Chomsky Normal Form Examples
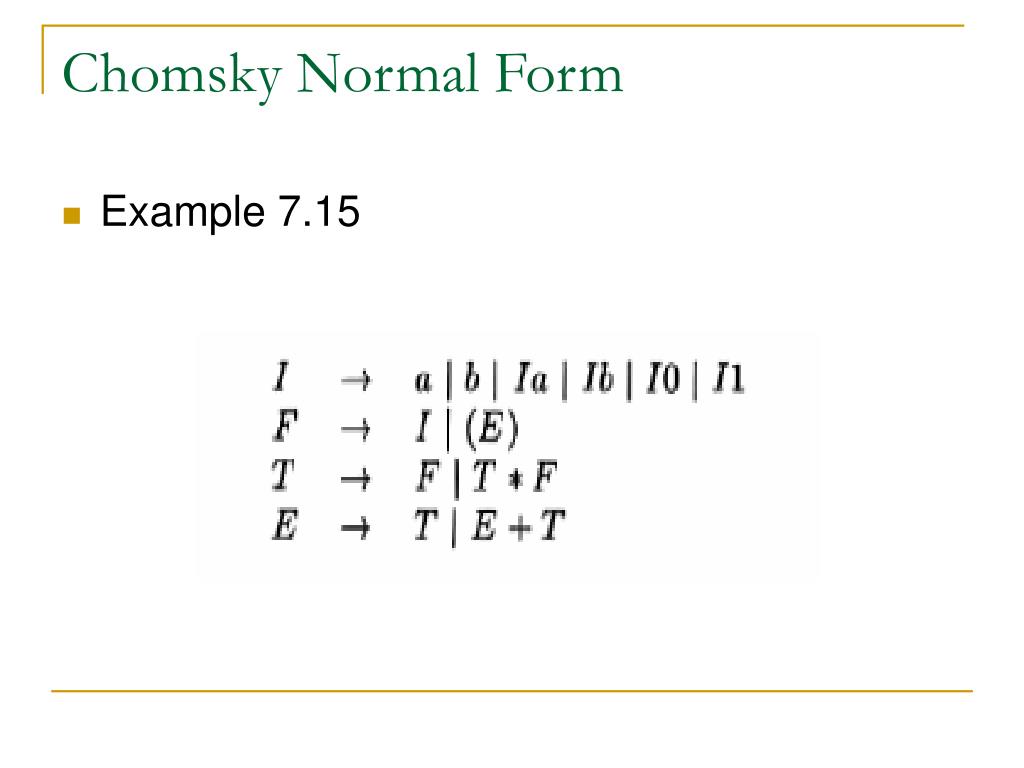
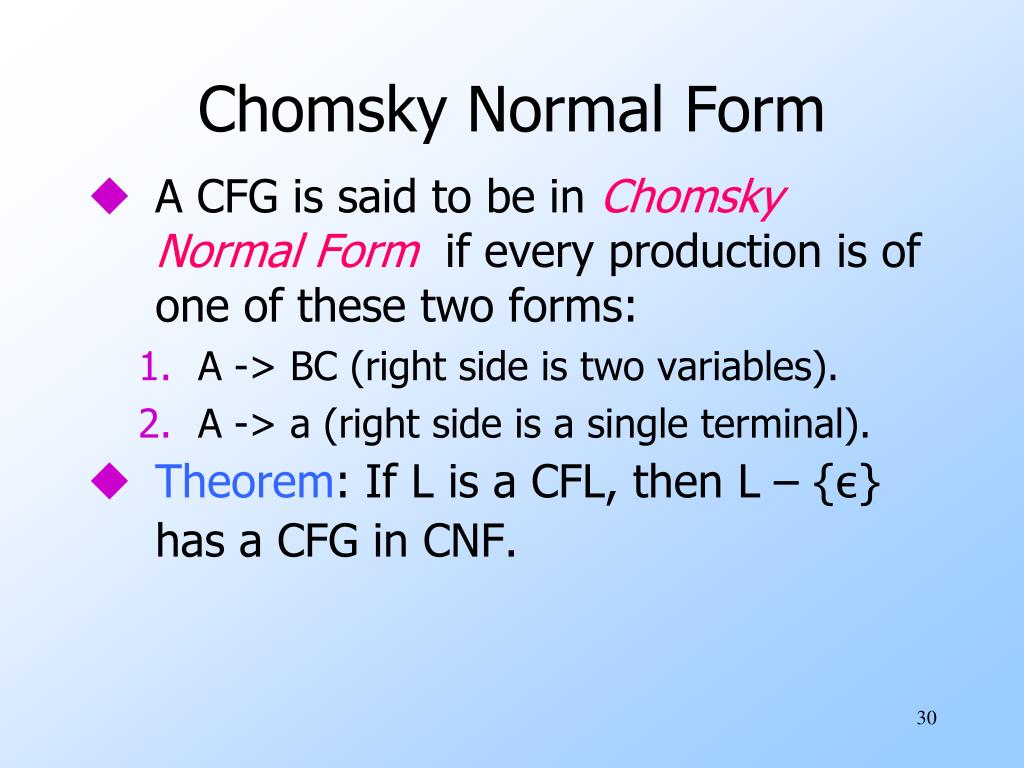
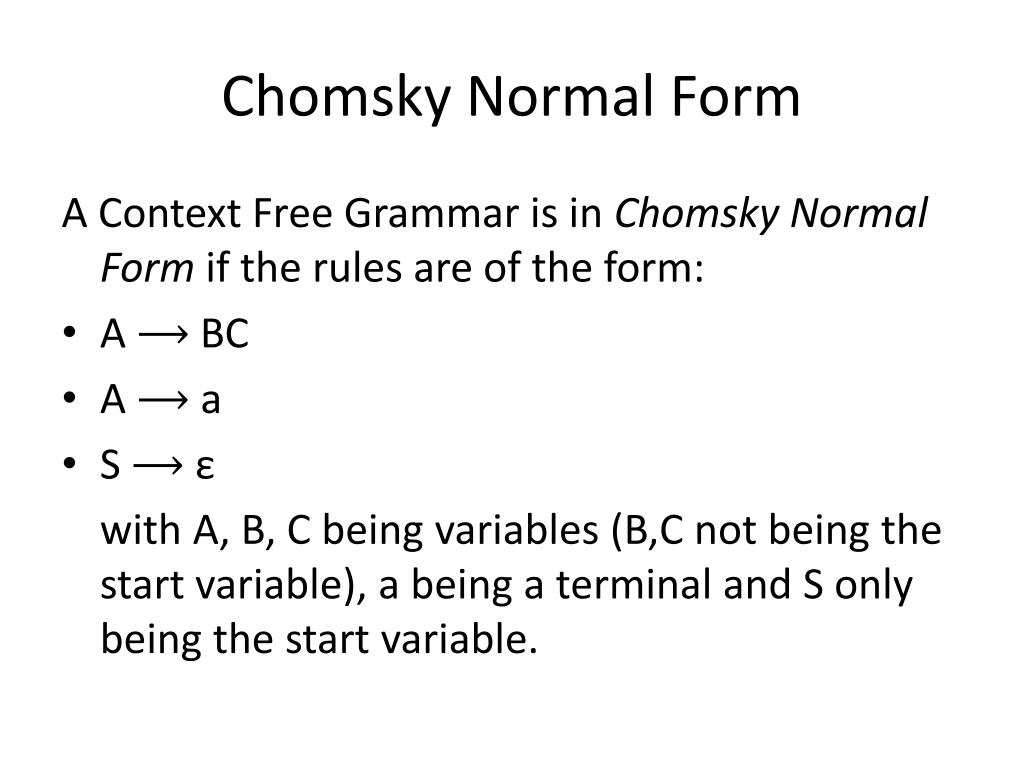
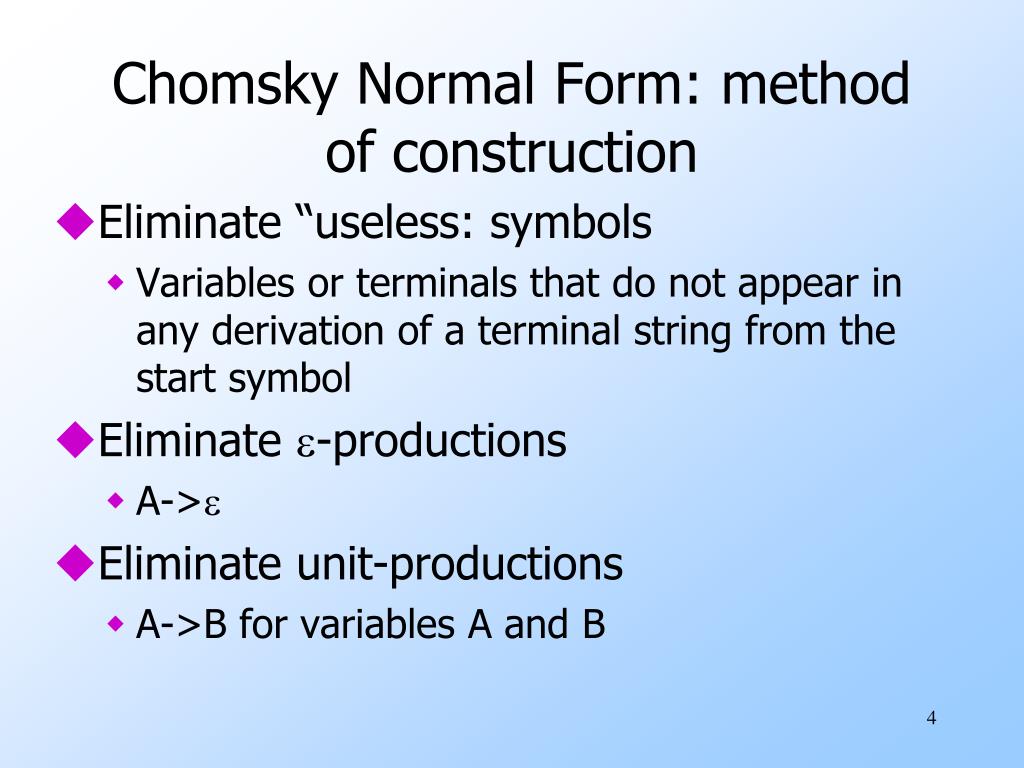
Chomsky Normal Form Examples - A→bc a→a •b and c may not be the start variable •only the start variable can transition to 𝜀 •each variable goes to two other variables or two one terminal •the start variable may not point back to the start variable 3 So, the grammar takes the following form: S, where s is the starting variable of the original grammar. C (where a, b, c are arbitrary variables and c an arbitrary symbol). Sa j b (if language contains , then we allow s ! Web a context free grammar (cfg) is in chomsky normal form (cnf) if all production rules satisfy one of the following conditions: Algorithm to convert into chomsky normal form − step 1 − if the start symbol s occurs on some right side, create a new start symbol s’ and a new production s’→ s. 3 for one thing, you can use the cyk algorithm on chomsky normal form grammars share improve this answer follow answered feb 3, 2011 at 8:25 jetru 1,974 4 17 24 if you have a grammar in chomsky normal form can you deduce the no of steps required to parse a given string ? Cfg is in chomsky normal form if every rule takes form: Remove epsilon rules there are no such rules in this cfg. C (where a, b, c are arbitrary variables and c an arbitrary symbol). Sa j b (if language contains , then we allow s ! A→bc a→a •b and c may not be the start variable •only the start variable can transition to 𝜀 •each variable goes to two other variables or two one terminal •the start variable may not. So, the grammar takes the following form: A→bc a→a •b and c may not be the start variable •only the start variable can transition to 𝜀 •each variable goes to two other variables or two one terminal •the start variable may not point back to the start variable 3 where s is start symbol, and forbid on rhs.) why chomsky. Web what is the structure of chomsky normal form? S, where s is the starting variable of the original grammar. Algorithm to convert into chomsky normal form − step 1 − if the start symbol s occurs on some right side, create a new start symbol s’ and a new production s’→ s. 3 for one thing, you can use. Remove epsilon rules there are no such rules in this cfg. 3 for one thing, you can use the cyk algorithm on chomsky normal form grammars share improve this answer follow answered feb 3, 2011 at 8:25 jetru 1,974 4 17 24 if you have a grammar in chomsky normal form can you deduce the no of steps required to. Web 4 answers sorted by: A→bc a→a •b and c may not be the start variable •only the start variable can transition to 𝜀 •each variable goes to two other variables or two one terminal •the start variable may not point back to the start variable 3 The example grammar (top) and its chomsky normal form (bottom) the following grammar,. The example grammar (top) and its chomsky normal form (bottom) the following grammar, with start symbol expr , describes a simplified version of the set of all syntactical valid arithmetic expressions in programming languages like c or algol60. S, where s is the starting variable of the original grammar. Web 4 answers sorted by: Web what is the structure of. Web abstract syntax tree of the arithmetic expression a^2+4*b wrt. Introduce a new starting variable s0 and a rule s0 ! S, where s is the starting variable of the original grammar. The example grammar (top) and its chomsky normal form (bottom) the following grammar, with start symbol expr , describes a simplified version of the set of all syntactical. Web abstract syntax tree of the arithmetic expression a^2+4*b wrt. C (where a, b, c are arbitrary variables and c an arbitrary symbol). So, the grammar takes the following form: where s is start symbol, and forbid on rhs.) why chomsky normal form? The example grammar (top) and its chomsky normal form (bottom) the following grammar, with start symbol expr. Algorithm to convert into chomsky normal form − step 1 − if the start symbol s occurs on some right side, create a new start symbol s’ and a new production s’→ s. Introduce a new starting variable s0 and a rule s0 ! Step 2 − remove null. A→bc a→a •b and c may not be the start variable. Give all the intermediate steps. Grammar where every production is either of the form ! Introduce a new starting variable s0 and a rule s0 ! Cfg is in chomsky normal form if every rule takes form: Remove epsilon rules there are no such rules in this cfg. Step 2 − remove null. Web 4 answers sorted by: In the above example, we add the new rule s0 ! Algorithm to convert into chomsky normal form − step 1 − if the start symbol s occurs on some right side, create a new start symbol s’ and a new production s’→ s. Web abstract syntax tree of the arithmetic expression a^2+4*b wrt. A→bc a→a •b and c may not be the start variable •only the start variable can transition to 𝜀 •each variable goes to two other variables or two one terminal •the start variable may not point back to the start variable 3 S, where s is the starting variable of the original grammar. Web a context free grammar (cfg) is in chomsky normal form (cnf) if all production rules satisfy one of the following conditions: Sa j b (if language contains , then we allow s ! Web what is the structure of chomsky normal form? Introduce a new starting variable s0 and a rule s0 ! The example grammar (top) and its chomsky normal form (bottom) the following grammar, with start symbol expr , describes a simplified version of the set of all syntactical valid arithmetic expressions in programming languages like c or algol60. Give all the intermediate steps. Grammar where every production is either of the form ! Cfg is in chomsky normal form if every rule takes form: Web 12 convert the grammar below into chomsky normal form. 3 for one thing, you can use the cyk algorithm on chomsky normal form grammars share improve this answer follow answered feb 3, 2011 at 8:25 jetru 1,974 4 17 24 if you have a grammar in chomsky normal form can you deduce the no of steps required to parse a given string ? where s is start symbol, and forbid on rhs.) why chomsky normal form? Remove epsilon rules there are no such rules in this cfg. C (where a, b, c are arbitrary variables and c an arbitrary symbol).PPT Chomsky Normal Form of CFG’s PowerPoint Presentation, free
PPT ContextFree Grammars Chomsky Normal Form PowerPoint
PPT Chapter 6 Simplification of CFGs and Normal Forms PowerPoint
PPT Normal forms for ContextFree Grammars PowerPoint Presentation
PPT Chomsky Normal Form of CFG’s PowerPoint Presentation, free
PPT Chomsky Normal Form PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
PPT ContextFree Grammars Chomsky Normal Form PowerPoint
PPT Chomsky Normal Form CYK Algorithm PowerPoint Presentation, free
PPT Chomsky Normal Form of CFG’s PowerPoint Presentation, free
Conversion of CFG to Chomsky Normal Form YouTube
Related Post: