Why Does Carbon Form Covalent Bonds
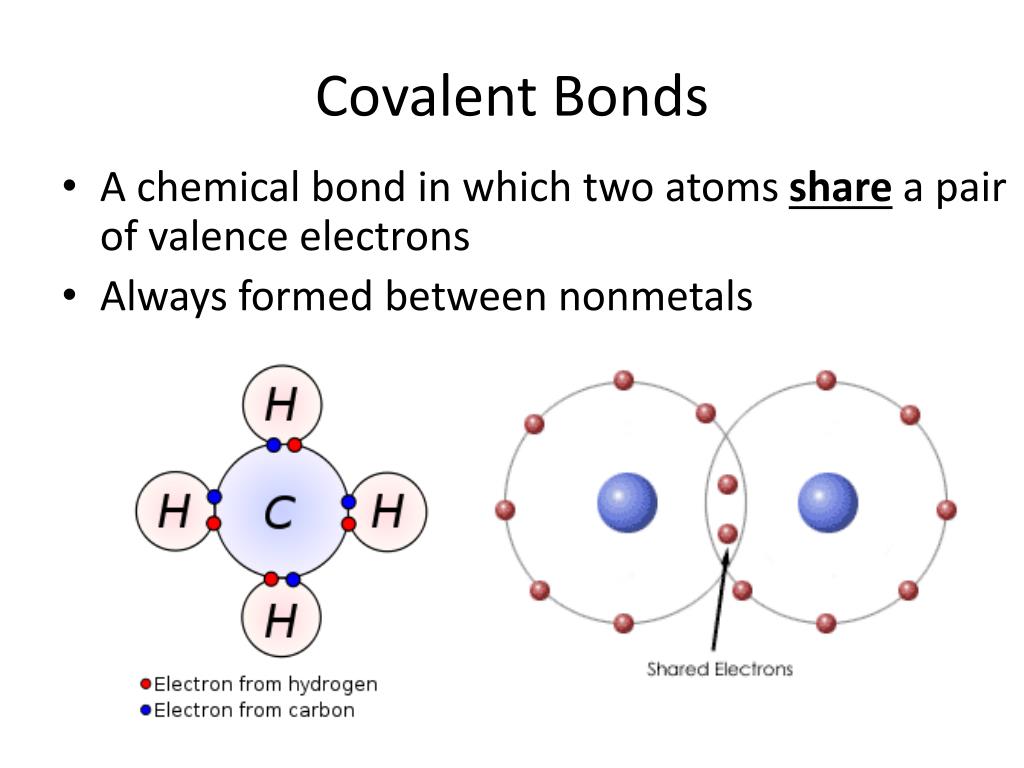
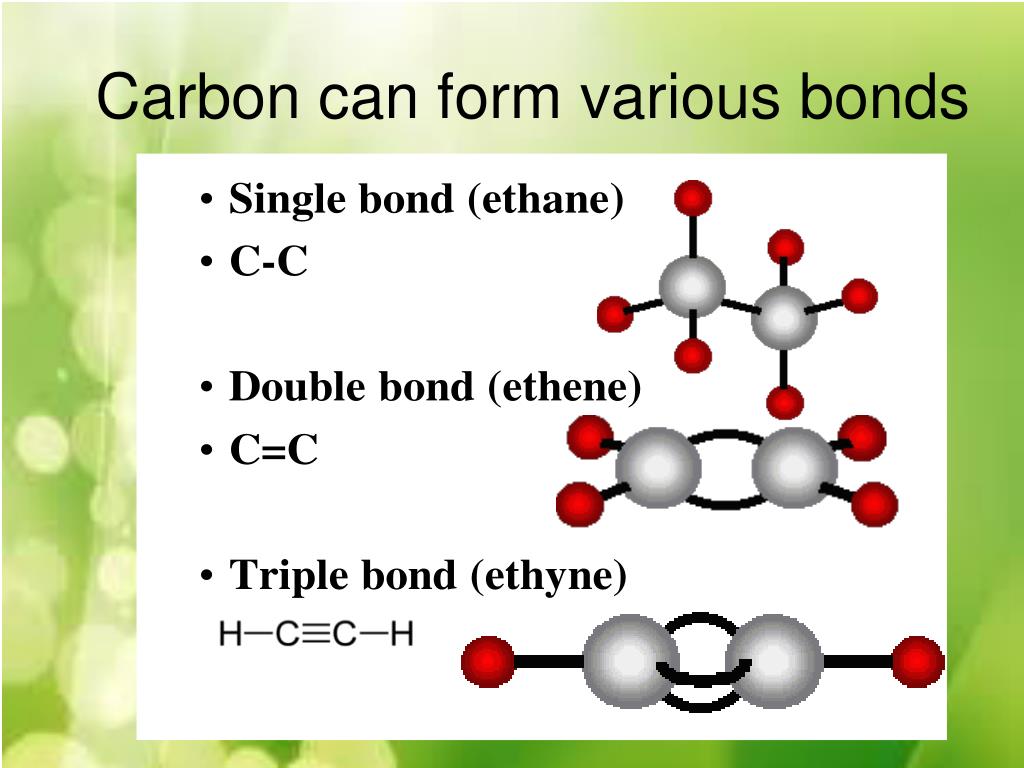
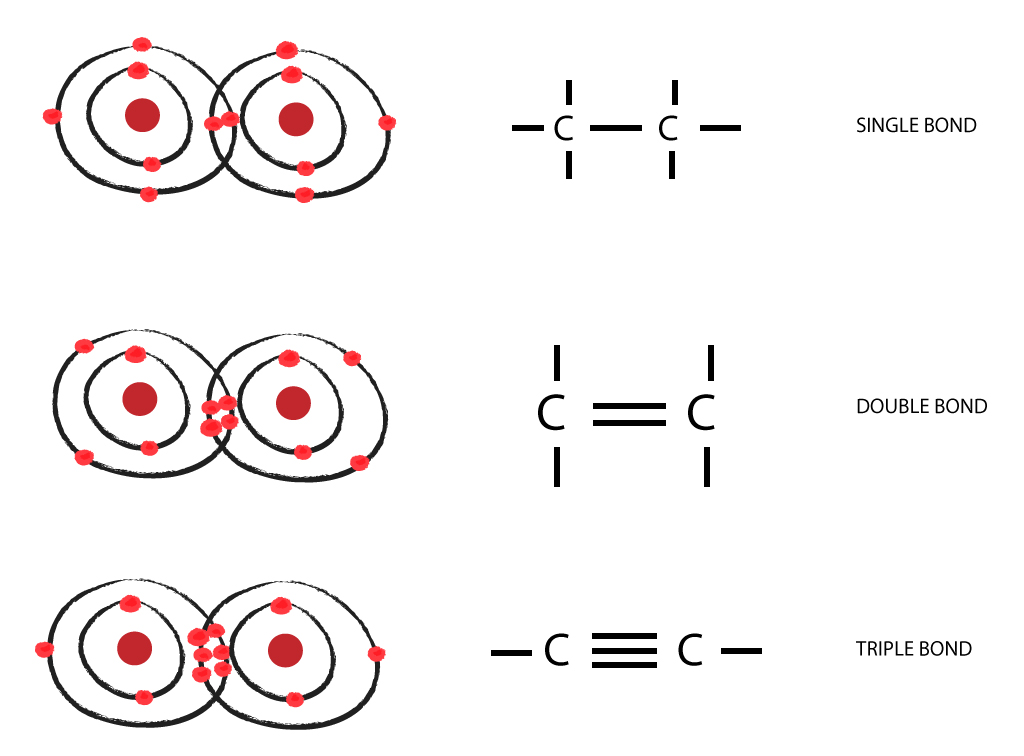
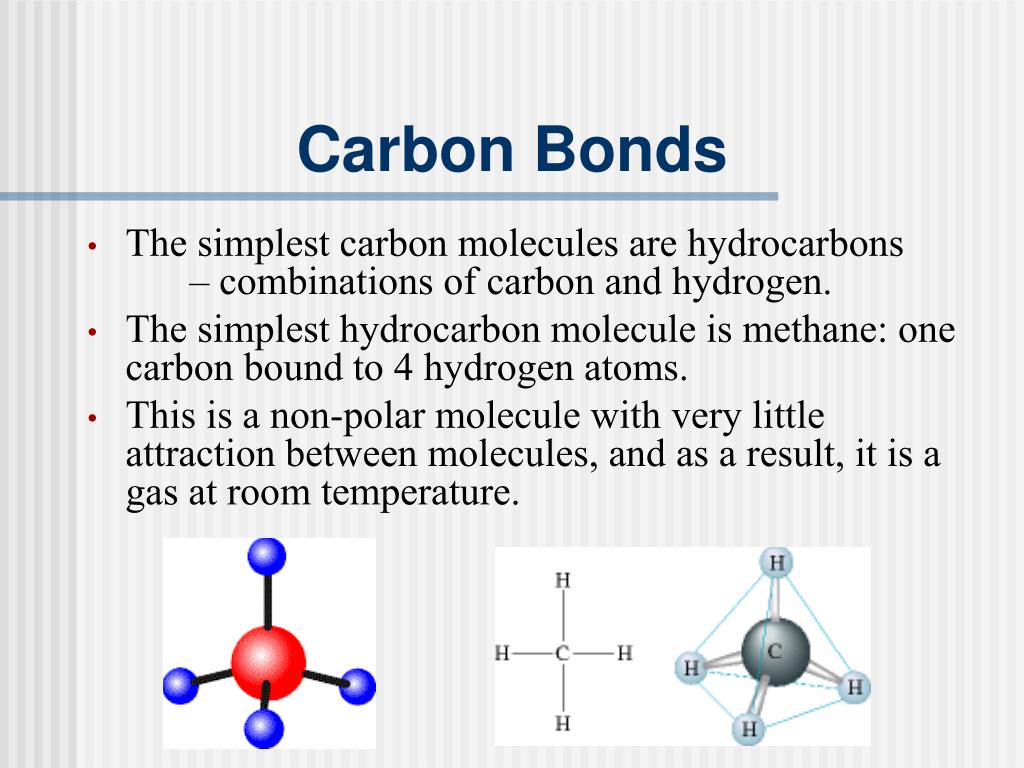
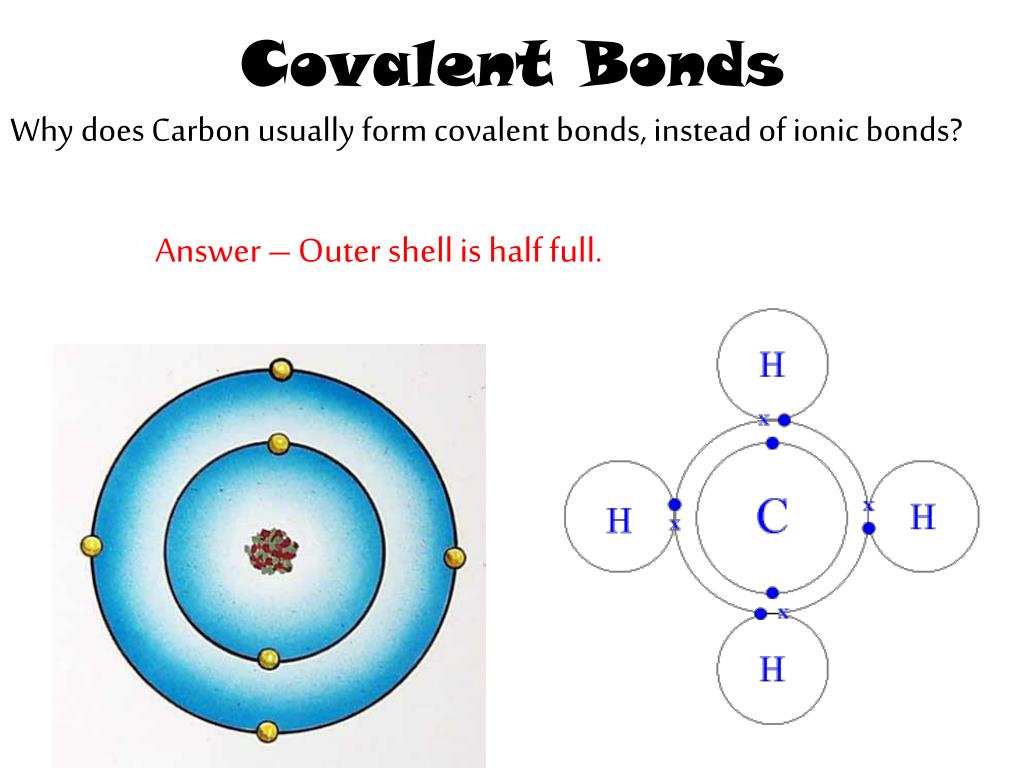
Why Does Carbon Form Covalent Bonds - Web the unique properties of carbon make it a central part of biological molecules. Web explain why carbon forms compound mainly by covalent bonds. A bond, that is, formed by sharing of electrons between the combining atoms is known as a covalent bond. Web one carbon atom forms four covalent bonds with four hydrogen atoms by sharing a pair of electrons between itself and each hydrogen (h) atom. There is only a small energy. The simplest carbon molecule is methane (ch 4 ), depicted here. Web why does carbon form covalent bonds? The number of bonds an element forms in a covalent compound is determined by the. Two atoms share a pair of electrons in a. Web a covalent bond is formed between two atoms by sharing electrons. Web we would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. The electrons involved are in the outer shells of the atoms. A bond, that is, formed by sharing of electrons between the combining atoms is known as a covalent bond. Web one carbon atom forms four covalent bonds with four hydrogen atoms by sharing. Each bond corresponds to a pair of shared electrons (one from carbon and one from hydrogen), giving carbon. With hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, and other heteroatoms. Web we would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Why does carbon form strong. There is only a small energy. The potential energy of two separate hydrogen atoms (right) decreases as. Web the unique properties of carbon make it a central part of biological molecules. Each bond corresponds to a pair of shared electrons (one from carbon and one from hydrogen), giving carbon. Web these four electrons can be gained by forming four covalent bonds, as illustrated here for carbon. Web carbon atoms may thus form bonds to as many as four other atoms. Chemical bonds between nonmetals are known as covalent bonds. Web why does carbon form covalent bonds? Carbon does not form ionic bonds because it has 4 valence electrons, half of an octet. In most cases, carbon shares electrons with other atoms. Web these four electrons can be gained by forming four covalent bonds, as illustrated here for carbon in ccl 4 (carbon tetrachloride) and silicon in sih 4 (silane). The number of bonds an element forms in a covalent compound is determined by the. Web if carbon forms 4 bonds rather than 2, twice as much energy is released and so. Carbon does not form ionic bonds because it has 4 valence electrons, half of an octet. For example, atomic number of. Each bond corresponds to a pair of shared electrons (one from carbon and one from hydrogen), giving carbon. With hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, and other heteroatoms. Web one carbon atom forms four covalent bonds with four hydrogen atoms by sharing. Web carbon atoms may thus form bonds to as many as four other atoms. In most cases, carbon shares electrons with other atoms. Web these four electrons can be gained by forming four covalent bonds, as illustrated here for carbon in ccl 4 (carbon tetrachloride) and silicon in sih 4 (silane). The simplest carbon molecule is methane (ch 4 ),. For example, atomic number of. Web the unique properties of carbon make it a central part of biological molecules. The most common type of bond formed by carbon is a covalent bond. The number of bonds an element forms in a covalent compound is determined by the. Web if carbon forms 4 bonds rather than 2, twice as much energy. The potential energy of two separate hydrogen atoms (right) decreases as. The number of bonds an element forms in a covalent compound is determined by the. Web explain why carbon forms compound mainly by covalent bonds. A bond, that is, formed by sharing of electrons between the combining atoms is known as a covalent bond. Is determined by the distance. Web these four electrons can be gained by forming four covalent bonds, as illustrated here for carbon in ccl 4 (carbon tetrachloride) and silicon in sih 4 (silane). The number of bonds an element forms in a covalent compound is determined by the. Chemical bonds between nonmetals are known as covalent bonds. Explain in brief two main reasons for carbon. The electrons involved are in the outer shells of the atoms. Web carbon can form four covalent bonds to create an organic molecule. Well, carbon can form up to four covalent bonds. Web explain why carbon forms compound mainly by covalent bonds. Carbon does not form ionic bonds because it has 4 valence electrons, half of an octet. Web we would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. With hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, and other heteroatoms. The simplest carbon molecule is methane (ch 4 ), depicted here. Web four covalent bonds can be formed by carbon. For example, in methane (ch 4 ), carbon forms covalent bonds with four hydrogen atoms. Web carbon atoms may thus form bonds to as many as four other atoms. They are important in the production of many man. The most common type of bond formed by carbon is a covalent bond. The valency of the carbon atom is 4. The potential energy of two separate hydrogen atoms (right) decreases as. With four valence electrons, carbon can covalently bond to oxygen, hydrogen, and nitrogen to. Web these four electrons can be gained by forming four covalent bonds, as illustrated here for carbon in ccl 4 (carbon tetrachloride) and silicon in sih 4 (silane). This is because carbon has 4 valence. Web the unique properties of carbon make it a central part of biological molecules. A bond, that is, formed by sharing of electrons between the combining atoms is known as a covalent bond.Four covalent bonds. Carbon has four valence electrons and here a
Chapter 8 Covalent Bonding Covalent bonding Usually forms
PPT Covalent Bonds PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6647183
Science class 10 Why carbon form covalent bonds YouTube
PPT Unit 1 Biochemistry The Chemistry of Life PowerPoint
Carbon to Carbon Single, Double & Triple Bonds Surfguppy
PPT Carbon Compounds PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2319022
PPT Biochemistry PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID89333
PPT 2.1 Nature of Matter PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
BONDING IN CARBON THE COVALENT BOND YouTube
Related Post: