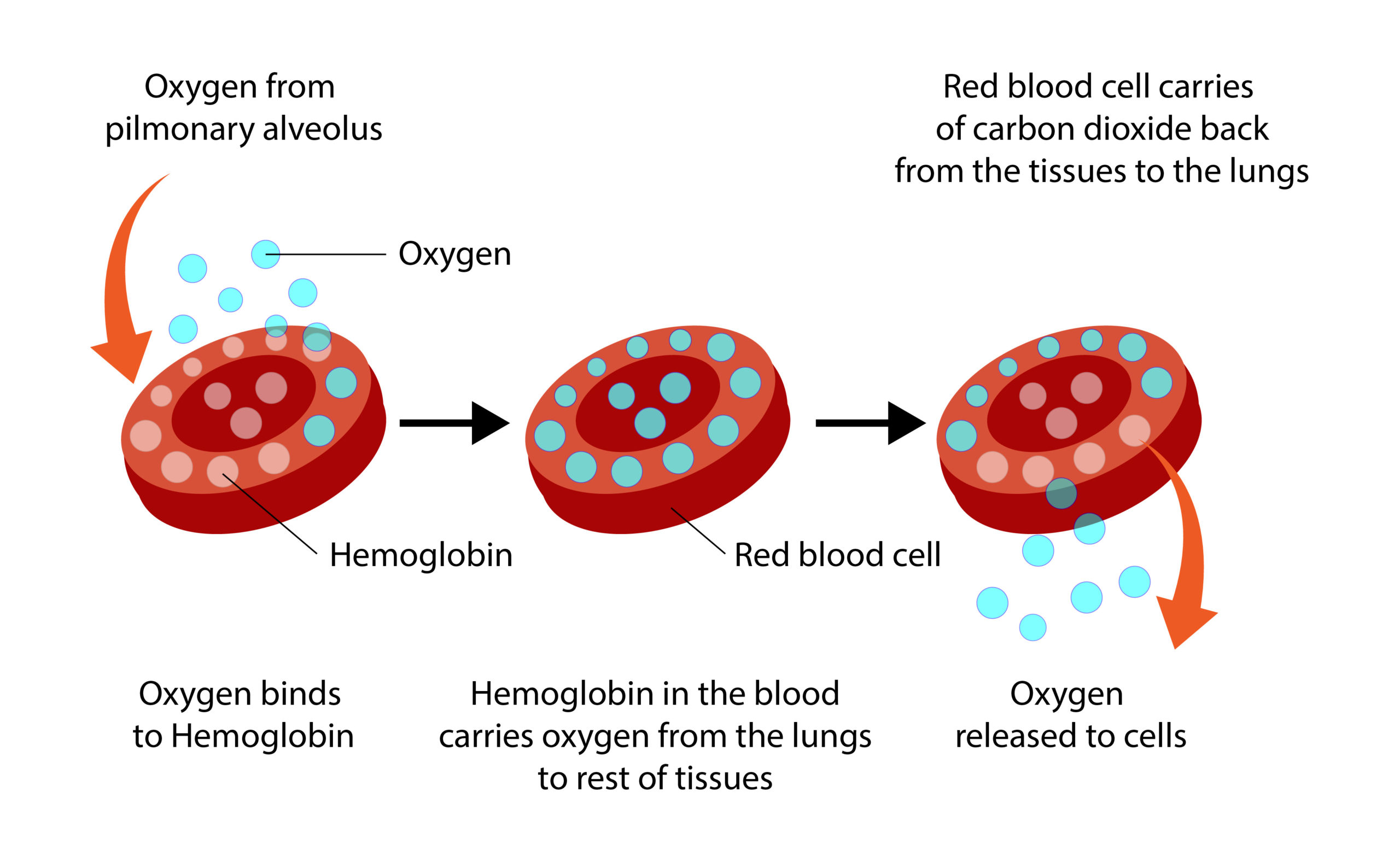
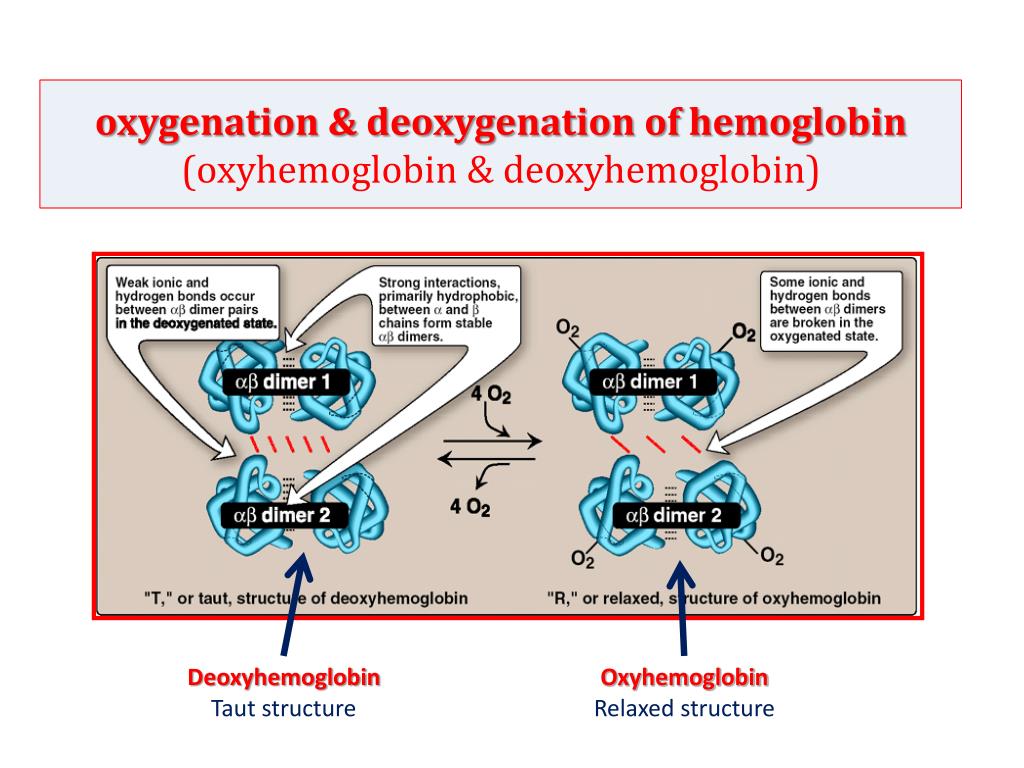
When Does Oxyhemoglobin Form During Respiration
When Does Oxyhemoglobin Form During Respiration - When levels of co2 rise in the blood, which of the. Web when does oxyhemoglobin form during respiration? Web when does oxyhemoglobin form during respiration? At the lower po2 in the peripheral tissues, oxygen begins to unbind. Hydrogen bonds stabilize the helical sections inside this protein, causing attractions within the molecule, which then causes each polypeptide chain to fold into a specific sha… Web when does oxyhemoglobin form during respiration? Web when does oxyhemoglobin form during respiration? Web the binding of oxygen to hemoglobin will be discussed, including the oxygen saturation (or dissociation) curve and factors (allosteric effectors) which cause it to shift. A) during external respiration b) immediately after carbon dioxide enters the blood c) when the chloride shift occurs. A) during external gas exchange 8) immediately after carbon dioxide enters the blood c during blood circulation d) during. Web the following reversible chemical reaction describes the production of the final product, oxyhemoglobin (hbo 2 ), which is formed when oxygen binds to hemoglobin. When carbon dioxide enters the. Web when does oxyhemoglobin form during respiration? At the lower po2 in the peripheral tissues, oxygen begins to unbind. The respiratory system is the collection of organs that help us. A) during external respiration b) immediately after carbon dioxide enters the blood c) when the chloride shift occurs d). The bohr effect and through the accumulation of carbamino compounds that are generated by chemical interactions. In the blood, it's major function. When carbon dioxide enters the. The respiratory system is the collection of organs that help us do gas exchange. Web under the influence of acidic environments, hemoglobin has a propensity for undergoing the reverse of this conformational change, releasing oxygen in favor of the. During pulmonary ventilation immediately after carbon dioxide enters the blood during external respiration during. A) during external gas exchange 8) immediately after carbon dioxide enters the blood c during blood circulation d) during. A) during. Oxyhemoglobin is a type of hemoglobin carrying oxygen which is bright red in color. Web the transport of oxygen is fundamental to aerobic respiration and the survival of complex organisms. A) during external respiration b) immediately after carbon dioxide enters the blood c) when the chloride shift occurs. Web when does oxyhemoglobin form during respiration? Web when does oxyhemoglobin form. Web when does oxyhemoglobin form during respiration? A) during external gas exchange 8) immediately after carbon dioxide enters the blood c during blood circulation d) during. A) during external respiration b) immediately after carbon dioxide enters the blood c) when the chloride shift occurs d). Methemoglobin is a nonfunctional form of hemoglobin in which. The respiratory system is the collection. Web when does oxyhemoglobin form during respiration? The curve shifts right when oxygen’s. Web under the influence of acidic environments, hemoglobin has a propensity for undergoing the reverse of this conformational change, releasing oxygen in favor of the. Web the transport of oxygen is fundamental to aerobic respiration and the survival of complex organisms. A) during external respiration b) immediately. Web the following reversible chemical reaction describes the production of the final product, oxyhemoglobin (hbo 2 ), which is formed when oxygen binds to hemoglobin. During pulmonary ventilation immediately after carbon dioxide enters the blood during external respiration during. This oxygen then binds to hemoglobin in. Web when does oxyhemoglobin form during respiration? Web carbon dioxide affects the curve in. Web when does oxyhemoglobin form during respiration? Web the binding of oxygen to hemoglobin will be discussed, including the oxygen saturation (or dissociation) curve and factors (allosteric effectors) which cause it to shift. During external respiration (/the exchange of gases between the lungs & blood). The bohr effect and through the accumulation of carbamino compounds that are generated by chemical. The respiratory system is the collection of organs that help us do gas exchange. Web as blood passes through the tissue capillaries, the uptake of carbon dioxide by red cells raises the oxygen tension of oxyhemoglobin at a given oxygen saturation by means of. In the blood, it's major function. Web when does oxyhemoglobin form during respiration? Web when does. Web the oxygen dissociation curve shows the amount of oxygen saturated in hemoglobin for a given partial pressure of oxygen. When levels of co2 rise in the blood, which of the. A) during external gas exchange 8) immediately after carbon dioxide enters the blood c during blood circulation d) during. Web the binding of oxygen to hemoglobin will be discussed,. Web when does oxyhemoglobin form during respiration? The bohr effect and through the accumulation of carbamino compounds that are generated by chemical interactions. Web as blood passes through the tissue capillaries, the uptake of carbon dioxide by red cells raises the oxygen tension of oxyhemoglobin at a given oxygen saturation by means of. A) during external gas exchange 8) immediately after carbon dioxide enters the blood c during blood circulation d) during. Web during external respiration, oxygen from the air we breathe enters the lungs and diffuses across the alveolar membrane into the blood. Methemoglobin is a nonfunctional form of hemoglobin in which. During pulmonary ventilation immediately after carbon dioxide enters the blood during external respiration during. When carbon dioxide enters the. A) during external respiration b) immediately after carbon dioxide enters the blood c) when the chloride shift occurs d). Web when does oxyhemoglobin form during respiration? Web carbon dioxide affects the curve in two ways: In the blood, it's major function. Web when does oxyhemoglobin form during respiration? Web the binding of oxygen to hemoglobin will be discussed, including the oxygen saturation (or dissociation) curve and factors (allosteric effectors) which cause it to shift. When levels of co2 rise in the blood, which of the. The curve shifts right when oxygen’s. This oxygen then binds to hemoglobin in. During external respiration (/the exchange of gases between the lungs & blood). At the lower po2 in the peripheral tissues, oxygen begins to unbind. Web the following reversible chemical reaction describes the production of the final product, oxyhemoglobin (hbo 2 ), which is formed when oxygen binds to hemoglobin.Cellular Respiration Biology Revision, Biology Units, Biology Labs
Oxygen saturation normal values & measurement cosinuss°
The Structure and Function of Red Blood Cells a.k.a. Erythrocytes
Oxyhemoglobin hemoglobin carries oxygen Royalty Free Vector
Oxygen And Hemoglobin Stock Illustration Download Image Now Oxygen
PPT Hemoglobin Structure & Function PowerPoint Presentation, free
Physiology Graph Oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve. (high resolution
Oxyhemoglobin hemoglobin carries oxygen Royalty Free Vector
Oxyhemoglobin hemoglobin carries oxygen Royalty Free Vector
9 Facts About The Respiratory System Nursing Students Should Know
Related Post: