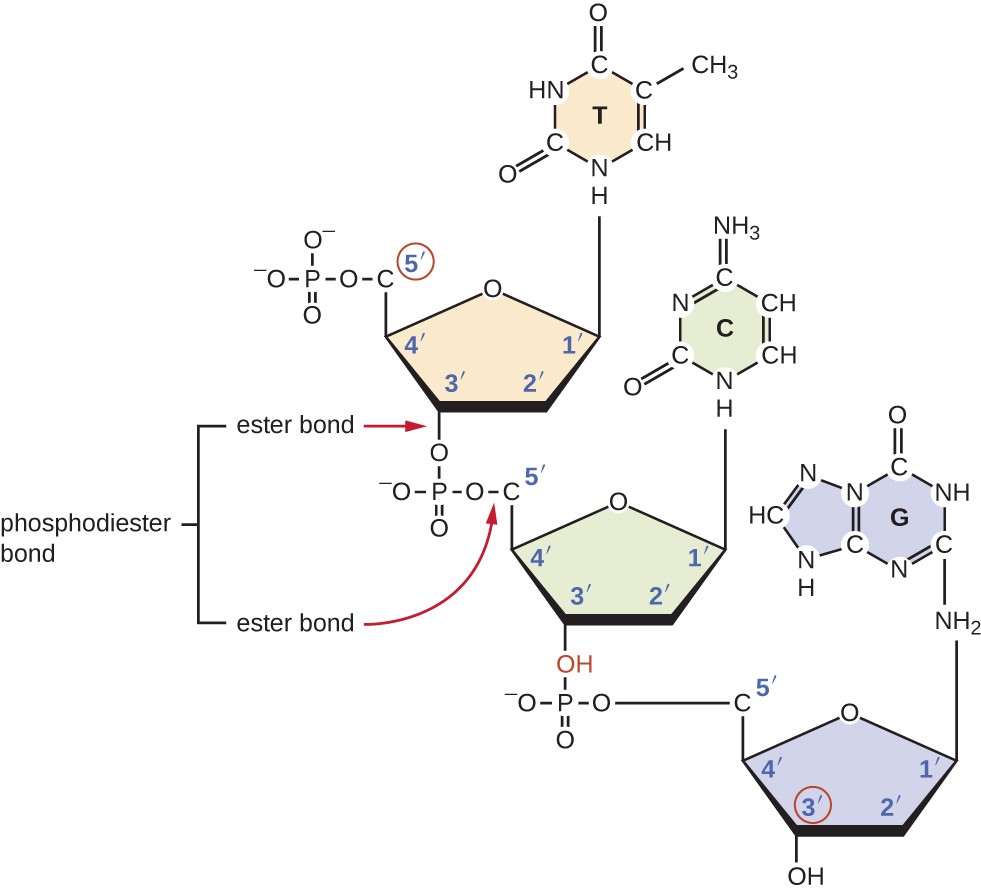
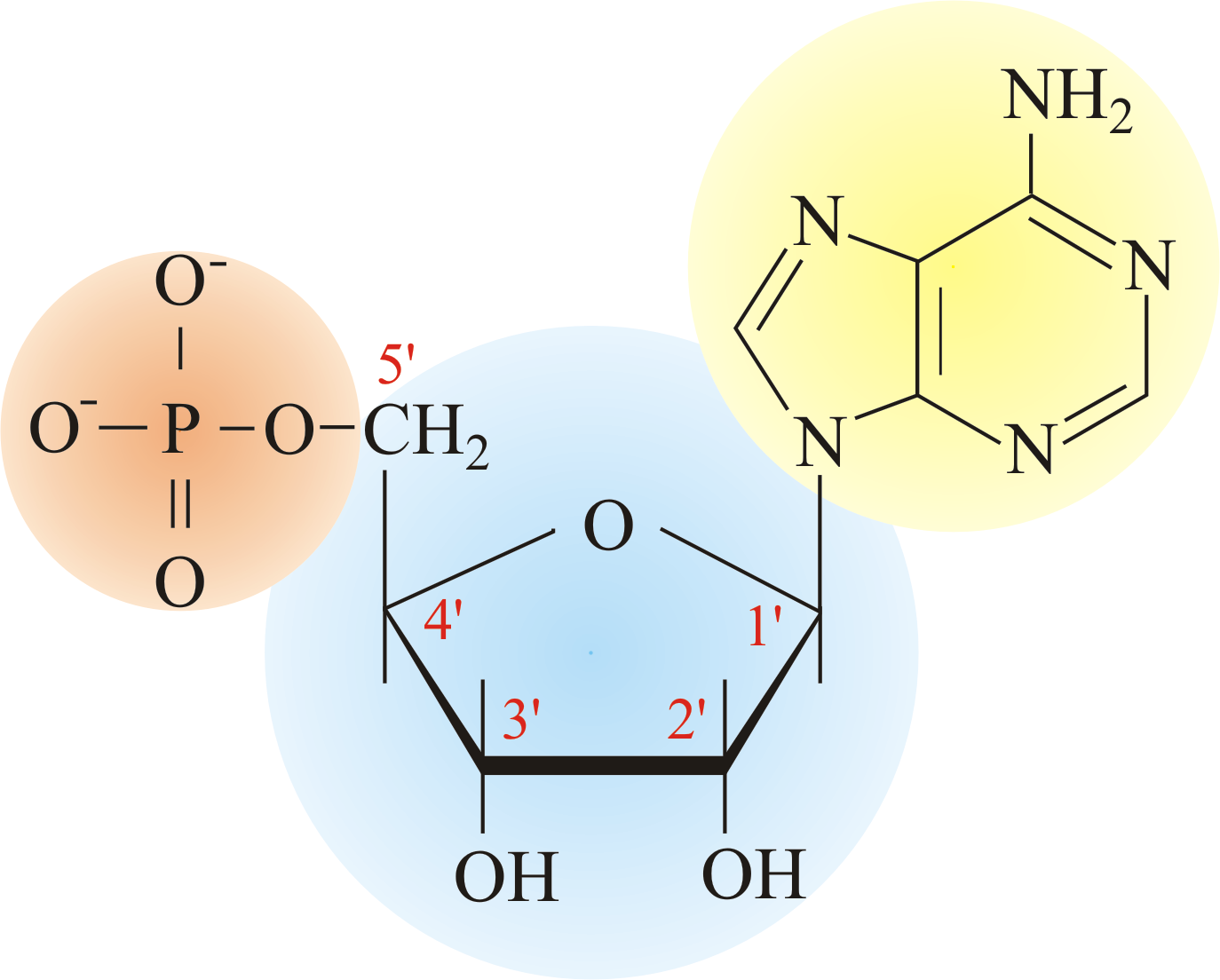
How Do Nucleotides Bond To Form Nucleic Acids
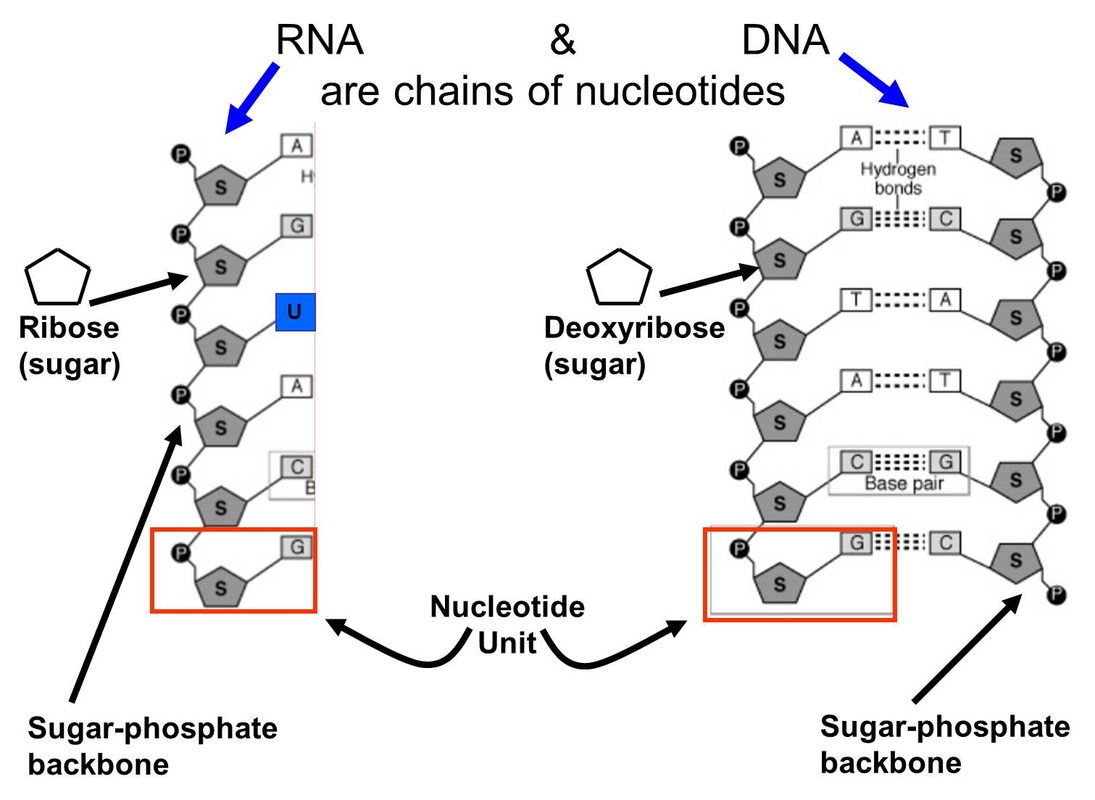
How Do Nucleotides Bond To Form Nucleic Acids - With all three joined, a nucleotide is also termed a nucleoside monophosphate, nucleoside diphosphate or nucleoside triphosphate, depending on how many phosphates make up the phosphate g… The hydroxyl group of phosphate on one nucleotide undergoes a. They are the most important macromolecules for the continuity of life. Web nucleic acids, deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid (rna), carry genetic information which is read in cells to make the rna and proteins by which. Nucleic acids, crucial macromolecules for life, were first discovered in cell nuclei and exhibit acidic. Web nucleic acids are polynucleotides—that is, long chainlike molecules composed of a series of nearly identical building blocks called nucleotides. The sugar in all four nucleotides is called deoxyribose. Web nucleic acids are large polymers formed by linking nucleotides together and are found in every cell. Web individual nucleotides condense with one another to form a nucleic acid polymer. Web nucleotides are joined together through the phosphate group of one nucleotide connecting in an ester linkage to the oh group on the 3' carbon atom of the sugar. Web nucleotides are joined together through the phosphate group of one nucleotide connecting in an ester linkage to the oh group on the third carbon atom of the. The two main types of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid (rna). Deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) is the nucleic acid that stores genetic. Web individual nucleotides condense with one another. Web nucleic acids are large polymers formed by linking nucleotides together and are found in every cell. Web individual nucleotides condense with one another to form a nucleic acid polymer. Web introduction to nucleic acids and nucleotides. The sugar in all four nucleotides is called deoxyribose. Web all four nucleotides (a, t, g and c) are made by sticking a. Each nucleotide is made up of three components: Web we would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Web introduction to nucleic acids and nucleotides. Deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) is the nucleic acid that stores genetic. Nucleotides link together by the formation of phosphate ester bonds. The two main types of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid (rna). Web the 3' hydroxyl group forms a bond to the phosphorus atom of the free nucleotide closest to the 5' oxygen atom. The hydroxyl group of phosphate on one nucleotide undergoes a. Web a first glance at a dna or rna structure reveals a myriad. Web the 3' hydroxyl group forms a bond to the phosphorus atom of the free nucleotide closest to the 5' oxygen atom. Web we would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Web all four nucleotides (a, t, g and c) are made by sticking a phosphate group and a nucleobase to a sugar.. Web nucleotides are joined together to form nucleic acids through the phosphate group of one nucleotide connecting in an ester linkage to the oh group on the third carbon atom of the. Web a first glance at a dna or rna structure reveals a myriad of possible hydrogen bond donors and acceptors in the bases of the nucleic acid. The. Web nucleic acids are polynucleotides—that is, long chainlike molecules composed of a series of nearly identical building blocks called nucleotides. Web individual nucleotides condense with one another to form a nucleic acid polymer. Each nucleotide is made up of three components: Web the 3' hydroxyl group forms a bond to the phosphorus atom of the free nucleotide closest to the. They carry the genetic information. Web individual nucleotides condense with one another to form a nucleic acid polymer. Each nucleotide is made up of three components: Web nucleotides are joined together through the phosphate group of one nucleotide connecting in an ester linkage to the oh group on the 3' carbon atom of the sugar. Web we would like to. Nucleic acidsare macromolecules made up of monomers called nucleotides. Nucleic acids, crucial macromolecules for life, were first discovered in cell nuclei and exhibit acidic. The two main types of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid (rna). Deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) is the nucleic acid that stores genetic. Web introduction to nucleic acids and nucleotides. Dna is the genetic material in all living organisms, ranging from. Web nucleotides are joined together through the phosphate group of one nucleotide connecting in an ester linkage to the oh group on the third carbon atom of the. Web we would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. With all three joined, a. Web introduction to nucleic acids and nucleotides. Each nucleotide is made up of three components: Web all four nucleotides (a, t, g and c) are made by sticking a phosphate group and a nucleobase to a sugar. Web sugars and phosphate groups of adjacent nucleotides bind together to form the backbone of the polynucleotide. They are the most important macromolecules for the continuity of life. Deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) is the nucleic acid that stores genetic. Web individual nucleotides condense with one another to form a nucleic acid polymer. Nucleic acidsare macromolecules made up of monomers called nucleotides. They carry the genetic information. The hydroxyl group of phosphate on one nucleotide undergoes a. Web we would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. The sugar in all four nucleotides is called deoxyribose. Nucleic acids, crucial macromolecules for life, were first discovered in cell nuclei and exhibit acidic. Web nucleotides are joined together through the phosphate group of one nucleotide connecting in an ester linkage to the oh group on the third carbon atom of the. Web nucleic acids are polynucleotides—that is, long chainlike molecules composed of a series of nearly identical building blocks called nucleotides. Web a first glance at a dna or rna structure reveals a myriad of possible hydrogen bond donors and acceptors in the bases of the nucleic acid. Web nucleic acids are large polymers formed by linking nucleotides together and are found in every cell. The two main types of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid (rna). Web nucleotides are joined together to form nucleic acids through the phosphate group of one nucleotide connecting in an ester linkage to the oh group on the third carbon atom of the. With all three joined, a nucleotide is also termed a nucleoside monophosphate, nucleoside diphosphate or nucleoside triphosphate, depending on how many phosphates make up the phosphate g…Nucleic Acids Principles of Biology
What Are the Three Parts of a Nucleotide?
Nucleotides and Bases Generation
PPT Nucleotides PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID672807
Nucleotides Castell Alun High School Biology
3 Parts of a Nucleotide and How They Are Connected
how do the 4 bases of dna pair up Lamont Benwell
Nucleic Acids Broad Learnings
Nucleic Acids Jack's AP Biology Journal
Biochemistry Glossary Nucleosides vs. Nucleotides Draw It to Know It
Related Post:
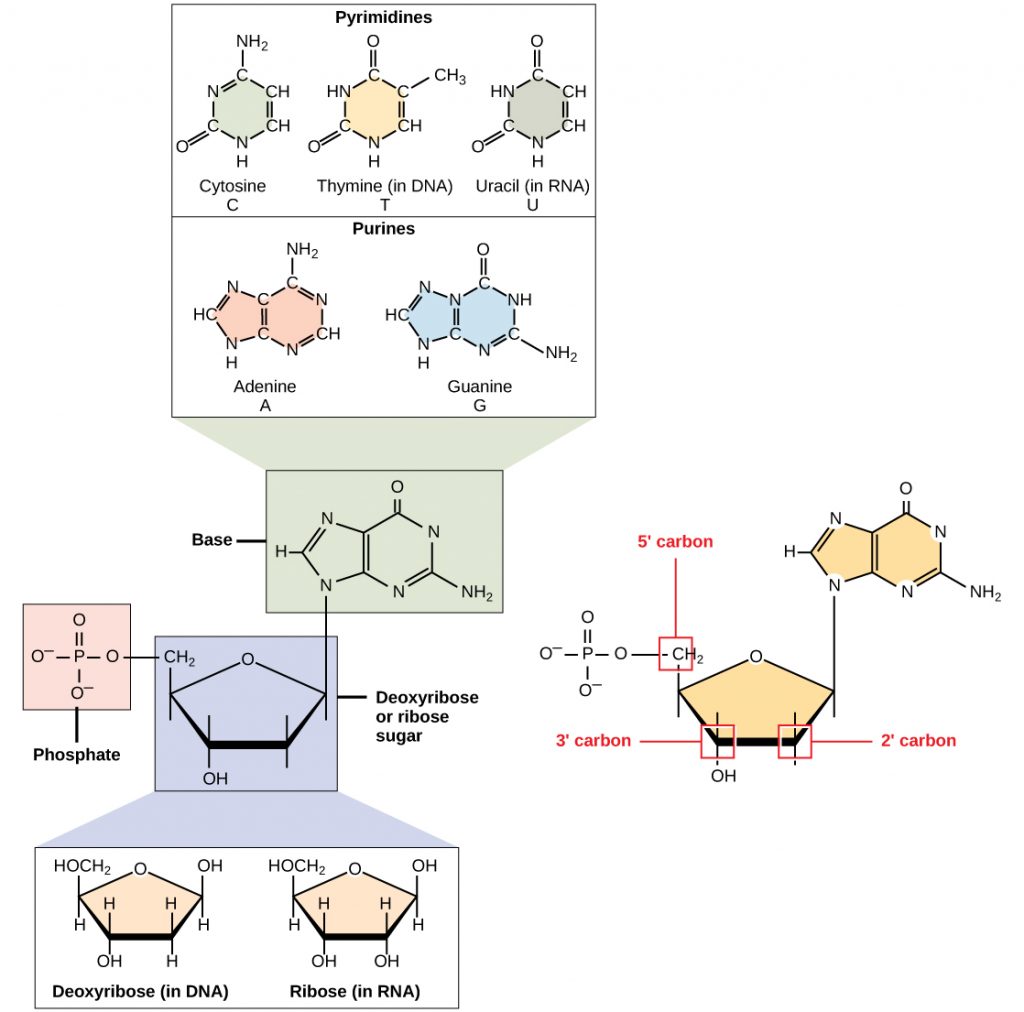


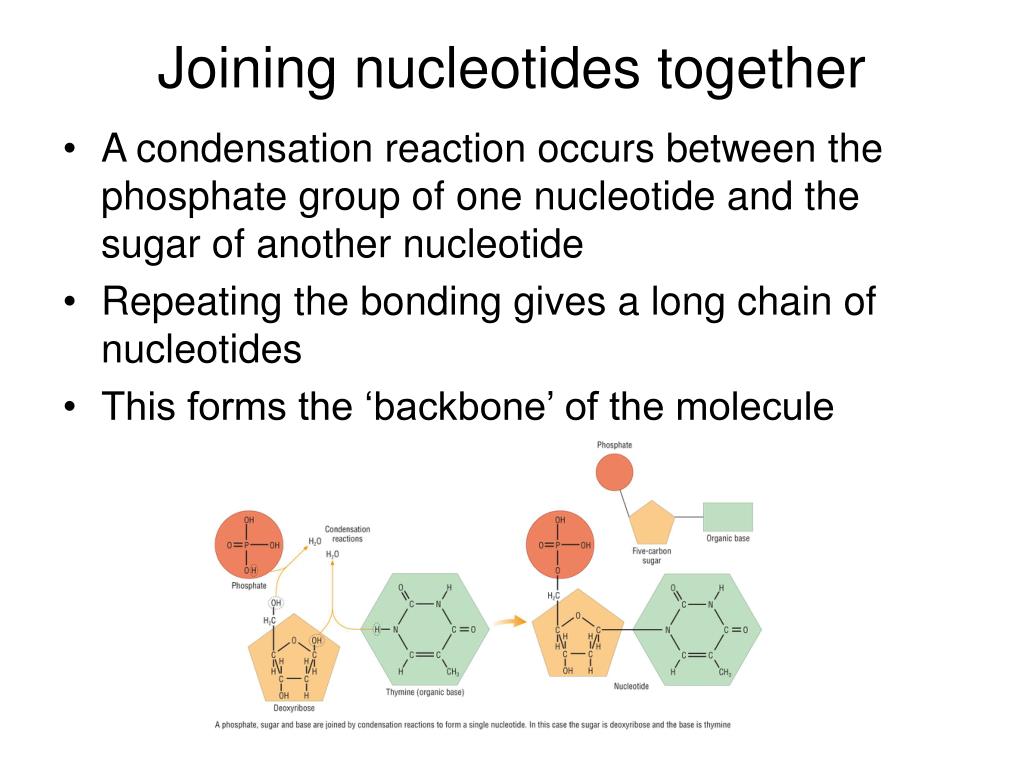
/Nucleotide-58e518d35f9b58ef7e62834d.jpg)