Gauss Law In Integral Form
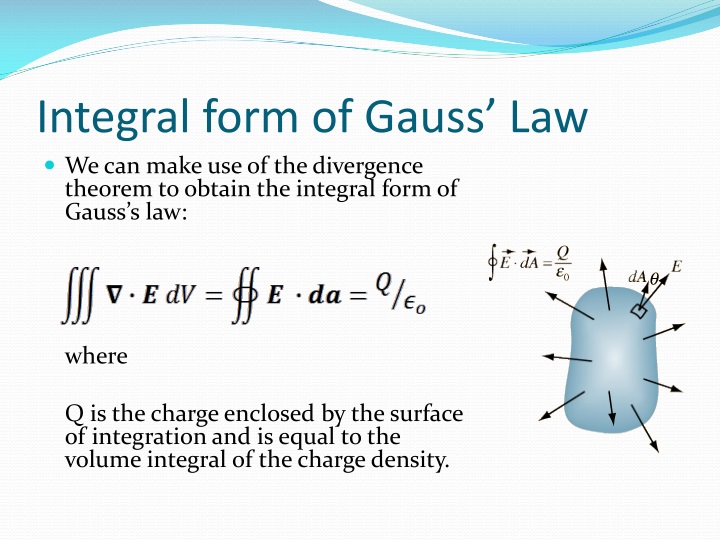
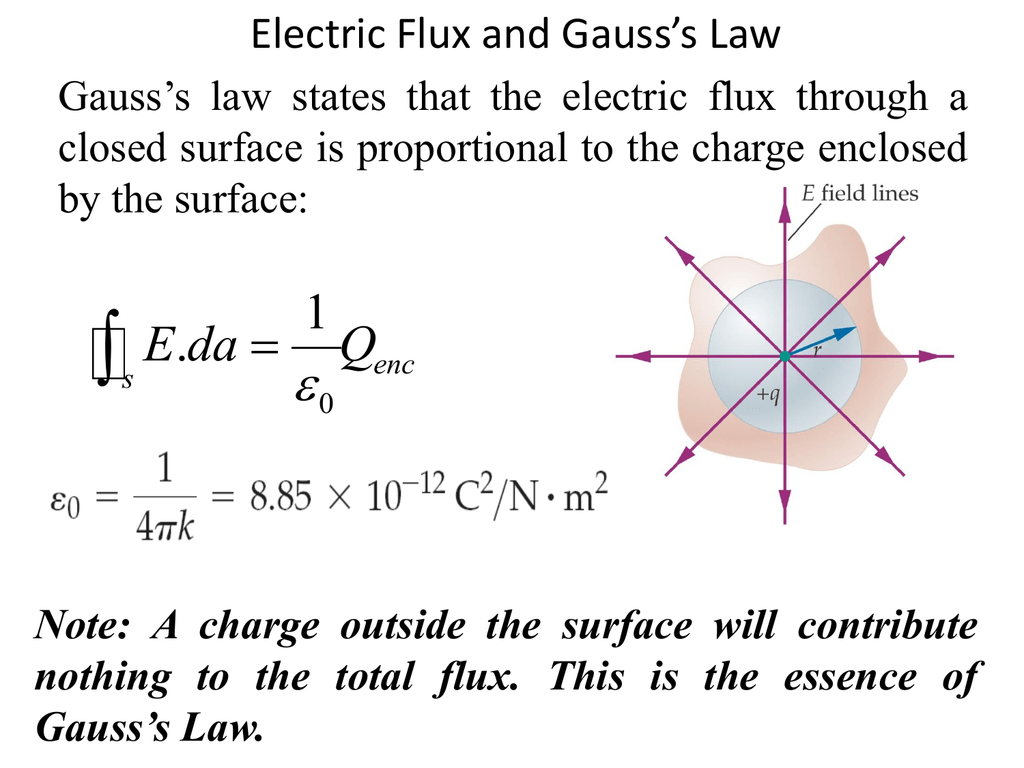
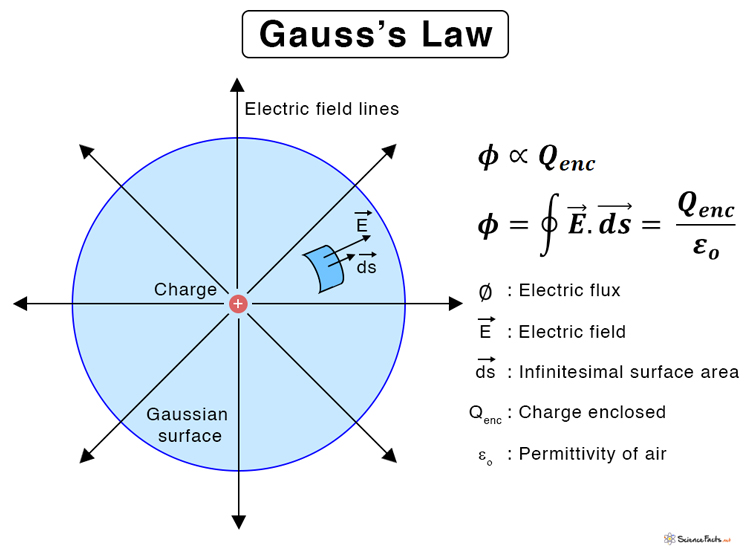
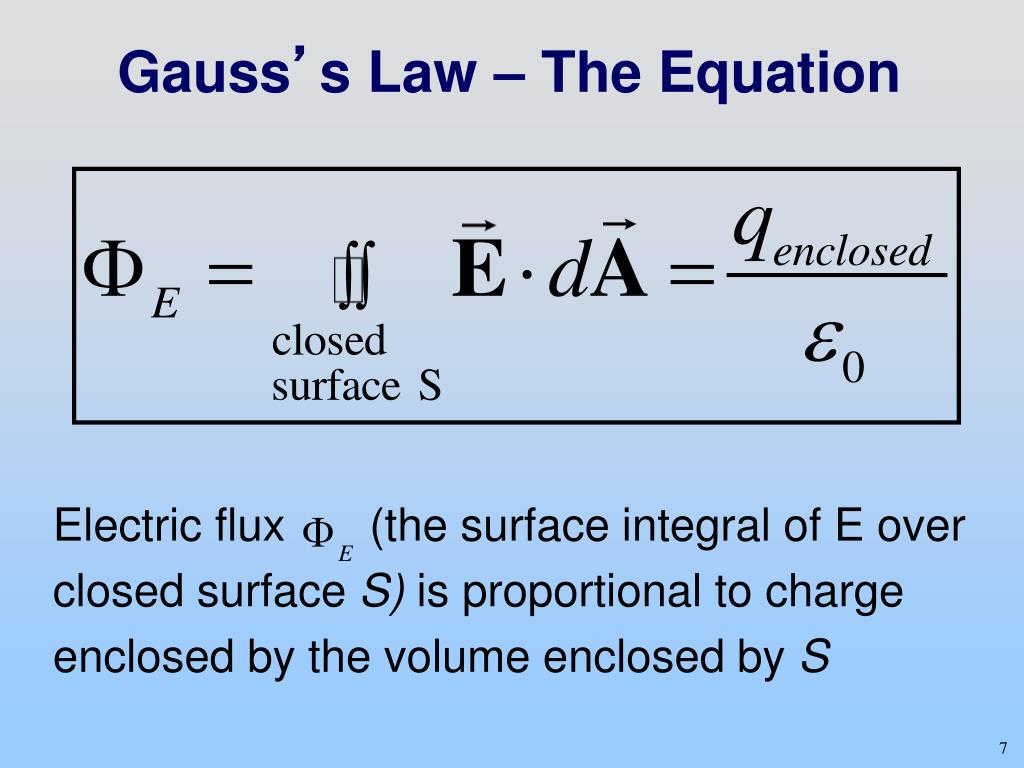
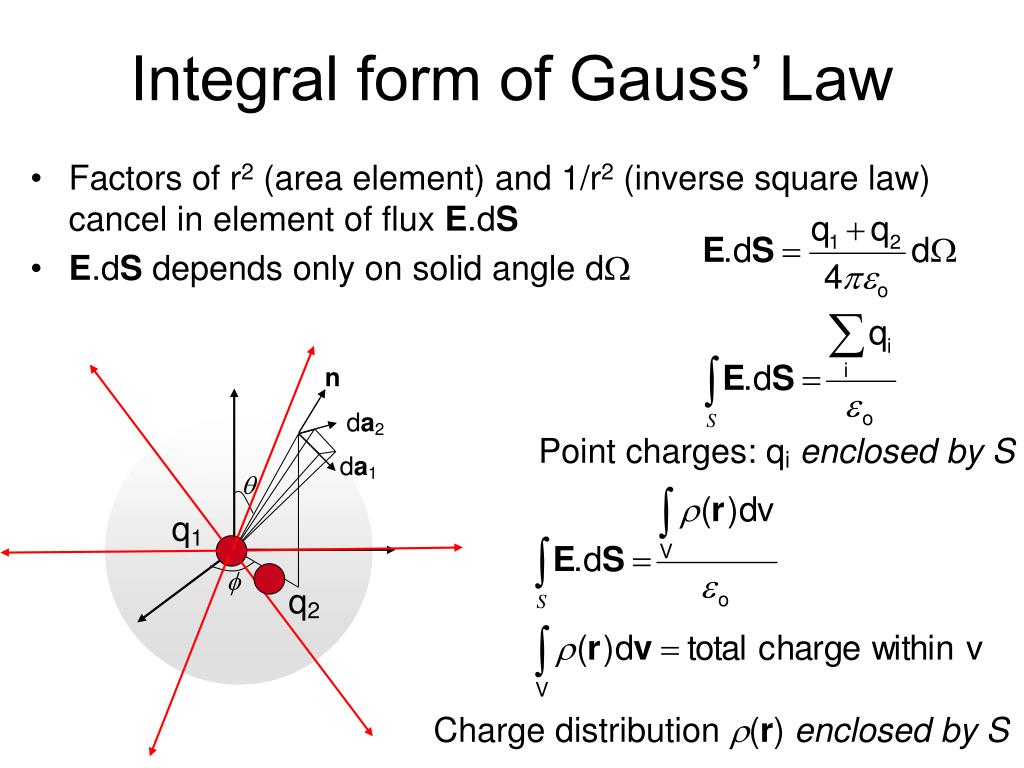
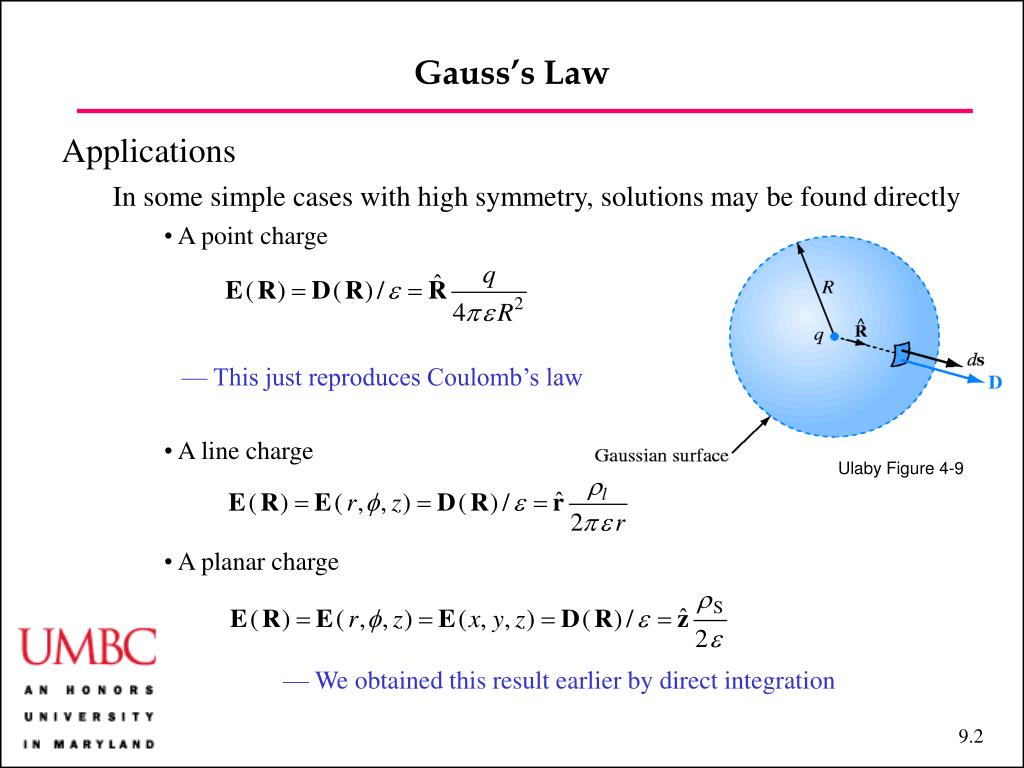
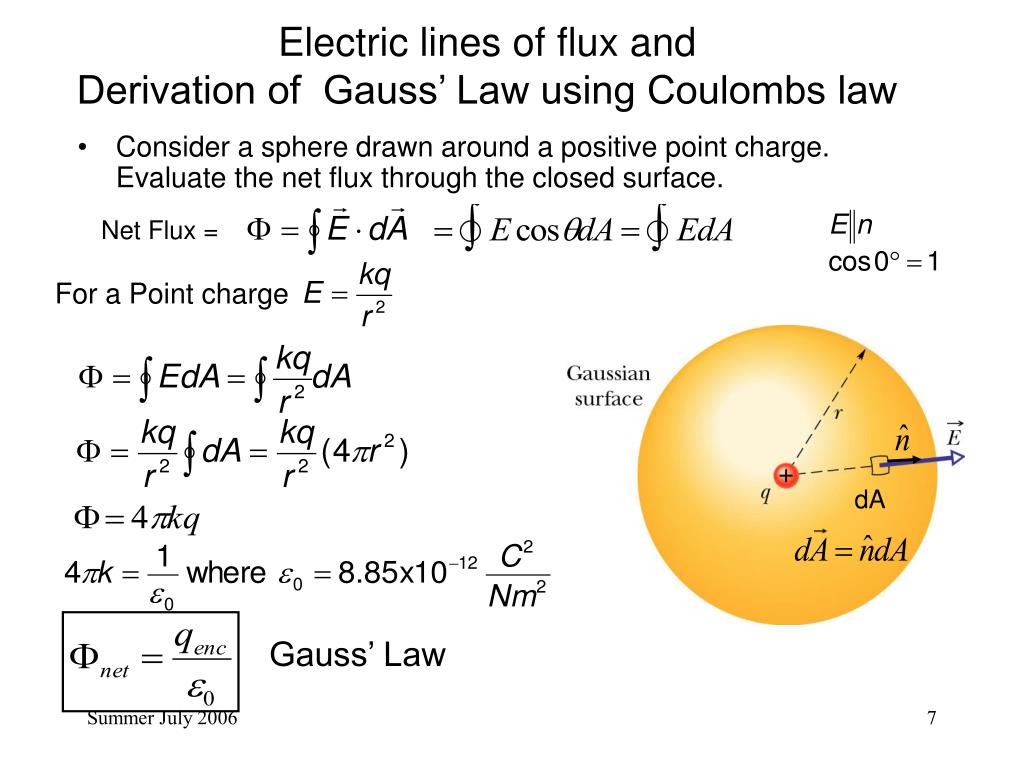
Gauss Law In Integral Form - Gauss's law and the divergence theorem; Electric field discontinuity across a sheet of surface. Web the integral form of gauss’ law is a calculation of enclosed charge qencl q e n c l using the surrounding density of electric flux: Web gauss’ law for magnetic fields (equation 7.2.1 7.2.1) states that the flux of the magnetic field through a closed surface is zero. According to gauss’s law, the flux through a closed surface is equal to the total charge enclosed within the closed surface divided by the permittivity of vacuum. Web this relation or form of the gauss law is known as the integral form. Web gauss's law in integral form; Web gauss' law, integral form. Note that q e n c l on the right. Web 13 gauss's law (integral form) flux; This is expressed mathematically as. The differential form of gauss law relates the. Named after the german mathematician. Web this equation has all the same physical implications as gauss' law. Web section 2.4 does not actually identify gauss’ law, but here it is: (1) where, e is the electric field vector q is the enclosed electric charge ε 0 is the electric permittivity of free space a. Web 13 gauss's law (integral form) flux; According to gauss’s law, the flux through a closed surface is equal to the total charge enclosed within the closed surface divided by the permittivity of vacuum. Electric field. Web gauss's law in integral form; ∮s b ⋅ ds = 0 (7.3.1) (7.3.1) ∮ s b ⋅ d s = 0. Web in vector calculus, the divergence theorem, also known as gauss's theorem or ostrogradsky's theorem, [1] is a theorem which relates the flux of a vector field through a. (1) where, e is the electric field vector q. ∮s d ⋅ ds = qencl (5.7.1) (5.7.1). Follow edited apr 13, 2017 at 12:39. Web this relation or form of the gauss law is known as the integral form. Web section 2.4 does not actually identify gauss’ law, but here it is: What is the differential form of the gauss theorem? Electric field discontinuity across a sheet of surface. ∮s b ⋅ ds = 0 (7.3.1) (7.3.1) ∮ s b ⋅ d s = 0. Web section 2.4 does not actually identify gauss’ law, but here it is: The integral form of gauss’ law (section 5.5) is a calculation of enclosed charge. Web the integral form of gauss’ law states that. Web gauss' law, integral form. Web this relation or form of the gauss law is known as the integral form. ∮s d ⋅ ds = qencl (5.7.1) (5.7.1). Gauss’ law (equation 5.5.1) states that the flux of the electric field through a closed surface is equal to. ∮s b ⋅ ds = 0 (7.3.1) (7.3.1) ∮ s b ⋅ d. After all, we proved gauss' law by breaking down space into little cubes like this. The area integral of the electric field over any closed surface is equal to the net charge enclosed in the surface divided by the permittivity of space. Web gauss’s law in integral form is given below: The integral form of gauss’ law (section 5.5) is. It is also sometimes necessary. Web 13 gauss's law (integral form) flux; Web in vector calculus, the divergence theorem, also known as gauss's theorem or ostrogradsky's theorem, [1] is a theorem which relates the flux of a vector field through a. Named after the german mathematician. Web gauss' law, integral form. (1) where, e is the electric field vector q is the enclosed electric charge ε 0 is the electric permittivity of free space a. Web gauss's law in integral form; Web section 2.4 does not actually identify gauss’ law, but here it is: Web gauss' law, integral form. It is also sometimes necessary. Electric field discontinuity across a sheet of surface. The area integral of the electric field over any closed surface is equal to the net charge enclosed in the surface divided by the permittivity of space. Web gauss’ law for magnetic fields (equation 7.2.1 7.2.1) states that the flux of the magnetic field through a closed surface is zero. Note that. Gauss's law and the divergence theorem; One of them, as explored below, is as a method to compute the electric field in response to a distribution. This is expressed mathematically as. ∮s b ⋅ ds = 0 (7.3.1) (7.3.1) ∮ s b ⋅ d s = 0. The area integral of the electric field over any closed surface is equal to the net charge enclosed in the surface divided by the permittivity of space. Web deduce gauss' law in integral form via the divergence theorem. After all, we proved gauss' law by breaking down space into little cubes like this. The differential form of gauss law relates the. Web 13 gauss's law (integral form) flux; Web this equation has all the same physical implications as gauss' law. Note that q e n c l on the right. Flux of the electric field; Named after the german mathematician. ∮s d ⋅ ds = qencl (5.7.1) (5.7.1). ∫ e ⋅d a =q/ε 0. Web gauss's law in integral form; Web gauss’ law for magnetic fields (equation 7.2.1 7.2.1) states that the flux of the magnetic field through a closed surface is zero. Web apply the gauss’s law strategy given above, where we work out the enclosed charge integrals separately for cases inside and outside the sphere. Web this relation or form of the gauss law is known as the integral form. Follow edited apr 13, 2017 at 12:39.PPT EE3321 ELECTROMAGENTIC FIELD THEORY PowerPoint Presentation ID
5. Gauss Law and it`s applications
Gauss’s Law Definition, Equations, Problems, and Examples
PPT W02D2 Gauss ’ s Law PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
PPT 2). Gauss’ Law and Applications PowerPoint Presentation, free
Gauss´s Law for Electrical Fields (integral form) Physics 101, Learn
integral form of gauss's law Gauss's law, Law, Definitions
PPT Gauss’s Law PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1402148
PPT Gauss’ Law PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5373915
PPT Lecture 3 Gauss’s Law Chp. 24 PowerPoint Presentation, free
Related Post: