The Inactive Form Of Pepsin Is
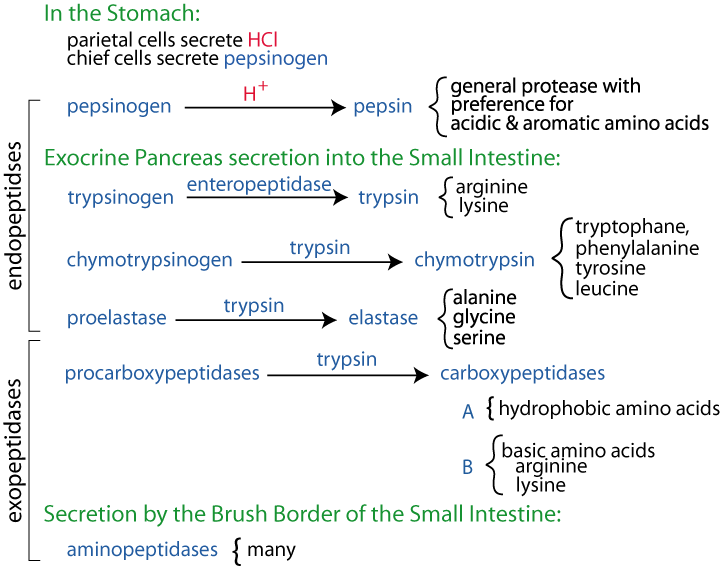
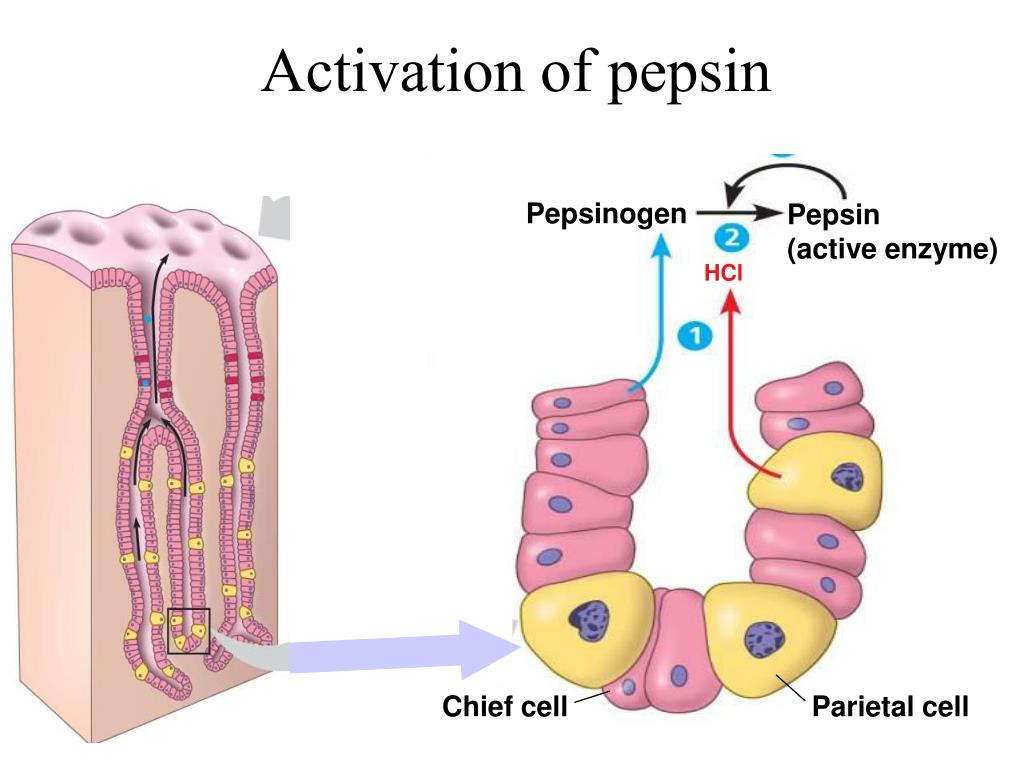
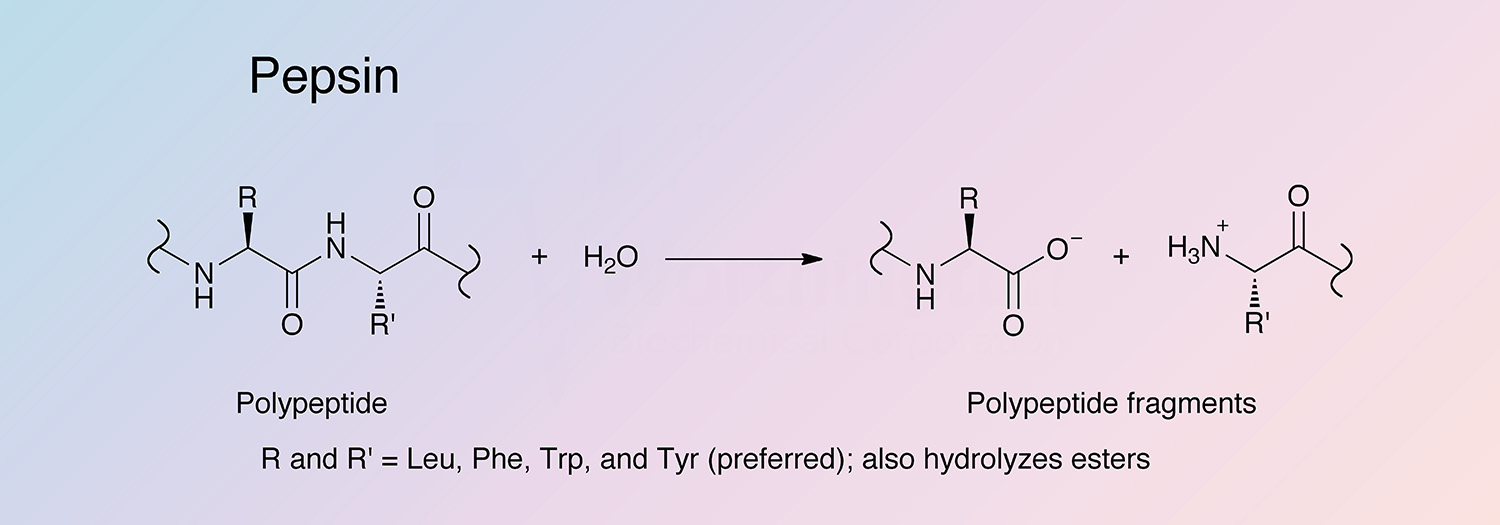
The Inactive Form Of Pepsin Is - Web thus, at neutral ph, the inhibitory piece maintains the enzyme in its inactive form by sterically blocking access to the active site and neutralizing negative charges in pepsin,. Web thus, at neutral ph, the inhibitory piece maintains the enzyme in its inactive form by sterically blocking access to the active site and neutralizing negative charges in pepsin,. When it reaches the duodenum, though, it assumes an inactive form as the ph rises above 6. When it reaches the duodenum, though, it assumes an inactive. Web specific cells within the gastric lining, known as chief cells, release pepsin in an inactive form, or zymogen form, called pepsinogen. What happens if pepsinogen is stored in the small intestine too long? Pepsinogen is synthesized and secreted by chief cells (c) in the stomach,. Pepsinogen was first crystallized from the gastric mucosa of. Web pepsin is the mature active form of pepsinogen, which is an inactive protein. Web pepsinogen is the zymogen, or inactive precursor, of pepsin, the principal proteolytic enzyme of gastric juice. Accordingly, its primary site of synthesis and activity is in the stomach (ph 1.5 to 2). Web pepsin is activated by the enzyme pepsinogen, which is made by the stomach. What happens if pepsinogen is stored in the small intestine too long? In fact, the inactive form of pepsin is the only. Web pepsin, the first animal enzyme discovered (florkin,. Web on secretion and exposure to stomach acid, inactive pepsinogen undergoes a conformational change, exposing its catalytically active site. When it reaches the duodenum, though, it assumes an inactive. Therefore, it is most effective at a ph of approximately 1.5 to 2. What happens if pepsinogen is stored in the small intestine too long? By doing so, the stomach. Web thus, at neutral ph, the inhibitory piece maintains the enzyme in its inactive form by sterically blocking access to the active site and neutralizing negative charges in pepsin,. Web trypsinogen is the inactive form of trypsin. It is the main component of the digestive enzyme pepsin. Pepsinogen was first crystallized from the gastric mucosa of. Web pepsin depends on. It is the main component of the digestive enzyme pepsin. It is secreted by the pancreas and found in pancreatic juice. Web thus, at neutral ph, the inhibitory piece maintains the enzyme in its inactive form by sterically blocking access to the active site and neutralizing negative charges in pepsin,. Its principal role is digesting protein in the stomach. Pepsinogen. Web pepsin, the first animal enzyme discovered (florkin, 1957), is an acidic protease that catalyzes the breakdown of proteins into peptides in the stomach, while it does not digest. Web pepsin is secreted in the form of pepsinogen, which is a zymogen (proenzyme or an inactive precursor). Web pepsin is the mature active form of pepsinogen, which is an inactive. What happens if pepsinogen is stored in the small intestine too long? It is released from chief cells as pepsinogen, its. It is the release of hydrochloric acid by the parietal cells in the. Its principal role is digesting protein in the stomach. Web pepsin is the mature active form of pepsinogen, which is an inactive protein. It is secreted by the pancreas and found in pancreatic juice. Web you don't want trypsin or pepsin active when they're not in the stomach/small intestine (they will literally start digesting parts of your own body),. Web pepsin is activated by the enzyme pepsinogen, which is made by the stomach. Web pepsin is secreted in the form of pepsinogen, which. The pancreatic juice contains many different. Web we would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Web pepsin is activated by the enzyme pepsinogen, which is made by the stomach. Web on secretion and exposure to stomach acid, inactive pepsinogen undergoes a conformational change, exposing its catalytically active site. Web trypsinogen is the inactive. It is the main component of the digestive enzyme pepsin. Therefore, it is most effective at a ph of approximately 1.5 to 2. Web thus, at neutral ph, the inhibitory piece maintains the enzyme in its inactive form by sterically blocking access to the active site and neutralizing negative charges in pepsin,. Accordingly, its primary site of synthesis and activity. Once activated in the duodenum, trypsin cleaves peptide. Pepsin is most active in acidic environments between ph 1.5 to 2.5. Its principal role is digesting protein in the stomach. Web pepsin is activated by the enzyme pepsinogen, which is made by the stomach. Web low ph allows pepsinogen to cleave itself and form active pepsin. Therefore, it is most effective at a ph of approximately 1.5 to 2. Pepsinogen is inactive when it is in the inactive form. Web pepsinogen is the zymogen, or inactive precursor, of pepsin, the principal proteolytic enzyme of gastric juice. Web pepsin is activated by the enzyme pepsinogen, which is made by the stomach. Therefore, pepsin in solutions of up to ph 8.0 can be reactivated upon r… Web pepsin is the mature active form of pepsinogen, which is an inactive protein. Pepsinogen was first crystallized from the gastric mucosa of. The pancreatic juice contains many different. Accordingly, its primary site of synthesis and activity is in the stomach (ph 1.5 to 2). Web trypsinogen is the inactive form of trypsin. By doing so, the stomach. It is the release of hydrochloric acid by the parietal cells in the. Web this is called the “inactive pepsin form.” this is the process that pepsin is in when it’s not being broken down by stomach acid. Pepsin is most active in acidic environments between ph 1.5 to 2.5. Pepsin is inactive at ph 6.5 and above, however pepsin is not fully denatured or irreversibly inactivated until ph 8.0. Web we would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Low ph allows pepsinogen to cleave itself and form active pepsin. Pepsinogen is synthesized and secreted by chief cells (c) in the stomach,. Web you don't want trypsin or pepsin active when they're not in the stomach/small intestine (they will literally start digesting parts of your own body),. Web on secretion and exposure to stomach acid, inactive pepsinogen undergoes a conformational change, exposing its catalytically active site.💣 Inactive form of pepsin. Digestive System. 20221013
PPT Animal Nutrition II (Ch. 41) PowerPoint Presentation, free
Pepsin Worthington Enzyme Manual Worthington Biochemical
Pepsin stomach enzyme, molecular model. Pepsin is a protease enzyme
💣 Inactive form of pepsin. Digestive System. 20221013
💣 Inactive form of pepsin. Digestive System. 20221013
Pepsin is inactivated at pH
Activation of pepsin
💣 Inactive form of pepsin. Digestive System. 20221013
What is Pepsin?
Related Post: