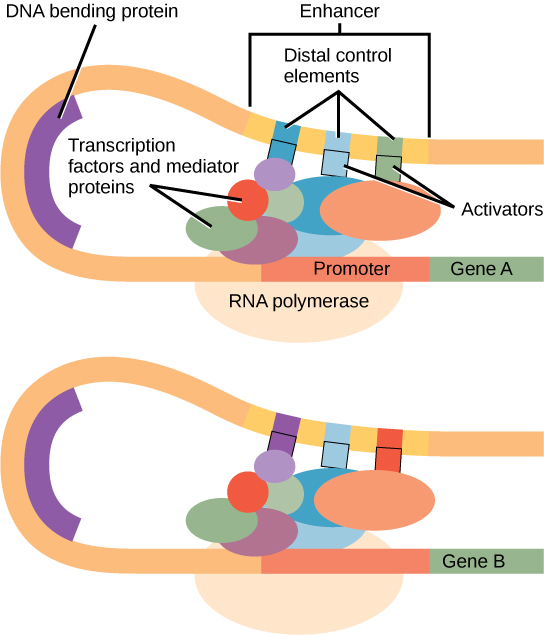
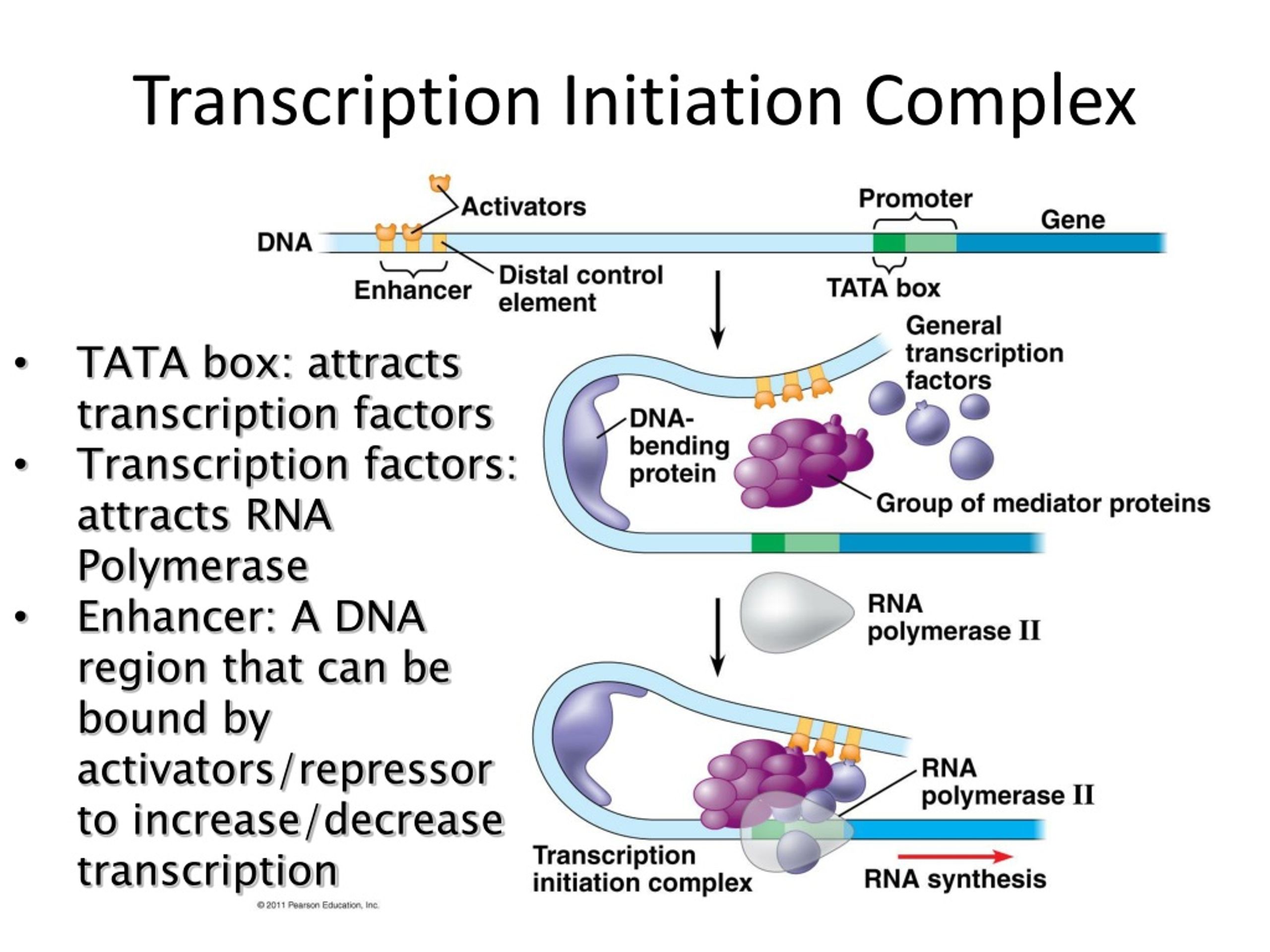
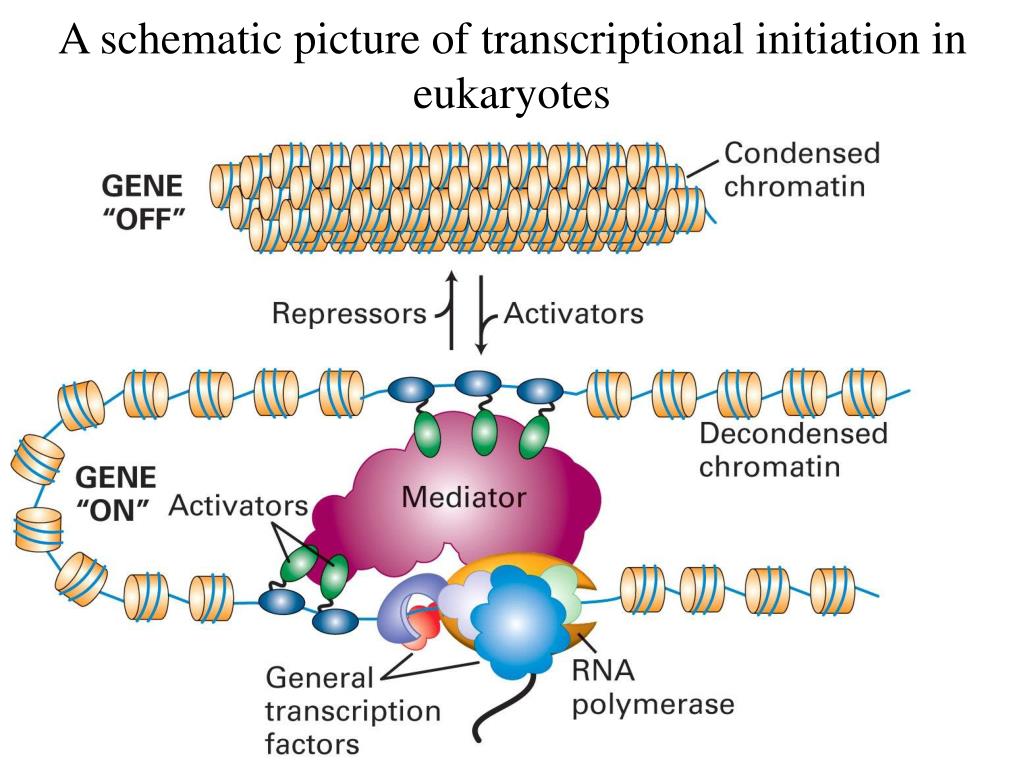
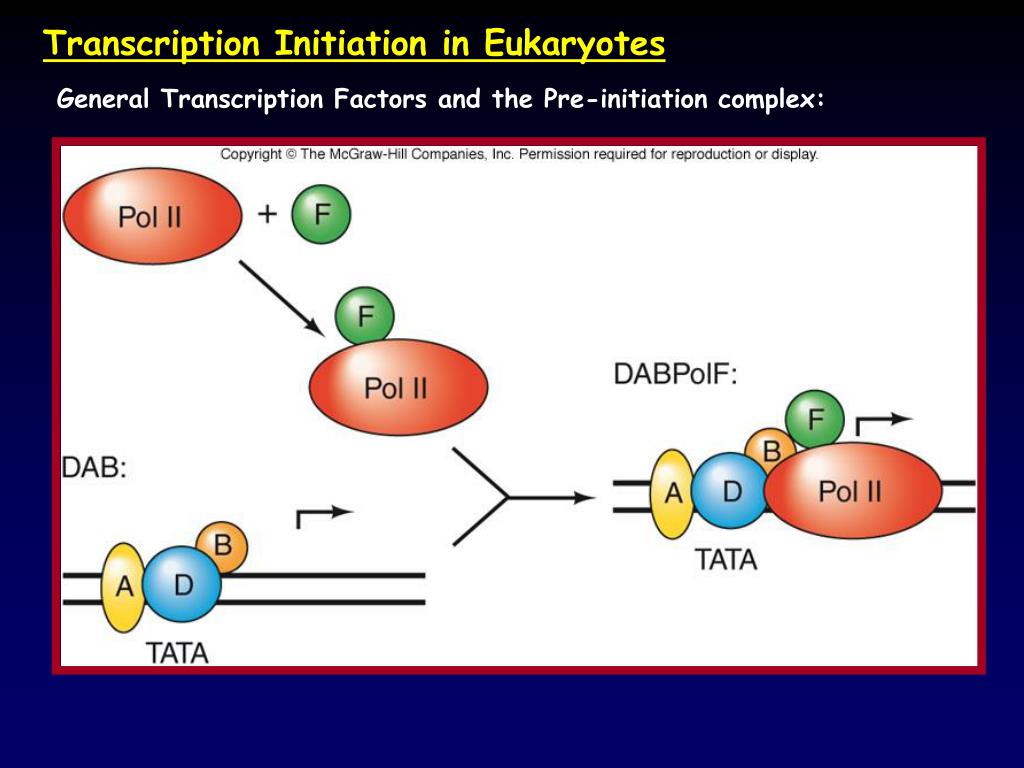
How Do Eukaryotic Transcription Factors Help Form The Initiation Complex
How Do Eukaryotic Transcription Factors Help Form The Initiation Complex - Web transcription initiation complex & looping. Formation of the transcription preinitiation complex (pic) is nucleated by the tata. Web unlike the prokaryotic polymerase that can bind to a dna template on its own, eukaryotes require several other proteins, called transcription factors, to first bind to the promoter. Web eukaryotic transcription is carried out in the nucleus of the cell by one of three rna polymerases, depending on the rna being transcribed, and proceeds in Web transcription factors recognize the promoter, rna polymerase ii then binds and forms the transcription initiation complex. The three eukaryotic rna polymerases (rnaps) the features of eukaryotic mrna synthesis are markedly more complex those of. Additional factors of the eif4f complex (eif4a, e, and g… Eukaryotic initiation factors (eifs) are proteins or protein complexes involved in the initiation phase of eukaryotic translation. Transcription factors are proteins that help turn specific genes on or off by binding. Web the initiation of mrna synthesis requires pol ii and the general transcription factors tfiia, tfiib, tfiid, tfiie, tfiif, and tfiih (sainsbury et al. Web the two main tasks of transcription initiation are to provide rna polymerase with an access to the promoter and to assemble general transcription factors with polymerase. Web the initiation of mrna synthesis requires pol ii and the general transcription factors tfiia, tfiib, tfiid, tfiie, tfiif, and tfiih (sainsbury et al. Transcription factors are proteins that help turn specific genes. Web unlike the prokaryotic polymerase that can bind to a dna template on its own, eukaryotes require several other proteins, called transcription factors, to first bind to the promoter. Web most eukaryotic genes have promoters that consist of the tata box close to the 5' end of the gene and, farther upstream, several motifs recognized by specific transcription. Web eukaryotic. Web these general transcription factors include tfiib, tfiid, tfiie, tfiif and tfiih. Web the two main tasks of transcription initiation are to provide rna polymerase with an access to the promoter and to assemble general transcription factors with polymerase. Web the initiation of mrna synthesis requires pol ii and the general transcription factors tfiia, tfiib, tfiid, tfiie, tfiif, and tfiih. Formation of the transcription preinitiation complex (pic) is nucleated by the tata. Web most eukaryotic genes have promoters that consist of the tata box close to the 5' end of the gene and, farther upstream, several motifs recognized by specific transcription. Web the initiation of transcription in eukaryotes involves the binding of several transcription factors to complex promoter sequences that. The three eukaryotic rna polymerases (rnaps) the features of eukaryotic mrna synthesis are markedly more complex those of. Additional factors of the eif4f complex (eif4a, e, and g… Formation of the transcription preinitiation complex (pic) is nucleated by the. Formation of the transcription preinitiation complex (pic) is nucleated by the tata. Web transcription factors recognize the promoter, rna polymerase ii. Web unlike the prokaryotic polymerase that can bind to a dna template on its own, eukaryotes require several other proteins, called transcription factors, to first bind to the promoter. Web the two main tasks of transcription initiation are to provide rna polymerase with an access to the promoter and to assemble general transcription factors with polymerase. Web most eukaryotic genes. Web elongation following the formation of the preinitiation complex, the polymerase is released from the other transcription factors, and elongation is allowed to proceed as it does in. Web bacterial σ factors are critical components of rna polymerase (rnap) holoenzymes for initiation of transcription by specifically recognizing dna promoter. The three eukaryotic rna polymerases (rnaps) the features of eukaryotic mrna. Additional factors of the eif4f complex (eif4a, e, and g… Formation of the transcription preinitiation complex (pic) is nucleated by the tata. Web unlike the prokaryotic polymerase that can bind to a dna template on its own, eukaryotes require several other proteins, called transcription factors, to first bind to the promoter. Web transcription initiation complex & looping. Web these general. Transcription factors are proteins that help turn specific genes on or off by binding. Web the two main tasks of transcription initiation are to provide rna polymerase with an access to the promoter and to assemble general transcription factors with polymerase. Eukaryotic initiation factors (eifs) are proteins or protein complexes involved in the initiation phase of eukaryotic translation. This chapter. Web transcription factors recognize the promoter, rna polymerase ii then binds and forms the transcription initiation complex. Additional factors of the eif4f complex (eif4a, e, and g… Web the initiation of mrna synthesis requires pol ii and the general transcription factors tfiia, tfiib, tfiid, tfiie, tfiif, and tfiih (sainsbury et al. Web unlike the prokaryotic polymerase that can bind to. Additional factors of the eif4f complex (eif4a, e, and g… Web bacterial σ factors are critical components of rna polymerase (rnap) holoenzymes for initiation of transcription by specifically recognizing dna promoter. Web eukaryotic transcription is carried out in the nucleus of the cell by one of three rna polymerases, depending on the rna being transcribed, and proceeds in Web the initiation of mrna synthesis requires pol ii and the general transcription factors tfiia, tfiib, tfiid, tfiie, tfiif, and tfiih (sainsbury et al. The three eukaryotic rna polymerases (rnaps) the features of eukaryotic mrna synthesis are markedly more complex those of. Transcription factors are proteins that help turn specific genes on or off by binding. Web these general transcription factors include tfiib, tfiid, tfiie, tfiif and tfiih. Web unlike the prokaryotic polymerase that can bind to a dna template on its own, eukaryotes require several other proteins, called transcription factors, to first bind to the promoter. Web unlike the prokaryotic polymerase that can bind to a dna template on its own, eukaryotes require several other proteins, called transcription factors, to first bind to the promoter. Web transcription initiation complex & looping. Formation of the transcription preinitiation complex (pic) is nucleated by the. Web most eukaryotic genes have promoters that consist of the tata box close to the 5' end of the gene and, farther upstream, several motifs recognized by specific transcription. Eukaryotic initiation factors (eifs) are proteins or protein complexes involved in the initiation phase of eukaryotic translation. Web the processes of bringing rna polymerases i and iii to the dna template involve slightly less complex collections of transcription factors, but the general theme is the same. Web transcription factors recognize the promoter, rna polymerase ii then binds and forms the transcription initiation complex. This chapter discussed aspects of this process and the transcription factors that bind to specific dna sequences that have been exposed by changes in. Web elongation following the formation of the preinitiation complex, the polymerase is released from the other transcription factors, and elongation is allowed to proceed as it does in. Formation of the transcription preinitiation complex (pic) is nucleated by the tata. Web initiation of transcription in eukaryotes unlike the prokaryotic polymerase that can bind to a dna template on its own, eukaryotes require several other proteins, called. Web these general transcription factors include tfiib, tfiid, tfiie, tfiif and tfiih.Model of canonical translation initiation in eukaryotic cells. a
Pathway of eukaryotic translation initiation translation is a cyclical
Eukaryotic transcription The core of eukaryotic gene activation
Biology, Gene Expression, Eukaryotic Transcription Gene
Structure of the transcription initiation complex. A, schematic of the
Graphic representation of eukaryotic transcriptional machinery. (A
PPT Regulation of Gene Expression by Eukaryotes PowerPoint
PPT Transcription control in eukaryotes PowerPoint Presentation, free
Graphic representation of the bacterial transcription process
PPT Transcription in Eukaryotes PowerPoint Presentation, free
Related Post: