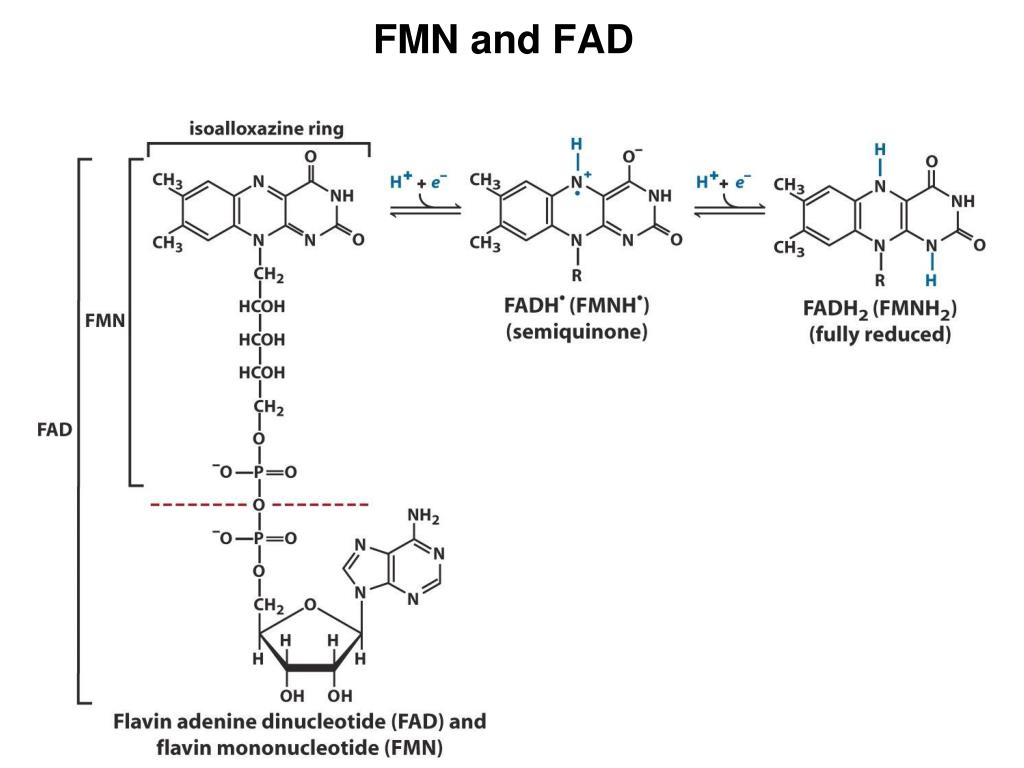
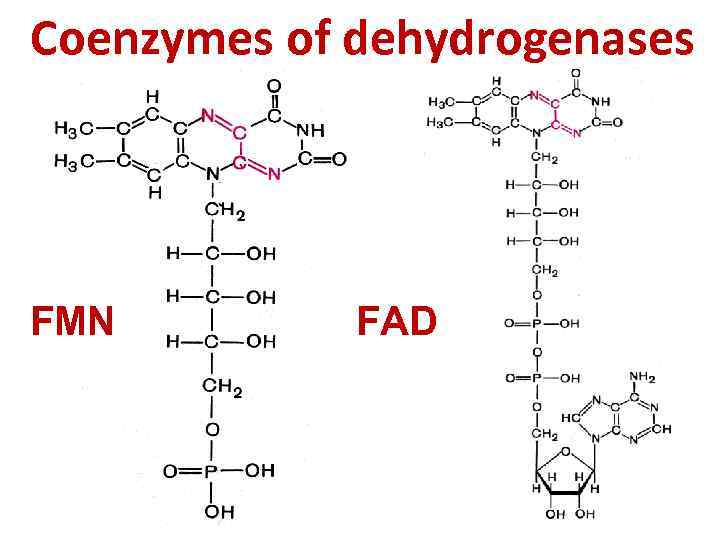
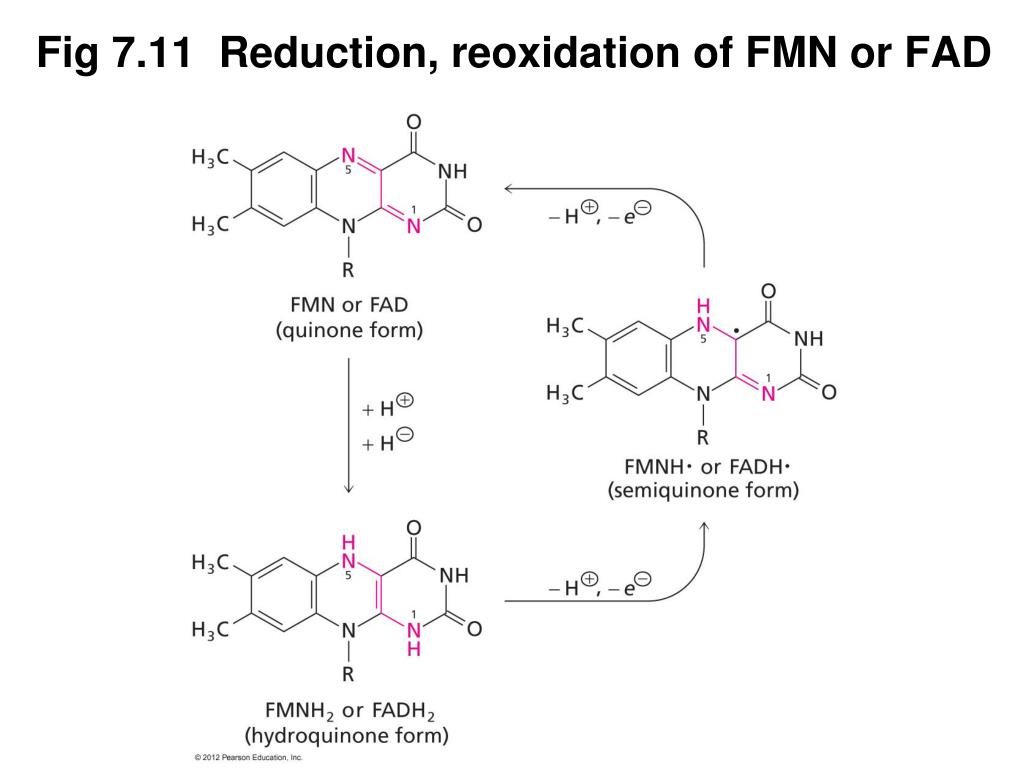
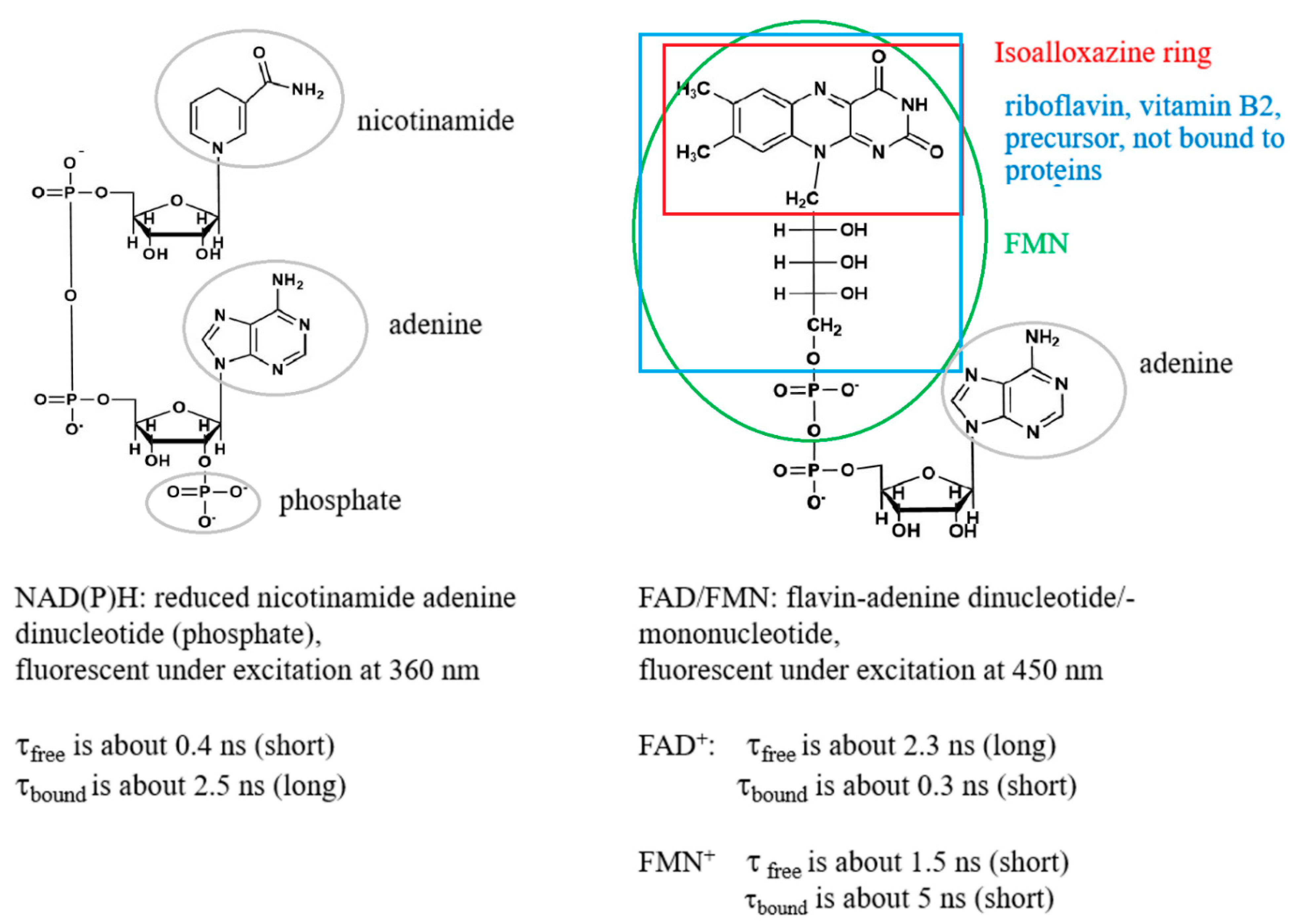
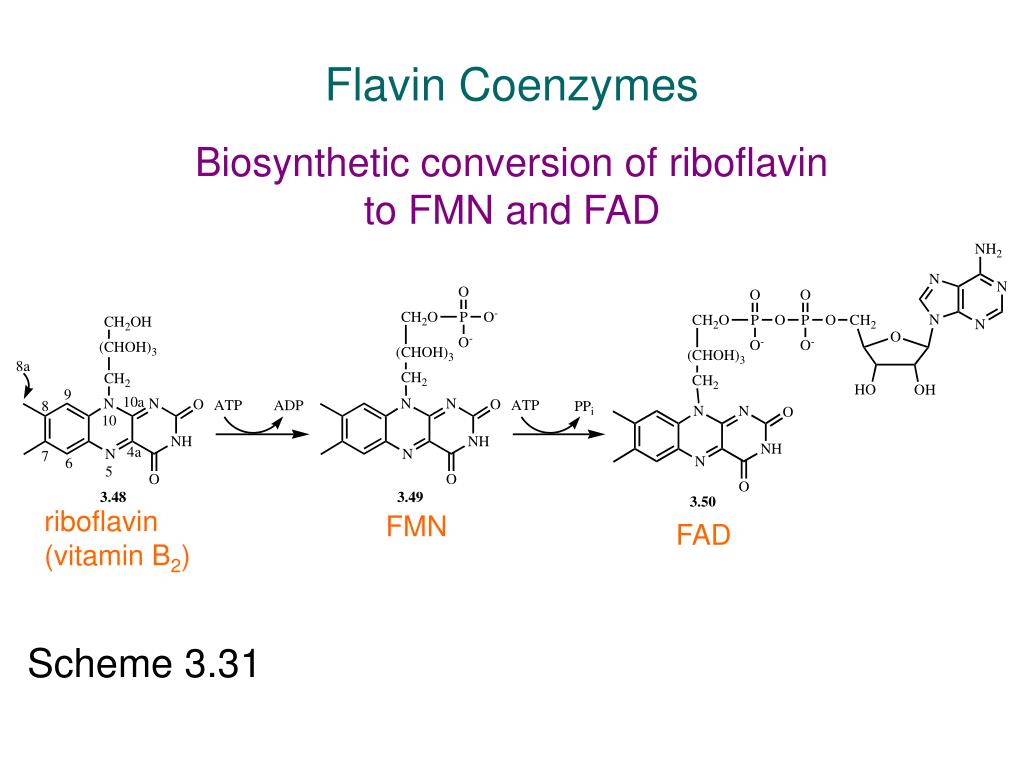
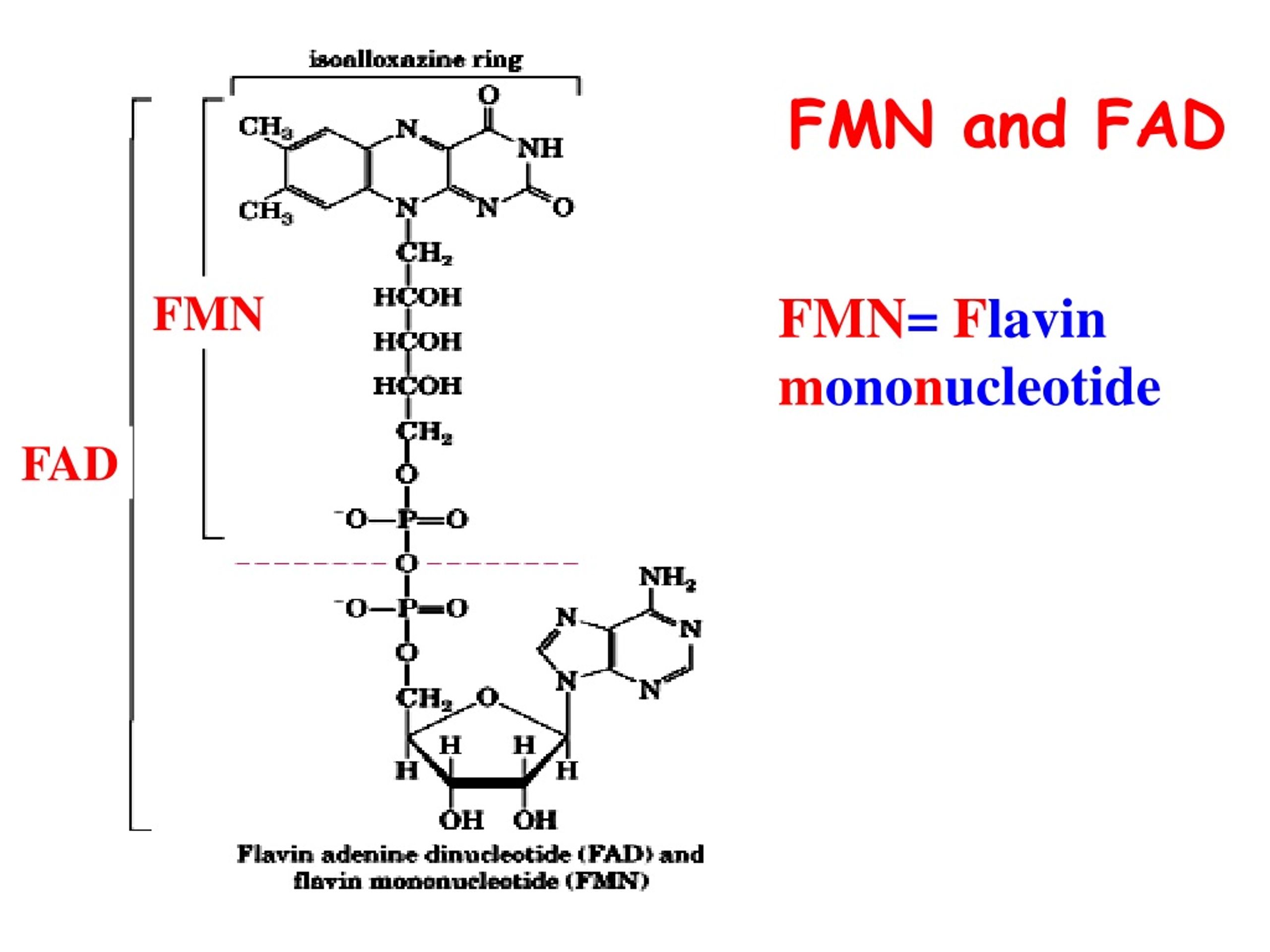
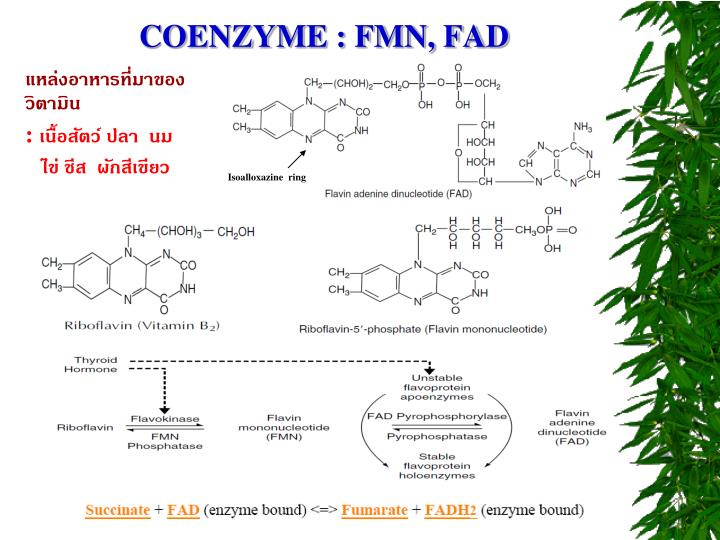
Fad And Fmn Are Coenzyme Form Of
Fad And Fmn Are Coenzyme Form Of - Web flavins most commonly bound to proteins are flavin mononucleotide (fmn) and flavin adenine dinucleotide (fad). Web flavin mononucleotide (fmn) and flavin dinucleotide (fad) are tightly bound (to their enzymes) cofactors that can accept (or donate) two electrons and two protons (to. Web the isoalloxazine ring of flavins can exist in any one of three oxidations states. Web riboflavin, or vitamin b2, is an essential nutrient that serves as a precursor to flavin adenine dinucleotide (fad) and flavin mononucleotide (fmn). About 75% of flavoproteins utilize fad as a. A) riboflavin b) adenosine c) amp d). During the catalytic cycle, a reversible interconversion of the oxidized (fmn),. Web several extant coenzymes such as fmn (2 a) and fad (2 b) as well as related derivatives 70, coenzyme f 420 (71) and remarkably also folic acid (5) are. Web fmn and fad, commonly called flavoproteins, are also hydrogen transferring coenzymes associated with hydrogenases. Web fad and fmn are cofactors usually used in aerobic processes, functioning as cofactors for oxidases. Web riboflavin, or vitamin b2, is an essential nutrient that serves as a precursor to flavin adenine dinucleotide (fad) and flavin mononucleotide (fmn). Web fmn and fad, commonly called flavoproteins, are also hydrogen transferring coenzymes associated with hydrogenases. Web although not used in the electron transport chain, coenzyme a is a major cofactor which is used to transfer a two. The underlying mechanisms that govern these reactions are based predominantly on the. Web flavin mononucleotide (fmn) and flavin dinucleotide (fad) are tightly bound (to their enzymes) cofactors that can accept (or donate) two electrons and two protons (to. Web fad and fmn are cofactors usually used in aerobic processes, functioning as cofactors for oxidases. Ad natural supplement form of coenzyme. Web the isoalloxazine ring of flavins can exist in any one of three oxidations states. Web flavin adenine dinucleotide (fad) and flavin mononucleotide (fmn) are the active form of riboflavin, which is also popularly known as vitamin b2. However, one important component was neglected so far—namely, contributions from fmn during fad. Web fmn and fad, commonly called flavoproteins, are also. Web although not used in the electron transport chain, coenzyme a is a major cofactor which is used to transfer a two carbon unit commonly referred to as the acetyl group. Web several extant coenzymes such as fmn (2 a) and fad (2 b) as well as related derivatives 70, coenzyme f 420 (71) and remarkably also folic acid (5). About 75% of flavoproteins utilize fad as a. However, one important component was neglected so far—namely, contributions from fmn during fad. Web flavoenzymes are capable of conducting electron transfer reactions. Web riboflavin, or vitamin b2, is an essential nutrient that serves as a precursor to flavin adenine dinucleotide (fad) and flavin mononucleotide (fmn). Web several extant coenzymes such as fmn. Web flavins most commonly bound to proteins are flavin mononucleotide (fmn) and flavin adenine dinucleotide (fad). Web through mathematical separation, this proposed analytical method efficiently achieved the simultaneous quantitative analysis of metabolic coenzymes fad and fmn. The underlying mechanisms that govern these reactions are based predominantly on the. Web when tyrosine becomes an essential amino acid →. A) riboflavin b). Web flavin adenine dinucleotide (fad) and flavin mononucleotide (fmn) are the active form of riboflavin, which is also popularly known as vitamin b2. The underlying mechanisms that govern these reactions are based predominantly on the. Web contrast to nad+ and nadp+, fmn and fad are prosthetic groups which remain tightly bound to their enzymes and do not shuttle back and. Web flavin adenine dinucleotide (fad) and flavin mononucleotide (fmn) are the active form of riboflavin, which is also popularly known as vitamin b2. Ad natural supplement form of coenzyme q10, antioxidant for heart health. However, one important component was neglected so far—namely, contributions from fmn during fad. About 75% of flavoproteins utilize fad as a. Web the consideration of fad. Web fmn and fad, commonly called flavoproteins, are also hydrogen transferring coenzymes associated with hydrogenases. Web the isoalloxazine ring of flavins can exist in any one of three oxidations states. Web bioenergetic alterations of metabolic redox coenzymes as nadh, fad and fmn by means of fluorescence lifetime imaging techniques. Web flavin mononucleotide (fmn) and flavin dinucleotide (fad) are tightly bound. Web the isoalloxazine ring of flavins can exist in any one of three oxidations states. The underlying mechanisms that govern these reactions are based predominantly on the. Web fad and fmn are cofactors usually used in aerobic processes, functioning as cofactors for oxidases. Web the consideration of fad flim is complicated enough; However, one important component was neglected so far—namely,. In other word, riboflavin is the. Web the isoalloxazine ring of flavins can exist in any one of three oxidations states. A) riboflavin b) adenosine c) amp d). Web although not used in the electron transport chain, coenzyme a is a major cofactor which is used to transfer a two carbon unit commonly referred to as the acetyl group. However, fad also can function in anaerobic environments as cofactor. However, one important component was neglected so far—namely, contributions from fmn during fad. The underlying mechanisms that govern these reactions are based predominantly on the. Web fmn and fad, commonly called flavoproteins, are also hydrogen transferring coenzymes associated with hydrogenases. Web the consideration of fad flim is complicated enough; Web bioenergetic alterations of metabolic redox coenzymes as nadh, fad and fmn by means of fluorescence lifetime imaging techniques. The coenzyme parts of these flavoproteins contain the b. About 75% of flavoproteins utilize fad as a. Web fad and fmn are cofactors usually used in aerobic processes, functioning as cofactors for oxidases. Web contrast to nad+ and nadp+, fmn and fad are prosthetic groups which remain tightly bound to their enzymes and do not shuttle back and forth between enzymes. Web when tyrosine becomes an essential amino acid →. Web flavoenzymes are capable of conducting electron transfer reactions. Web several extant coenzymes such as fmn (2 a) and fad (2 b) as well as related derivatives 70, coenzyme f 420 (71) and remarkably also folic acid (5) are. Yet little attention has been given to the release of. During the catalytic cycle, a reversible interconversion of the oxidized (fmn),. Web flavin mononucleotide (fmn) and flavin dinucleotide (fad) are tightly bound (to their enzymes) cofactors that can accept (or donate) two electrons and two protons (to.PPT Overview of oxidative phosphorylation PowerPoint Presentation
PPT Part II and Chapter 13 PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Metabolism and transport of riboflavin and flavocoenzyme. Dietary FAD
Abbildung 1. Coenzyme FMN/FAD (2 a,b), SAM (3) und TPP (4), THF (5
Biological oxidation Metabolism ATP Energyrich
PPT Chapter 7 Coenzymes and Vitamins PowerPoint Presentation, free
IJMS Free FullText Bioenergetic Alterations of Metabolic Redox
PPT The Organic Chemistry of EnzymeCatalyzed Reactions Chapter 3
PPT Chapter 3 Enzymes PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID9213427
PPT ENZYMES & COENZYMES PowerPoint Presentation ID6040687
Related Post: