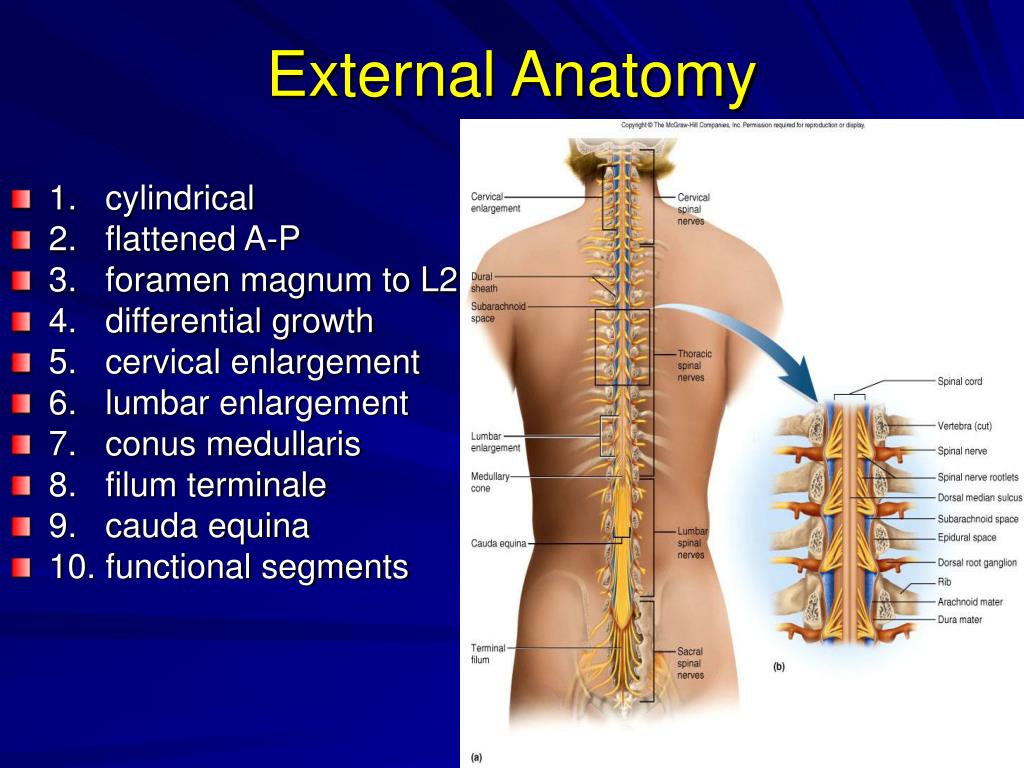
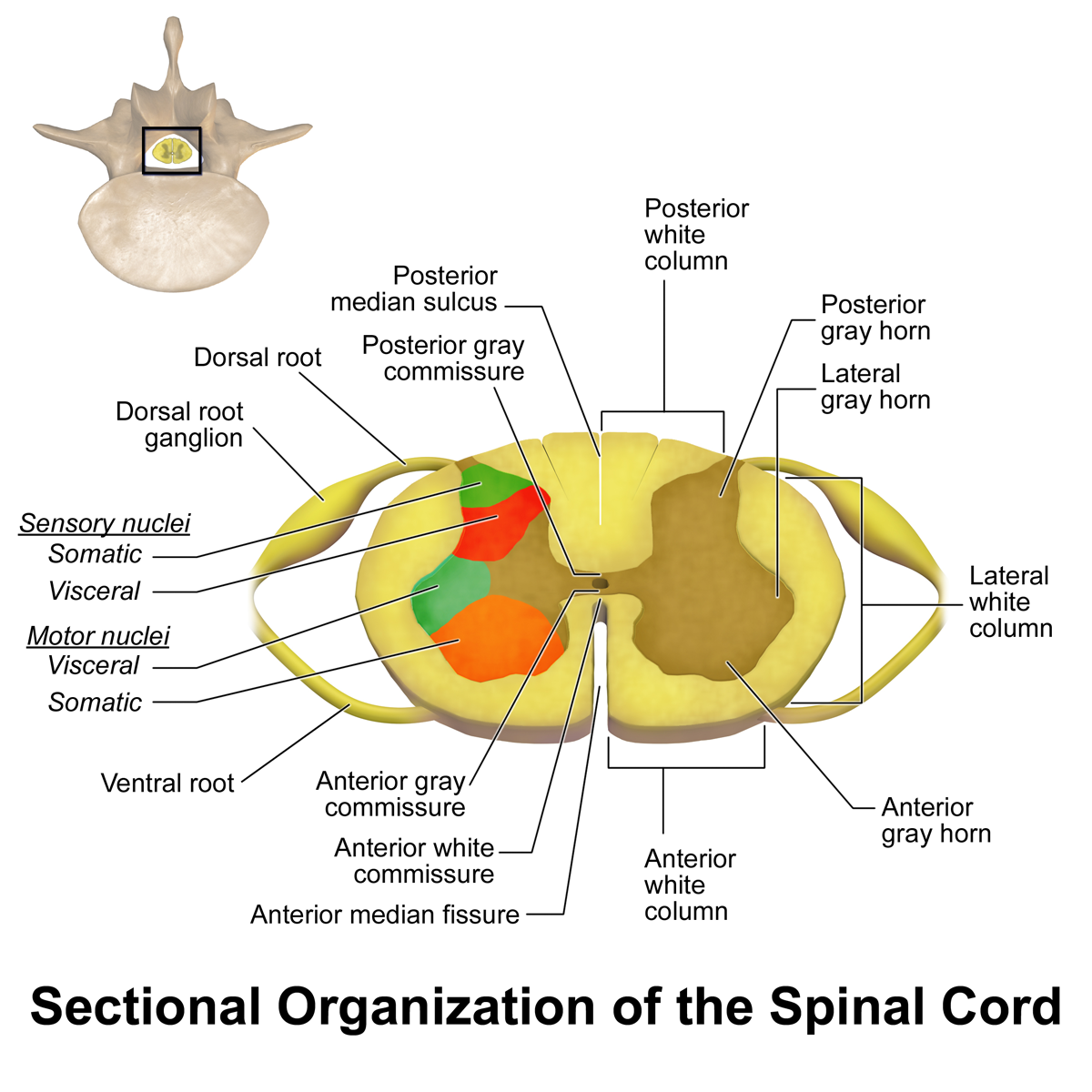
Structures That Form An Enclosure For The Spinal Cord
Structures That Form An Enclosure For The Spinal Cord - Web your lumbar spine supports the upper two sections of your spine — the seven vertebrae in your neck (cervical spine) and 12 vertebrae in your chest (thoracic spine) — and the. There are seven cervical vertebrae in the neck, 12 thoracic vertebrae in the torso and five lumbar vertebrae in the. Provides levers for the muscles to pull against: Web structure that encloses the nerve cord: Cervical, thoracic, lumbar and sacral, two of these are marked by an upper (cervical) and a lower. It serves not only as a pathway for nerve impulses to and from the brain, but also as a center for. Web the vertebral column (and the spinal cord within it) is divided into cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, and coccygeal regions. Web according to its rostrocaudal location the spinal cord can be divided into four parts: Web the vertebral column (spine or backbone) is a curved structure composed of bony vertebrae that are interconnected by cartilaginous intervertebral discs. Web the spinal cord is part of the central nervous system. Each segment of the spinal cord provides several pairs of spinal nerves, which exit from vertebral canal through the intervertebral foramina. Cervical, thoracic, lumbar and sacral, two of these are marked by an upper (cervical) and a lower. There are seven cervical vertebrae in the neck, 12 thoracic vertebrae in the torso and five lumbar vertebrae in the. Web structure. Web the spine has three normal curves: Each segment of the spinal cord provides several pairs of spinal nerves, which exit from vertebral canal through the intervertebral foramina. Web the vertebral column (and the spinal cord within it) is divided into cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, and coccygeal regions. Web the spinal cord (similar to the brain) is protected by three. Web structure that encloses the nerve cord: Web like the vertebral column, the spinal cord is divided into segments: The foramina of all the vertebrae line up to form the. Web the vertebral column (and the spinal cord within it) is divided into cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, and coccygeal regions. The peripheral nerves (called the spinal or segmental. Cervical, thoracic, lumbar and sacral, two of these are marked by an upper (cervical) and a lower. Cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, and coccygeal. Web your lumbar spine supports the upper two sections of your spine — the seven vertebrae in your neck (cervical spine) and 12 vertebrae in your chest (thoracic spine) — and the. Structures that form the vertebral. There are seven cervical vertebrae in the neck, 12 thoracic vertebrae in the torso and five lumbar vertebrae in the. It relays sensations to the brain and allows the brain to control movements and function of the internal organs, trunk, and. The foramina of all the vertebrae line up to form the. Web branching off from each section of the. Cervical, thoracic, lumbar and sacral, two of these are marked by an upper (cervical) and a lower. Provides levers for the muscles to pull against: The foramina of all the vertebrae line up to form the. Web according to its rostrocaudal location the spinal cord can be divided into four parts: Web the vertebral column (spine or backbone) is a. The foramina of all the vertebrae line up to form the. The spinal cord extends from the foramen magnum to the lowest border of the first. Web the vertebral column (and the spinal cord within it) is divided into cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, and coccygeal regions. Web the spine has three normal curves: Cervical, thoracic, lumbar and sacral, two of. Cervical, thoracic, lumbar and sacral, two of these are marked by an upper (cervical) and a lower. Web the spinal cord is part of the central nervous system. Web your lumbar spine supports the upper two sections of your spine — the seven vertebrae in your neck (cervical spine) and 12 vertebrae in your chest (thoracic spine) — and the.. Web your lumbar spine supports the upper two sections of your spine — the seven vertebrae in your neck (cervical spine) and 12 vertebrae in your chest (thoracic spine) — and the. Web the spine has three normal curves: Web the vertebral column (and the spinal cord within it) is divided into cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, and coccygeal regions. Provides. Web the vertebral column (spine or backbone) is a curved structure composed of bony vertebrae that are interconnected by cartilaginous intervertebral discs. Web like the vertebral column, the spinal cord is divided into segments: Web the spine has three normal curves: It serves not only as a pathway for nerve impulses to and from the brain, but also as a. Web branching off from each section of the spinal cord are two pairs of nerves, the afferent (incoming to the cns) sensory nerve roots, which branch from the dorsal side of the. The foramina of all the vertebrae line up to form the. Provides levers for the muscles to pull against: It relays sensations to the brain and allows the brain to control movements and function of the internal organs, trunk, and. There are seven cervical vertebrae in the neck, 12 thoracic vertebrae in the torso and five lumbar vertebrae in the. Web the spinal cord is a cylindrical structure of nervous tissue composed of white and gray matter, is uniformly organized and is divided into four regions: Structures that form the vertebral arch. Web like the vertebral column, the spinal cord is divided into segments: Web your lumbar spine supports the upper two sections of your spine — the seven vertebrae in your neck (cervical spine) and 12 vertebrae in your chest (thoracic spine) — and the. Cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, and coccygeal. Web the spinal cord is part of the central nervous system. The spinal cord extends from the foramen magnum to the lowest border of the first. Web the spine has three normal curves: It serves not only as a pathway for nerve impulses to and from the brain, but also as a center for. Web the spinal cord (similar to the brain) is protected by three layers of meninges (membranes). Each segment of the spinal cord provides several pairs of spinal nerves, which exit from vertebral canal through the intervertebral foramina. The peripheral nerves (called the spinal or segmental. Structures that form an enclosure for the spinal cord. Web the vertebral column (spine or backbone) is a curved structure composed of bony vertebrae that are interconnected by cartilaginous intervertebral discs. Web structure that encloses the nerve cord:I Anatomy II Physiology Spinal Cord 1 The
Spinal Cord Functional Anatomy Semantic Scholar
The Spinal Cord Neurologic Clinics
Operative Spinal Cord Anatomy The Neurosurgical Atlas
Operative Spinal Cord Anatomy The Neurosurgical Atlas, by Aaron Cohen
Formation of the spinal cord and its surrounding structures with normal
PPT Spinal Cord PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID491741
Spinal Cord Summary Neuroanatomy Geeky Medics
awesome projects spinal cord anatomy and physiology Spinal cord
Spinal Cord Spinal cord, Spinal, Anatomy organs
Related Post: