Why Do Lipid Bilayers Form Spontaneously
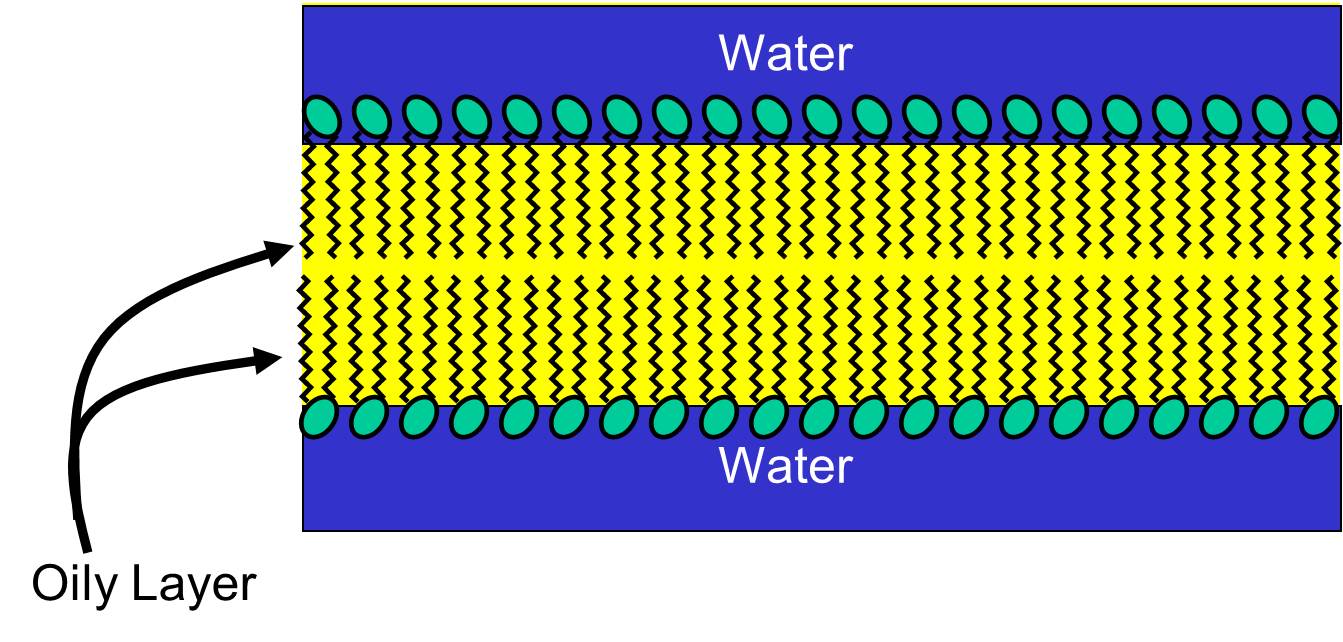
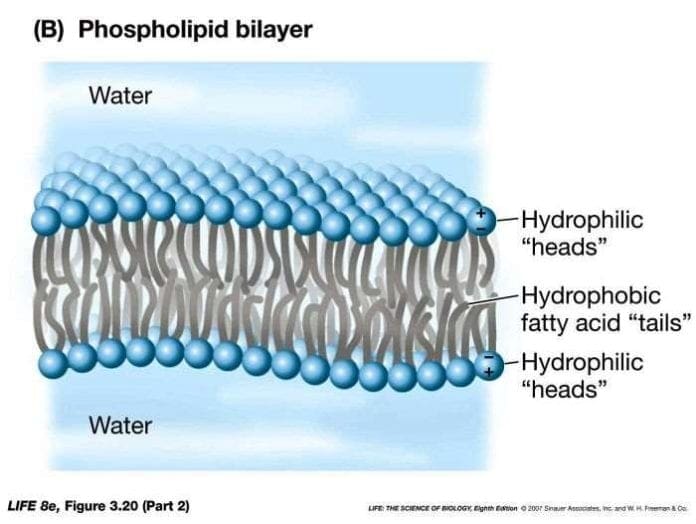
Why Do Lipid Bilayers Form Spontaneously - Web why do lipid bilayers form spontaneously? Web phospholipids spontaneously form various structures in aqueous solution, including lipid bilayers. Together, these observations suggested that there may be a. Two experiments in 1925 laid the groundwork to fill in this gap. Web the structure of the lipid bilayer explains its function as a barrier. Web why do lipid bilayers form spontaneously? Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like why do phospholipids spontaneously form bilayer structures, while oils form small droplets?, which. Web why do lipid bilayers form spontaneously? B) the process is exergonic. By measuring the capacitance of erythrocyte solutions, hugo fricke determined that the cell membrane was 3.3 nm thick. Together, these observations suggested that there may be a. Web why do lipid bilayers form spontaneously? Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like why do phospholipids spontaneously form bilayer structures, while oils form small droplets?, which. Web why do lipid bilayers form spontaneously? These are formed because the phospholipid tails are hydrophobic and the. However, under the right condition, single. By measuring the capacitance of erythrocyte solutions, hugo fricke determined that the cell membrane was 3.3 nm thick. Web additional experiments showed that lipids could spontaneously form a bilayer when mixed with water (figure 1). Web phospholipids spontaneously form various structures in aqueous solution, including lipid bilayers. Lipids are fats, like oil, that are. Web why does the lipid bilayer form spontaneously? Web why do lipid bilayers form spontaneously? C) the process leads to a huge decrease in entropy and no change in. However, under the right condition, single. Together, these observations suggested that there may be a. C) the process leads to a huge decrease in entropy and no change in. These are formed because the phospholipid tails are hydrophobic and the. Web it is the shape and the amphipatic nature of the phospholipid molecules that cause them to form bilayers spontaneously in aqueous solution. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like why do. Web it is the shape and the amphipatic nature of the phospholipid molecules that cause them to form bilayers spontaneously in aqueous solution. B) the process is exergonic. Together, these observations suggested that there may be a. A) the process is endergonic. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like why do phospholipids spontaneously form bilayer structures, while. However, under the right condition, single. Web why does the lipid bilayer form spontaneously? Lipids are fats, like oil, that are insoluble in water because of its long hydrophobic tails. A) the process is endergonic. Together, these observations suggested that there may be a. Web additional experiments showed that lipids could spontaneously form a bilayer when mixed with water (figure 1). Web why does the lipid bilayer form spontaneously? Web it is the shape and the amphipatic nature of the phospholipid molecules that cause them to form bilayers spontaneously in aqueous solution. Web why do lipid bilayers form spontaneously? Web the bilayer is arranged. B) the process is exergonic. Web why do lipid bilayers form spontaneously? Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like why do phospholipids spontaneously form bilayer structures, while oils form small droplets?, which. Web the structure of the lipid bilayer explains its function as a barrier. These are formed because the phospholipid tails are hydrophobic and the. Web why do lipid bilayers form spontaneously? By measuring the capacitance of erythrocyte solutions, hugo fricke determined that the cell membrane was 3.3 nm thick. Web the bilayer is arranged so that the phospholipid heads face outwards and the fatty acid chains face inwards, with cholesterol and proteins scattered throughout the membrane. Web why does the lipid bilayer form spontaneously?. Because their hydrophobic tails cluster together spontaneously limiting their contact with water, since they are non polar,. Web why do lipid bilayers form spontaneously? By measuring the capacitance of erythrocyte solutions, hugo fricke determined that the cell membrane was 3.3 nm thick. Web additional experiments showed that lipids could spontaneously form a bilayer when mixed with water (figure 1). Web. C) the process leads to a huge decrease in entropy and no change in. Web it is the shape and the amphipatic nature of the phospholipid molecules that cause them to form bilayers spontaneously in aqueous solution. Web phospholipids spontaneously form various structures in aqueous solution, including lipid bilayers. Two experiments in 1925 laid the groundwork to fill in this gap. A) the process is endergonic. By measuring the capacitance of erythrocyte solutions, hugo fricke determined that the cell membrane was 3.3 nm thick. However, under the right condition, single. Although the results of this experiment were accurate, fricke misinterpreted the data to mean th… Web why does the lipid bilayer form spontaneously? Because their hydrophobic tails cluster together spontaneously limiting their contact with water, since they are non polar,. These are formed because the phospholipid tails are hydrophobic and the. Web why do lipid bilayers form spontaneously? Web why do lipid bilayers form spontaneously? Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like why do phospholipids spontaneously form bilayer structures, while oils form small droplets?, which. Web the structure of the lipid bilayer explains its function as a barrier. Web additional experiments showed that lipids could spontaneously form a bilayer when mixed with water (figure 1). Web why do lipid bilayers form spontaneously? Together, these observations suggested that there may be a. Web the bilayer is arranged so that the phospholipid heads face outwards and the fatty acid chains face inwards, with cholesterol and proteins scattered throughout the membrane. B) the process is exergonic.Phospholipids Expii
TJ. Schematic diagram of typical membrane proteins in a biological
LabXchange
PPT Lipids, Membranes & the First Cells PowerPoint Presentation ID
Phospholipid Bilayers ( Read ) Biology CK12 Foundation
Diagram showing the effect of unsaturated lipids on a bilayer. The
Components and Structure OpenStax Biology 2e
Overview of Cell Structure and Function
microbiology Why do cell membranes have a lipid bilayer instead of a
Phospholipid Bilayer Lipid Bilayer Structures & Functions
Related Post: