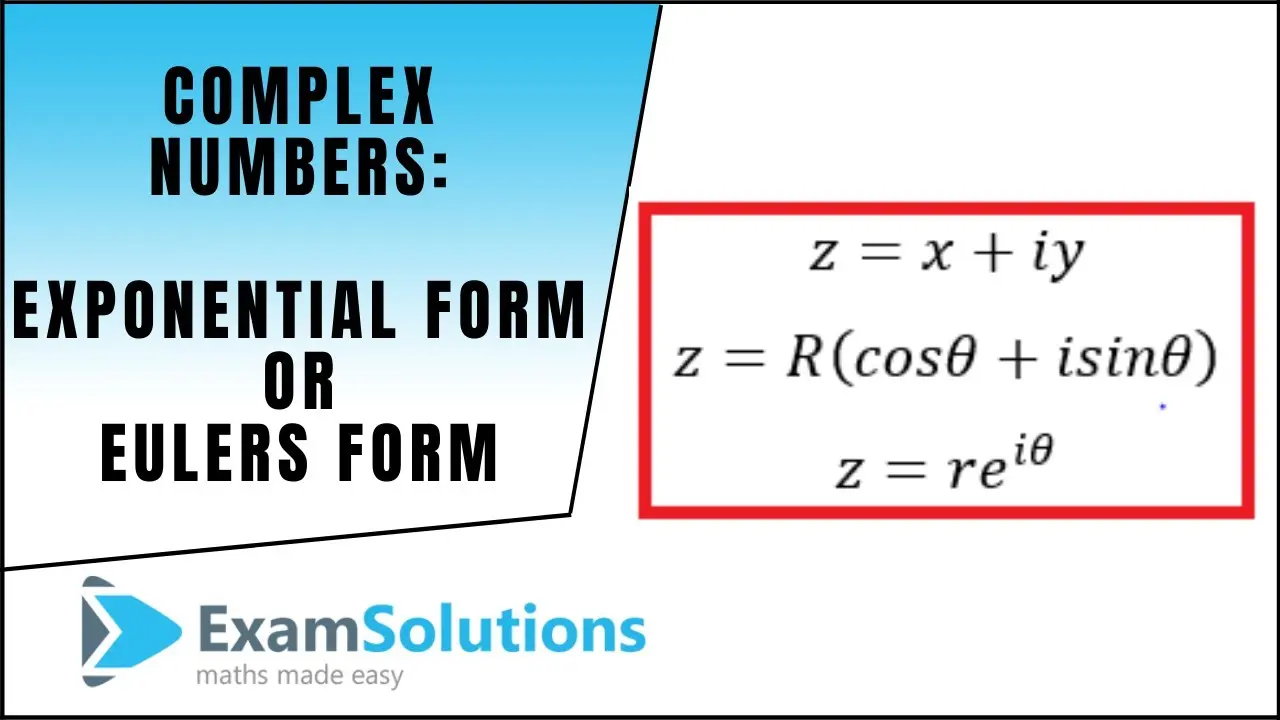
Cos In Complex Form - Web the trigonometric functions can be defined for complex variables as well as real ones. Web to write complex numbers in polar form, we use the formulas \(x=r \cos \theta\), \(y=r \sin \theta\), and \(r=\sqrt{x^2+y^2}\). Enter the complex number for which you want to find the trigonometric form. Web for any complex number. Eiπ + 1 = 0. We review the steps for conversion below. So what exactly is euler’s. Web this page is about the one used in complex numbers) first, you may have seen the famous euler's identity: It is important to be able to convert from rectangular to trigonometric form of complex numbers and from trigonometric to rectangular form. Web z = r(cos(θ) + isin(θ)). We review the steps for conversion below. Alternate proofs of de moivre’s theorem and trigonometric additive identities. Web the sine and cosine of a complex variable \(z\) are defined as follows: Trigonometric or polar form of a complex number (r cis θ) An easier procedure, however, is to use the identities from the previous section: Complex number trigonometric form calculator. Web trigonometric form of complex numbers a convenient form for numbers in the complex plane, other than rectangular form, is the trigonometric form of complex numbers. Web complex exponential function. See example \(\pageindex{4}\) and example \(\pageindex{5}\). The product of two numbers with absolute values r 1 and r 2 and angles θ 1 and θ. It is important to be able to convert from rectangular to trigonometric form of complex numbers and from trigonometric to rectangular form. Let a a and b b be real numbers. We review the steps for conversion below. It seems absolutely magical that such a neat equation combines: Functions ( inverse) generalized trigonometry. Web euler’s formula for complex exponentials. Exp(a + ib) = exp(a) exp(ib) = exp(a)(cos b + i sin b) the trigonmetric addition formulas (equation 1) are equivalent to the usual property of the exponential, now extended to any complex numbers c1 = a1+ib1 and c2 = a2 + ib2, giving. Then, \(z=r(\cos \theta+i \sin \theta)\). Complex number trigonometric form calculator.. Depending on what you need to do with your complex numbers, the trigonometric form can be very useful or very thorny. This formula can be interpreted as saying that the function e iφ is a unit complex number, i.e., it traces out the unit circle in the complex plane as φ. Cos cos denotes the cosine function ( real and. Web sine and cosine are used to connect the real and imaginary parts of a complex number with its polar coordinates (r, φ): Z = r ( cos ( φ ) + i sin ( φ ) ) {\displaystyle z=r(\cos(\varphi )+i\sin(\varphi ))} Today, the most common versions of these abbreviations are sin for sine, cos for cosine, tan. For example, let z1 = 1 + i, z2 = √3 +i and z3 = −1 +i√3. Let a a and b b be real numbers. Cos(a + bi) = cos a cosh b − i sin a sinh b cos. Cos cos denotes the cosine function ( real and complex) Z = r ( cos ( φ ). Web euler's formula e iφ = cos φ + i sin φ illustrated in the complex plane. It seems absolutely magical that such a neat equation combines: The complex number trigonometric form calculator converts complex numbers to their trigonometric form. Enter the complex number for which you want to find the trigonometric form. The trigonometric form of complex numbers uses. Web z = r(cos(θ) + isin(θ)). Alternate proofs of de moivre’s theorem and trigonometric additive identities. The other four trigonometric functions are defined in terms of the sine and cosine functions with the following relations: It is important to be able to convert from rectangular to. Then, \(z=r(\cos \theta+i \sin \theta)\). Eit = cos t + i sin t. Web trigonometric form of complex numbers a convenient form for numbers in the complex plane, other than rectangular form, is the trigonometric form of complex numbers. Complex logarithm and general complex exponential. Z = r ( cos ( φ ) + i sin ( φ ) ) {\displaystyle z=r(\cos(\varphi )+i\sin(\varphi. When we write z in the form given in equation 5.2.1 :, we say that z is written in trigonometric form (or polar form). Trigonometric or polar form of a complex number (r cis θ) Polar system and complex numbers. Cos ( i x) = cosh (x) sin ( i x) = i sinh (x) One way is to use the power series for sin (x) and cos (x), which are convergent for all real and complex numbers. Web trigonometric form of complex numbers a convenient form for numbers in the complex plane, other than rectangular form, is the trigonometric form of complex numbers. All the same rules and procedures for converting points represented by a real pairs of numbers in the rectangular plane apply to converting complex numbers into polar form. Web the sine and cosine of a complex variable \(z\) are defined as follows: The trigonometric form of complex numbers uses the modulus and an angle to describe a complex number’s location. Integrals ( inverse functions) derivatives. Alternate proofs of de moivre’s theorem and trigonometric additive identities. It seems absolutely magical that such a neat equation combines: Let i i be the imaginary unit. For example, let z1 = 1 + i, z2 = √3 +i and z3 = −1 +i√3. = a + ib one can apply the exponential function to get. The complex number trigonometric form calculator converts complex numbers to their trigonometric form. Z = r ( cos ( φ ) + i sin ( φ ) ) {\displaystyle z=r(\cos(\varphi )+i\sin(\varphi ))} Web euler's formula e iφ = cos φ + i sin φ illustrated in the complex plane. See example \(\pageindex{4}\) and example \(\pageindex{5}\). This form is really useful for multiplying and dividing complex numbers, because of their special behavior:Complex Variables Trigonometric Identity Proof sin^2(z) + cos^2(z) = 1
FileSine Cosine Exponential qtl1.svg Wikimedia Commons Physics and
Example 15 Prove cos (pi/4 + x) + cos (pi/4 x) = root 2 cos x
Enjoy Revit Trigonometric Function
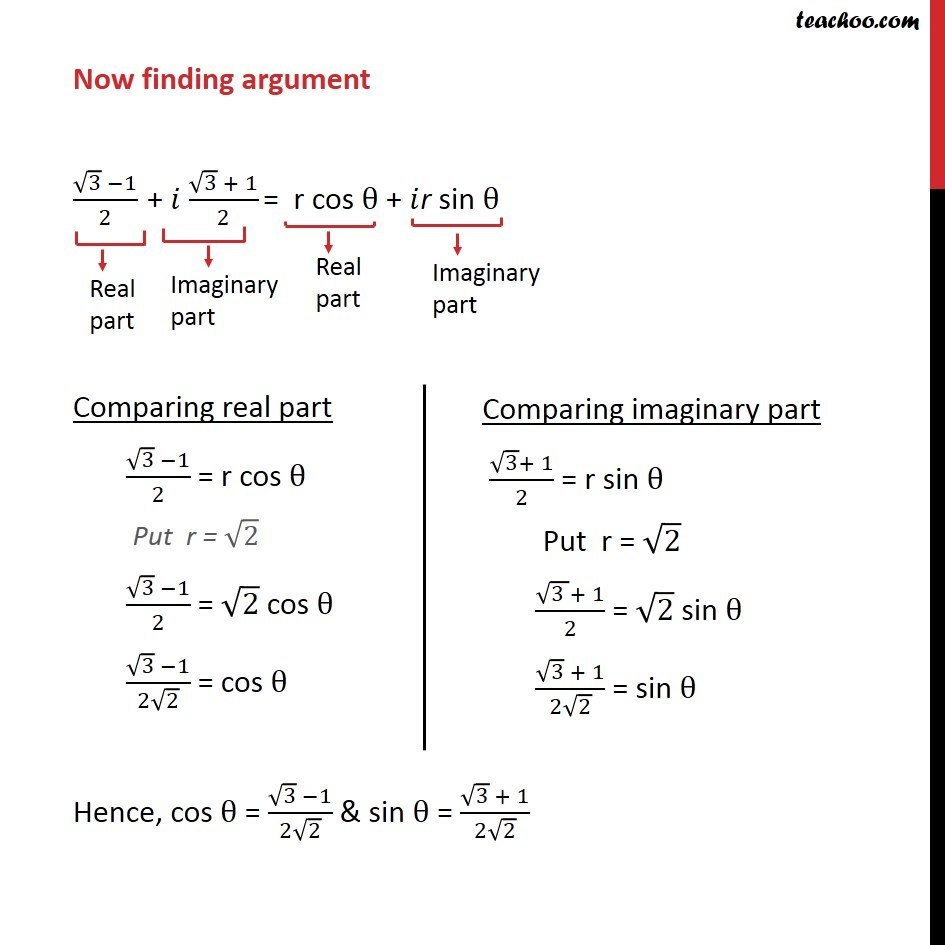
Example 16 Convert z = (i 1)/ cos pi/3 + i sin pi/3 Examples
CiS Notation for Trigonometric Form of a Complex Number YouTube
Complex Numbers 4/4 Cos and Sine to Complex Exponential YouTube
Question 8 Convert z = (i 1)/ cos pi/3 + i sin pi/3 Examples
Complex number notation forms trigonometric, exponential Healthy
Pin on Math Videos
Related Post: