Do Metalloids Form Ionic Bonds
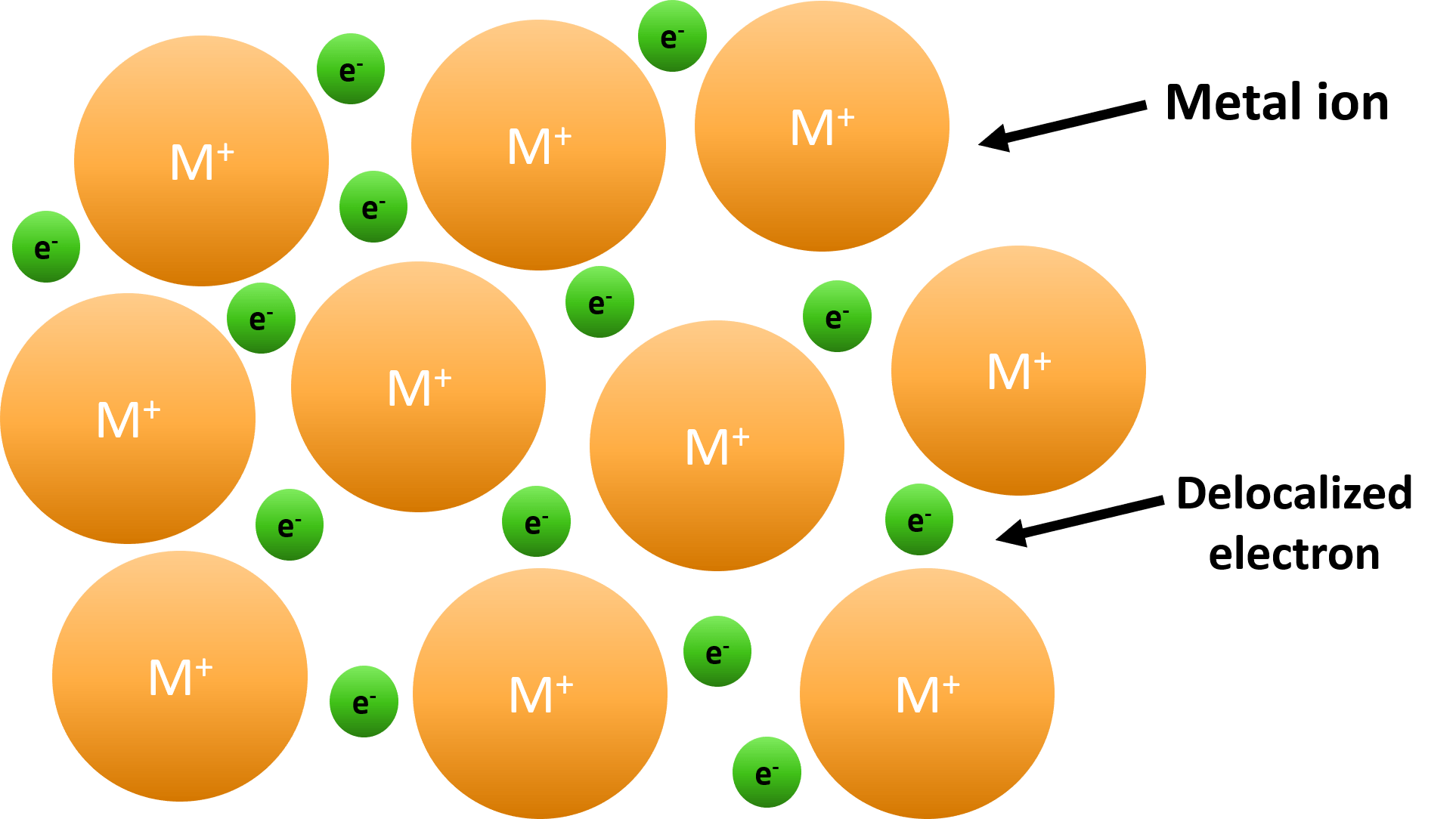
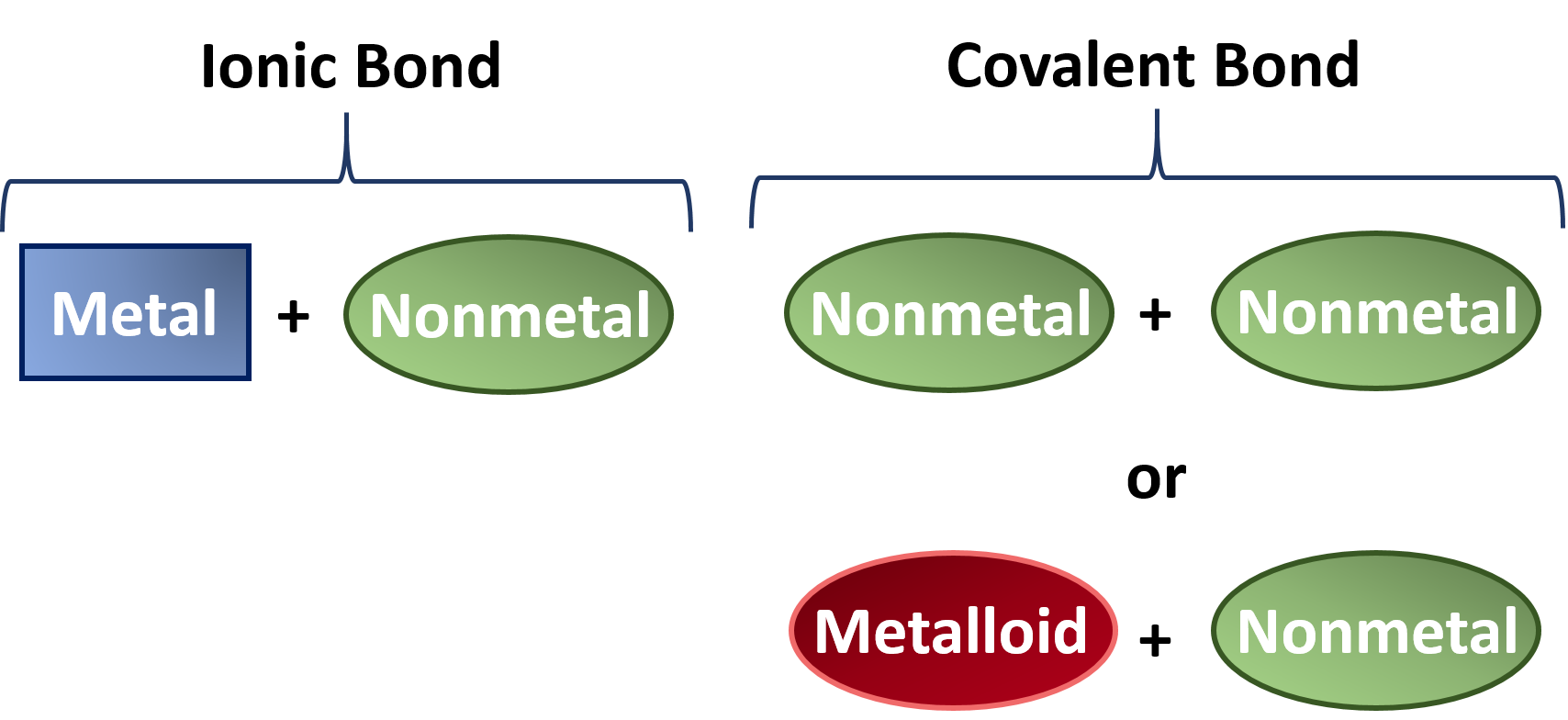
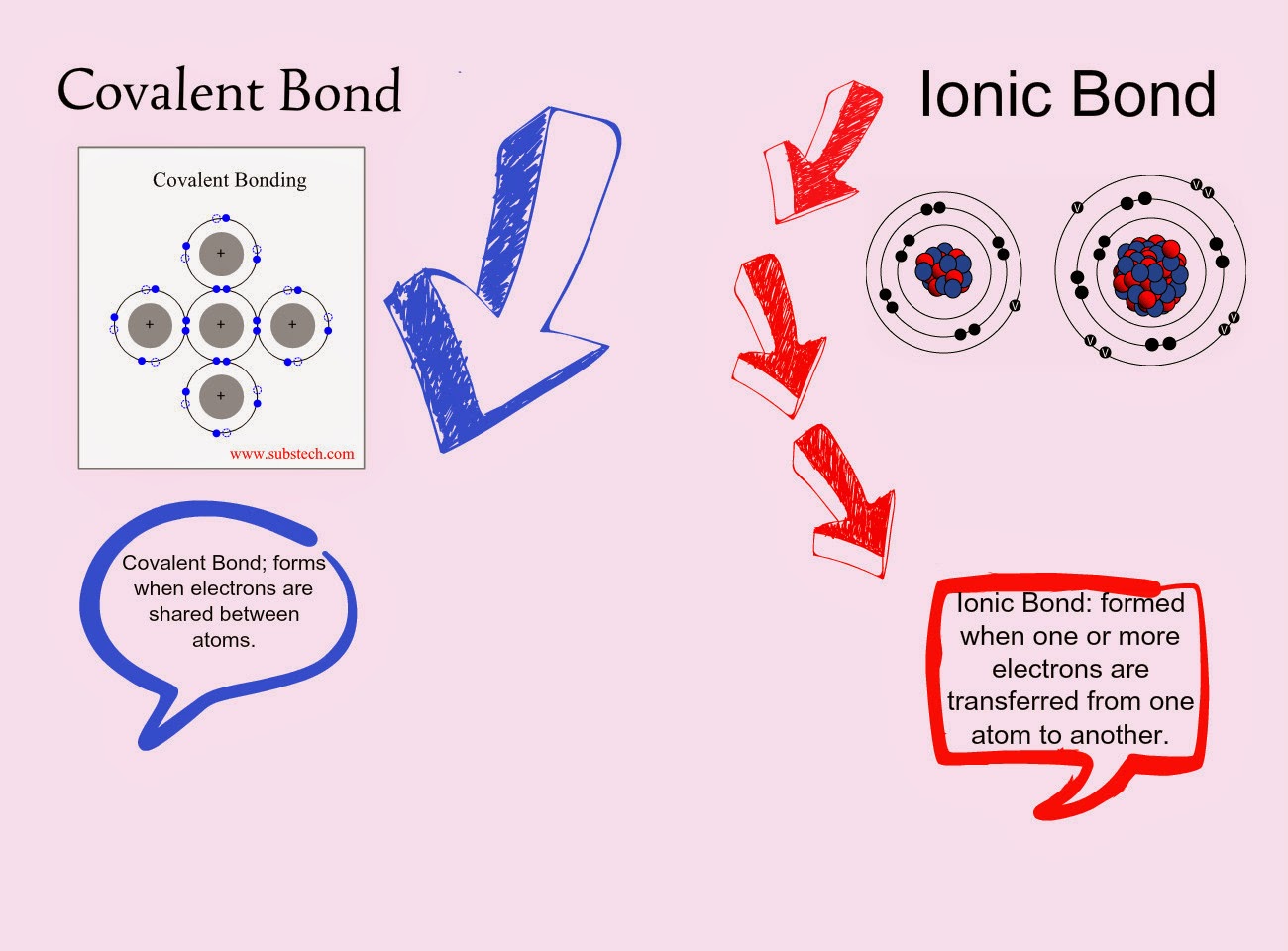
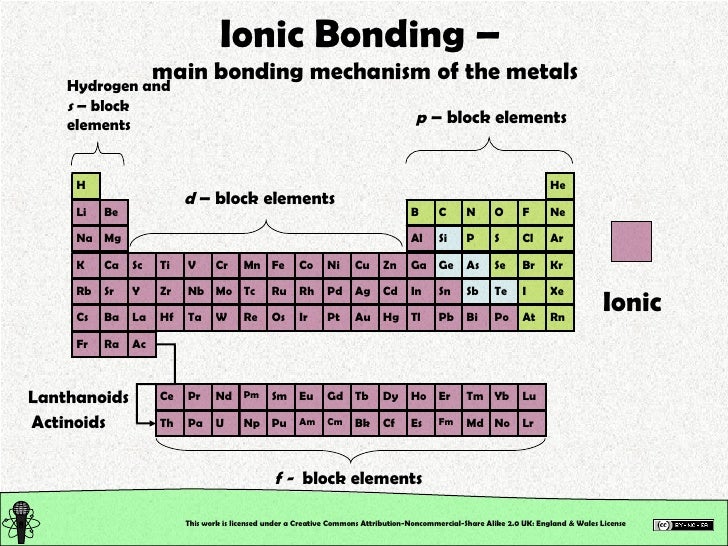
Do Metalloids Form Ionic Bonds - Web do metalloids form ionic bonds? Properties noted in this section refer to the elements in their most thermodynamically stable forms under ambient conditions. Create an account to view solutions. Web we would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. 2.70 g/cm ), and is hard and brittle. Web what kind of bonds do metalloids form? Ad uslegalforms.com has been visited by 100k+ users in the past month When metalloids bond with nonmetals, they tend to form covalent bonds. Web a metallic bond is a type of chemical bond formed between positively charged atoms in which the free electrons are shared among a lattice of cations. When atoms of nonmetal elements form ions, they. Web metalloids can form both covalent and ionic bonds, depending on the elements they are bonding with. Properties noted in this section refer to the elements in their most thermodynamically stable forms under ambient conditions. Web for example, the pure metalloids form covalent crystals like the nonmetals, but like the metals, they generally do not form monatomic anions. It is. Web a series of six elements called the metalloids separate the metals from the nonmetals in the periodic table. Web in the early 1900's, paul drüde came up with the sea of electrons metallic bonding theory by modeling metals as a mixture of atomic cores (atomic cores = positive. The metalloids are boron, silicon, germanium, arsenic,. The molecule possessing ionic. Web a metallic bond is a type of chemical bond formed between positively charged atoms in which the free electrons are shared among a lattice of cations. Web do metalloids form ionic bonds? Web a series of six elements called the metalloids separate the metals from the nonmetals in the periodic table. Create an account to view solutions. Web we. Web metalloids can form both covalent and ionic bonds, depending on the elements they are bonding with. Web do metalloids form ionic bonds? Create an account to view solutions. Properties noted in this section refer to the elements in their most thermodynamically stable forms under ambient conditions. It is less dense than aluminium (2.34 vs. Web a metallic bond is a type of chemical bond formed between positively charged atoms in which the free electrons are shared among a lattice of cations. Sodium chloride (nacl), potassium fluoride (kf), magnesium oxide (mgo) metalloids (semi. The bond formed by either losing or gaining an electron is called the ionic bond. For example, the pure metalloids form covalent. Web simply, metals lose electrons and can form only ionic bonds. 2.70 g/cm ), and is hard and brittle. Web what kind of bonds do metalloids form? Web a series of six elements called the metalloids separate the metals from the nonmetals in the periodic table. It is less dense than aluminium (2.34 vs. It is barely reactive under normal conditions, except for attack by fluorine, and has a melting point. Simply, metals lose electrons and can form only ionic bonds. Web do metalloids form ionic bonds? The molecule possessing ionic bond has. Web what kind of bonds do metalloids form? Web what kind of bonds do metalloids form? Ad uslegalforms.com has been visited by 100k+ users in the past month Web their chemical behavior falls between that of metals and nonmetals. Web a series of six elements called the metalloids separate the metals from the nonmetals in the periodic table. Web do metalloids form ionic bonds? Web their chemical behavior falls between that of metals and nonmetals. It is less dense than aluminium (2.34 vs. Web metalloids can form both covalent and ionic bonds, depending on the elements they are bonding with. Web a series of six elements called the metalloids separate the metals from the nonmetals in the periodic table. When atoms of nonmetal elements. The bond formed by either losing or gaining an electron is called the ionic bond. Properties noted in this section refer to the elements in their most thermodynamically stable forms under ambient conditions. For example, the pure metalloids form covalent crystals like the nonmetals, but like the metals, they generally do not form monatomic anions. The molecule possessing ionic bond. When metalloids bond with nonmetals, they tend to form covalent bonds. Web we would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. When atoms of nonmetal elements form ions, they. Are compounds with metalloids ionic or covalent? Web metallic solids are composed of metal cations held together by a delocalized sea of valence electrons. Web for example, the pure metalloids form covalent crystals like the nonmetals, but like the metals, they generally do not form monatomic anions. Because their electrons are mobile, metallic solids are good. Web in the early 1900's, paul drüde came up with the sea of electrons metallic bonding theory by modeling metals as a mixture of atomic cores (atomic cores = positive. For example, the pure metalloids form covalent crystals like the nonmetals, but like the metals, they generally do not form monatomic anions. Properties noted in this section refer to the elements in their most thermodynamically stable forms under ambient conditions. This intermediate behavior is in part due to their. Web metalloids can form both covalent and ionic bonds, depending on the elements they are bonding with. The bond formed by either losing or gaining an electron is called the ionic bond. Simply, metals lose electrons and can form only ionic bonds. 2.70 g/cm ), and is hard and brittle. Web metals and nonmetals are involved in ionic bonding, but it specifically refers to two elements that are oppositely charged being bonded to eachother. Web a metallic bond is a type of chemical bond formed between positively charged atoms in which the free electrons are shared among a lattice of cations. Web the name of a metal ion is the same as the name of the metal atom from which it forms, so ca 2+ is called a calcium ion. Web their chemical behavior falls between that of metals and nonmetals. Sodium chloride (nacl), potassium fluoride (kf), magnesium oxide (mgo) metalloids (semi.Ionic bonds Reaction of metals & Nonmetals Metals and non metals
Metallic Bond — Formation & Compounds Expii
PPT Ionic Bonding PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2435173
Metallic Bonding Definition, Properties, Examples, Diagram
CH150 Chapter 4 Covalent Bonds and Molecular Compounds Chemistry
Which Best Compares the Properties of Ionic and Metallic Substances
Metalloid staircase Diagram Quizlet
Covalent Bond Biology Dictionary
January 2015 to studycentre.A online portal for education
Chemical Structure Chemical Bonding. Ionic, Metallic & Coordinate Bo…
Related Post: